1. 简介
在JDK中 java.net.URL 适用于加载资源的类,但是 URL 的实现类都是访问网络资源的,并没有可以从类路径或者相对路径获取文件及 ServletContext , 虽然可以通过自定义扩展URL接口来实现新的处理程序,但是这是非常复杂的,同时 URL 接口中定义的行为也并不是很理想的 ,如检测资源的存在等的行为,这也是 spring 为什么自己全新的开发一套自己的资源加载策略, 同时它也满足下面的特点:
- 单一职责原则,将资源的定义和资源的加载的模型界限划的非常清晰
- 采用高度抽象,统一的资源定义和资源加载的策略和行为,资源加载返回给客户端的是抽象的资源,客户端根据资源的行为定义对其进行具体化的处理
2. Resource 接口
spring 中的 Resource 接口目的在于成为一种功能更加强大的接口,用于抽象化对具体资源的访问,它继承了 org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamSource 接口,作为资源定义的顶级接口, Resource 内部定义了通用的方法,并且有它的子类 AbstractResource 来提供统一的默认实现,
Resouerce 接口定义:
//资源定义接口
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 检验资源是否是物理存在
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 判断资源是否是可读的
*/
default boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
/**
* 判断资源是否是打开的,true为打开
*/
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
/**
* 判断该资源是否是文件 true为是
*/
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
/**
* 返回该资源的URL句柄
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回该资源的URI句柄
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取该资源的File句柄
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回一个ReadableByteChannel 作为NIO中的可读通道
*/
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
/**
* 获取资源内容的长度
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回该资源最后修改的时间戳
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 根据该资源的相对路径创建新资源
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 返回该资源的名称
*/
@Nullable
String getFilename();
/**
* 返回该资源的描述
*/
String getDescription();
}
InputStreamSource 接口定义:
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* Return an {@link InputStream} for the content of an underlying resource.
* <p>It is expected that each call creates a <i>fresh</i> stream.
* <p>This requirement is particularly important when you consider an API such
* as JavaMail, which needs to be able to read the stream multiple times when
* creating mail attachments. For such a use case, it is <i>required</i>
* that each {@code getInputStream()} call returns a fresh stream.
* @return the input stream for the underlying resource (must not be {@code null})
* @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if the underlying resource doesn't exist
* @throws IOException if the content stream could not be opened
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
该 Resource 中一些最重要的方法:
-
getInputStream():找到并打开资源,并返回一个资源以InputStream供读取,每次调用都会返回一个新的InputStream,调用者有责任关闭流 -
exists():返回boolean指示此资源是否实际以物理形式存在。 -
isOpen():返回,boolean指示此资源是否表示具有打开流的句柄, 如果为true,InputStream则不能多次读取,必须只读取一次,然后将其关闭以避免资源泄漏。返回false所有常用资源实现(除外)InputStreamResource可读 -
getDescription():返回对此资源的描述,以便在使用该资源时用于错误输出。这通常是标准文件名或资源的实际URL
** Resource 实现**
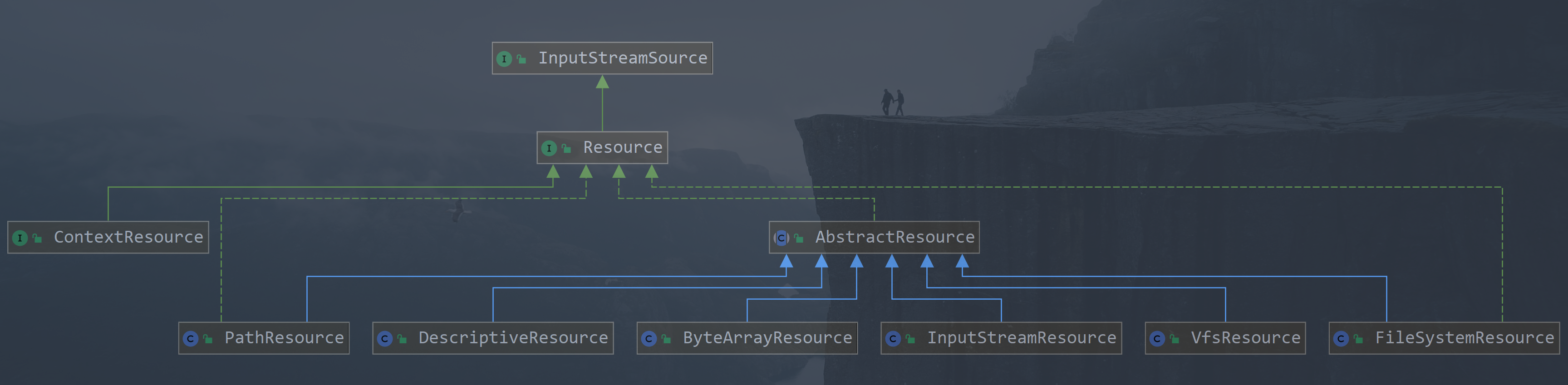
-
UrlResource: 包装一个java.net.URL,可用于访问通常可以通过URL访问的任何对象,例如文件,HTTP目标,FTP目标等。所有URL都有一个标准化的String表示形式,因此适当的标准化前缀可用于指示另一种URL类型。如:file: 访问文件系统路径,http: 通过HTTP协议ftp: 访问资源,通过FTP访问资源等 -
ClassPathResource: 此类表示应从类路径获取的资源。它使用线程上下文类加载器(ClassLoader),给定的类加载器或给定的类来加载资源 -
FileSystemResource: 是一个Resource执行java.io.File和java.nio.file.Path类型资源的封装,它支持File和URL, 实现WritableResource接口,且从Spring Framework 5.0开始,FileSystemResource使用NIO2 API进行读/写交互 -
ServletContextResource: 该ServletContext资源解释相关Web应用程序的根目录内的相对路径。 -
InputStreamResource: 将给定的 InputStream 作为一种资源的 Resource 的实现类 -
ByteArrayResource: 这是Resource给定字节数组的实现。它为给定的字节数组创建一个ByteArrayInputStream
3. ResourceLoader 接口
ResourceLoader 主要是用于返回(即加载) Resource 对象,主要定义:
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:". */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 返回指定路径的资源处理器
* 必须支持完全限定的网址: "file:C:/test.dat"
* 必须支持ClassPath 的 URL :"classpath:test.dat"
* 必须支持相对路径 : "WEB-INF/test.dat"
* 并不能保证资源是否物理存在,需要自己去检测通过existence
* 再spring中所有的应用上下文都去实现这个接口,可以进行资源的加载
*/
Resource getResource(String location);
/**
* 返回当前类的 ClassLoader 对象
*/
@Nullable
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
-
应用上下文即容器都有实现
ResourceLoader这个接口,所有的上下文都可以用于获取Resource实例对象 -
我们可以在特定的应用上下文中通过
getResource()来获取特定类型的Resource实例,但是的保证location路径没有特殊的前缀,如classpatch:等,如果有特定前缀慢么会强制使用相应的资源类型,与上下文无关。
| Prefix | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/myapp/config.xml | 从类路径加载 |
| file: | file:///data/config.xml | 从文件系统作为 URL 加载 |
| http: | https://myserver/logo.png | 按照URL形式加载 |
| (none) | /data/config.xml | 取决于应用上下文 |
ResourceLoader 的子类结构:
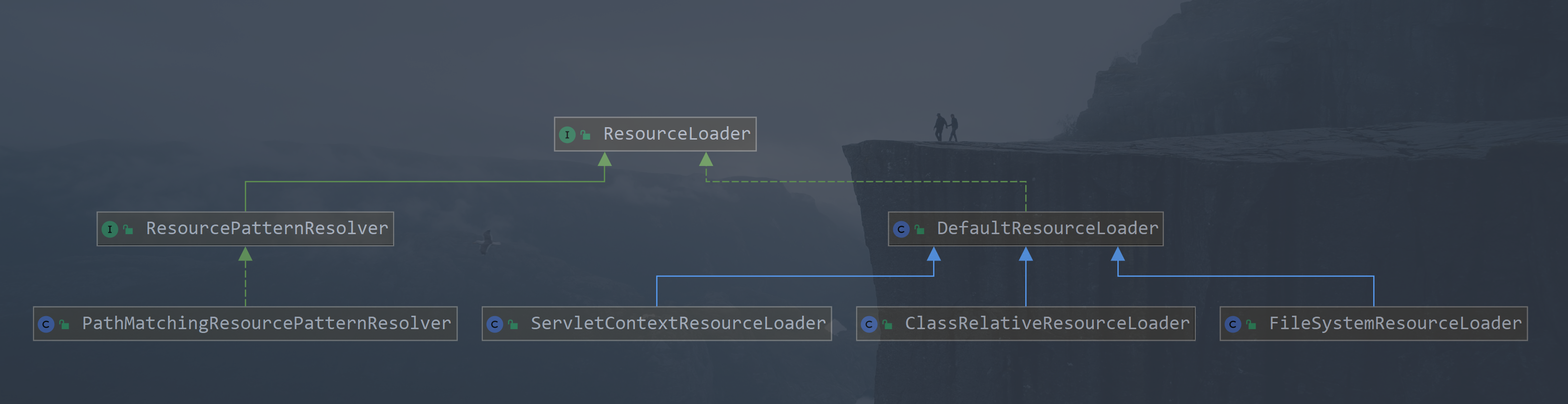
3.1 DefaultResourceLoader
这个类是 ResourceLoader 的默认实现类,与 Resource 接口的 AbstractResource 一样,
3.1.1. 构造函数
- 提供有参和无参的构造函数,有参构造函数接受
ClassLoader类型,如不带参数则使用默认的ClassLoader,Thread.currentThread()#getContextClassLoader()
核心代码代码,部分省去:
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
@Nullable
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private final Set<ProtocolResolver> protocolResolvers = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
private final Map<Class<?>, Map<Resource, ?>> resourceCaches = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(4);
/**
* 无参构造函数
* @see java.lang.Thread#getContextClassLoader()
*/
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
/**
* 带ClassLoader的有参构造函数
*/
public DefaultResourceLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
/**
* 设置 ClassLoader
*/
public void setClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
/**
* Return the ClassLoader to load class path resources with.、
* @see ClassPathResource
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
/**
* Obtain a cache for the given value type, keyed by {@link Resource}.
* @param valueType the value type, e.g. an ASM {@code MetadataReader}
* @return the cache {@link Map}, shared at the {@code ResourceLoader} level
* @since 5.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Map<Resource, T> getResourceCache(Class<T> valueType) {
return (Map<Resource, T>) this.resourceCaches.computeIfAbsent(valueType, key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
}
/**
* Clear all resource caches in this resource loader.
* @since 5.0
* @see #getResourceCache
*/
public void clearResourceCaches() {
this.resourceCaches.clear();
}
}
3.1.2 getResource() 核心方法
是 ResourceLoader 中最核心的方法,他根据传入的 location 来返回相应的Resource,而 DefaultResourceLoader 对其做了核心实现, 子类都没覆盖该方法,所以我们可以断定 ResourceLoader 加载资源的核心策略都在 DefaultResourceLoader 中
核心代码:
//DefaultResourceLoader.java
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
//1. 通过 ProtocolResolver 协议解析器来记载资源
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : getProtocolResolvers()) {
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
//2.如果location是以 / 开头则返回 ClassPathContextResource 类型的 资源
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}//3.如果是以 classpath: 开头,则返回 ClassPathResource 类型的资源
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
//4.如果不是以上两种,则判断是否是 File URL ,如果是返回FileUrlResource 否则 返回UrlResource
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
//5.最后则返回ClassPathContextResource
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
上述代码中具体说明了执行的流程,其中 getResourceByPath(location) 的具体实现代码如下:
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
3.1.3 ProtocolResolver
全限定类名: org.springframework.core.io.ProtocolResolver ,是一个接口,用于用户自定义协议资源解析策略,是 DefaultResourceLoader 的 SPI ,允许处理自定义协议而无需将加载程序实现(或应用程序上下文实现)为子类,即不需要继承 ResourceLoader 的子类 DefaultResourceLoader , 而直接实现 ProtocolResolver 接口就可以自定义 ResourceLoader
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ProtocolResolver {
/**
* 使用指定的ResourceLoader 来解析location路径的 资源
* Resolve the given location against the given resource loader
* if this implementation's protocol matches.
* @param location the user-specified resource location
* @param resourceLoader the associated resource loader
* @return a corresponding {@code Resource} handle if the given location
* matches this resolver's protocol, or {@code null} otherwise
*/
@Nullable
Resource resolve(String location, ResourceLoader resourceLoader);
}
在spring中该类并没有任何实现类,他需要用户自己实现,那么自定义的
ProtocolResolver如何加载到spring中呢?在我们DefaultResourceLoader类中有一个方法addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver)则是用来添加的
/**
* Register the given resolver with this resource loader, allowing for
* additional protocols to be handled.
* <p>Any such resolver will be invoked ahead of this loader's standard
* resolution rules. It may therefore also override any default rules.
* @since 4.3
* @see #getProtocolResolvers()
*/
public void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver) {
Assert.notNull(resolver, "ProtocolResolver must not be null");
this.protocolResolvers.add(resolver);
}
3.2 FileSystemResourceLoader
在 DefaultResourceLoader 中 getResourceByPath() 方法的处理是直接返回了一个 ClassPathContextResource 类型的资源,这其实是不完善的,在spring中 FileSystemResourceLoader 类继承了 DefaultResourceLoader ,同时重写了 getResourceByPath() 方法,使用标准的文件系统读入,并且返回 FileSystemContextResource 类型
public class FileSystemResourceLoader extends DefaultResourceLoader {
/**
* Resolve resource paths as file system paths.
* <p>Note: Even if a given path starts with a slash, it will get
* interpreted as relative to the current VM working directory.
* @param path the path to the resource
* @return the corresponding Resource handle
* @see FileSystemResource
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.ServletContextResourceLoader#getResourceByPath
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
return new FileSystemContextResource(path);
}
/**
* FileSystemResource that explicitly expresses a context-relative path
* through implementing the ContextResource interface.
*/
private static class FileSystemContextResource extends FileSystemResource implements ContextResource {
public FileSystemContextResource(String path) {
super(path);
}
@Override
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return getPath();
}
}
}
-
我们可以从 上面的代码中看到 在
FileSystemResourceLoader中有一个私有的内部类FileSystemContextResource, 这个类继承了FileSystemResource,同时实现了ContextResource接口 -
FileSystemContextResource通过构造函数调用FileSystemResource的构造函数,创建FileSystemResource类型资源定义,同时实现ContextResource是为了实现其中的getPathWithinContext()方法,这个方法是用来获取上下文根路径的, 源码中这样写的 :
/**
* Return the path within the enclosing 'context'.
* This is typically path relative to a context-specific root directory,
* e.g. a ServletContext root or a PortletContext root.
*/
3.3 ClassRelativeResourceLoader
org.springframework.core.io.ClassRelativeResourceLoader 类也是 DefaultResourceLoader 的另一个实现子类,与 FileSystemResourceLoader 类似,也同样重写了 getResourceByPath() 方法,也内部维护了一个私有的内部类 ClassRelativeContextResource , 具体代码如下:
/**
* 从给定的 class 下加载资源
* {@link ResourceLoader} implementation that interprets plain resource paths
* as relative to a given {@code java.lang.Class}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
* @see Class#getResource(String)
* @see ClassPathResource#ClassPathResource(String, Class)
*/
public class ClassRelativeResourceLoader extends DefaultResourceLoader {
private final Class<?> clazz;
/**
* Create a new ClassRelativeResourceLoader for the given class.
* @param clazz the class to load resources through
*/
public ClassRelativeResourceLoader(Class<?> clazz) {
Assert.notNull(clazz, "Class must not be null");
this.clazz = clazz;
setClassLoader(clazz.getClassLoader());
}
/**
* 重写getResourceByPath 方法 , 返回一个ClassRelativeContextResource 资源类型
* @param path the path to the resource
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassRelativeContextResource(path, this.clazz);
}
/**
* 继承 ClassPathResource 定义资源类型,实现ContextResource 中的 getPathWithinContext 方法,
*
* ClassPathResource that explicitly expresses a context-relative path
* through implementing the ContextResource interface.
*/
private static class ClassRelativeContextResource extends ClassPathResource implements ContextResource {
private final Class<?> clazz;
/**
* 调用父类 ClassPathResource 对资源进行初始化
* @param path
* @param clazz
*/
public ClassRelativeContextResource(String path, Class<?> clazz) {
super(path, clazz);
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return getPath();
}
/**
* 重写 ClassPathContext 中方法, 通过给定的路径返回一个ClassRelativeContextResource资源
* @param relativePath the relative path (relative to this resource)
* @return
*/
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(getPath(), relativePath);
return new ClassRelativeContextResource(pathToUse, this.clazz);
}
}
}
3.4 ResourcePatternResolver
org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver 是对 ResourceLoader 的一个扩展,我们在 ResourceLoader 中通过 getResource 方法获取 Resource 实例时,只能通过一个 location 来获取一个 Resource , 而不能获取到多个 Resource , 当我们需要加载多个资源时,只能通过调用多次的该方法来实现,所以spring 提供了 ResourcePatternResolver 对其进行了扩展,实现了通过 location 来加载多个资源,类的定义如下:
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
/**
* Pseudo URL prefix for all matching resources from the class path: "classpath*:"
* This differs from ResourceLoader's classpath URL prefix in that it
* retrieves all matching resources for a given name (e.g. "/beans.xml"),
* for example in the root of all deployed JAR files.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader#CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
/**
* Resolve the given location pattern into Resource objects.
* <p>Overlapping resource entries that point to the same physical
* resource should be avoided, as far as possible. The result should
* have set semantics.
* @param locationPattern the location pattern to resolve
* @return the corresponding Resource objects
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
*/
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
-
可以看到
ResourcePatternResolver新增加了一个方法getResources,返回一个Resource数组 -
这里我们要注意,
ResourcePatternResolver增加了一个新的协议前缀classpath*:, 看到这里是不是大家可以很熟悉的想起我们在平时配置路径时经常会写classpath:和classpath*:,那么他们的区别就在这里,他们的资源加载方式时不一样的
3.5 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是 ResourcePatternResolver 的一个主要实现类,也是使用较多的一个实现类,我们可以来看一下,它主要实现了 新增前缀的解析,同时还支持 Ant 风格的路径匹配模式(如 : "**/*.xml" )
3.5.1 构造函数
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 提供了三个构造函数:
/**
* 内置 资源定位加载器
*/
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
/**
* Ant路径匹配器
*/
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
/**
* 无参构造函数,当不指定内部加载器类型时,默认是 DefaultResourceLoader
* Create a new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver with a DefaultResourceLoader.
* <p>ClassLoader access will happen via the thread context class loader.
* @see org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader
*/
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
/**
* 指定特定的资源定位加载器
* Create a new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.
* <p>ClassLoader access will happen via the thread context class loader.
* @param resourceLoader the ResourceLoader to load root directories and
* actual resources with
*/
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
/**
* 使用默认的资源加载器,但是传入 classLoader ,使用特定的类加载
* Create a new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver with a DefaultResourceLoader.
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to load classpath resources with,
* or {@code null} for using the thread context class loader
* at the time of actual resource access
* @see org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader
*/
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader(classLoader);
}
- 我们可以看到,当构造函数不提供
ResourceLoader时,默认是DefaultResourceLoader
3.5.2 getResource
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 中的 getResource 方法的实现是调用了 传入的 ResourceLoader 或者默认的 DefaultResourceLoader , 具体的代码实现如下:
/**
* 调用getResourceLoader 获取当前的 ResourceLoader
* @param location the resource location
* @return
*/
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}
/**
* Return the ResourceLoader that this pattern resolver works with.
*/
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
3.5.3 getResources
实现了 ResourcePatternResolver 的 getResources 方法,可以通过 location 加载多个资源,进行分类处理,如果是没有 classpath*: 前缀以及不包含通配符的情况下直接调用当前类的 ResourceLoader 来进行处理,其他按具体来处理,主要涉及两个方法 #findPathMatchingResources(...) 与 #findAllClassPathResources(...)
@Override
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
//1. 判断 是不是classpath* 开头的
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
//1.1.进行路径匹配校验 是否包含通配符
// a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible)
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
//1.2 不包含通配符
// all class path resources with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// 2. 不是classpath前缀开头
// Generally only look for a pattern after a prefix here,
// and on Tomcat only after the "*/" separator for its "war:" protocol.
int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 :
locationPattern.indexOf(':') + 1);
//2.1 校验是否包含通配符
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
//2.2 不包含通配符 使用内部 ResourceLoader 进行资源加载 默认是 DefaultReourceLoader
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
3.5.4 findPathMatchingResources
上面代码中我们可以看到,当存在通配符时都会执行 #findPathMatchingResources(...) 方法,我们来看一下方法的定义:
/**
* 通过ant解析器来对给定的路径下的所有模糊资源进行解析和匹配
* 支持jar和zip以及系统中的文件资源
* Find all resources that match the given location pattern via the
* Ant-style PathMatcher. Supports resources in jar files and zip files
* and in the file system.
* @param locationPattern the location pattern to match
* @return the result as Resource array
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @see #doFindPathMatchingJarResources
* @see #doFindPathMatchingFileResources
* @see org.springframework.util.PathMatcher
*/
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
//解析根路径
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
//解析到子路径
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
//获取根路径的资源
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
//遍历
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
URL rootDirUrl = rootDirResource.getURL();
//判断资源是不是 bundle 类型
if (equinoxResolveMethod != null && rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) {
URL resolvedUrl = (URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null, rootDirUrl);
if (resolvedUrl != null) {
rootDirUrl = resolvedUrl;
}
rootDirResource = new UrlResource(rootDirUrl);
}
//判断资源是否是 vfs 类型的
if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirUrl, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
//判断是否是 jar 形式的
else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirUrl, subPattern));
}
//如果都不是
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);
}
//转换为数组返回
return result.toArray(new Resource[0]);
}
- 在
spring中很多真真做操作的方法命名都是以do开头,我们从上面可以看到核心方法#doFindPathMatchingFileResources(...)、#doFindPathMatchingJarResources(...)这两个基本一样知识解析不懂的文件类型,另外还有一个方法#determineRootDir(...)方法实现了路径的解析,下面我们简单看一这两个实现。
3.5.4.1 determineRootDir(... )
determineRootDir 方法主要用于根路径的获取,解析路径中的通配符,代码如下:
/**
* 通过给定的路径来获取根目录路径
* Determine the root directory for the given location.
* <p>Used for determining the starting point for file matching,
* resolving the root directory location to a {@code java.io.File}
* and passing it into {@code retrieveMatchingFiles}, with the
* remainder of the location as pattern.
* <p>Will return "/WEB-INF/" for the pattern "/WEB-INF/*.xml",
* for example.
* @param location the location to check
* @return the part of the location that denotes the root directory
* @see #retrieveMatchingFiles
*/
protected String determineRootDir(String location) {
//1. 找到最后 路径中出现的 : 的索引 +1 ,这里注意我们的路径时 类似 : classpath*: /web-inf/*.xml
int prefixEnd = location.indexOf(':') + 1;
//2. 获取跟路径长度
int rootDirEnd = location.length();
//3.判断冒号后面的路径是否包含通配符 如果包含,则截断最后一个由”/”分割的部分。
while (rootDirEnd > prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/', rootDirEnd - 2) + 1;
}
//
if (rootDirEnd == 0) {
rootDirEnd = prefixEnd;
}
return location.substring(0, rootDirEnd);
}
举例看一下:
| 原路径 | 获取跟路径 |
|---|---|
classpath*:/test/aa*/app-*.xml |
classpath*:/test/ |
classpath*:/test/aa/app-*.xml |
classpath*:/test/aa |
3.5.4.2 doFindPathMatchingFileResources(... )
#doFindPathMatchingFileResources(...) 、 #doFindPathMatchingJarResources(...) 方法的的内部基本一致,只是解析不同的类型文件,我们这里只看其中一个则可,大家可以自行比对两者的区别。
-
我们跟一下
#doFindPathMatchingFileResources(...)方法,方法内部调用较深,所以下面我主要把代码贴出来,注释已有,相信可以看的懂 -
#doFindPathMatchingFileResources(...)代码:
/**
* 查找文件系统符合给定的location的资源, 路径符合 ant 样式的通配符
* Find all resources in the file system that match the given location pattern
* via the Ant-style PathMatcher.
* @param rootDirResource the root directory as Resource
* @param subPattern the sub pattern to match (below the root directory)
* @return a mutable Set of matching Resource instances
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @see #retrieveMatchingFiles
* @see org.springframework.util.PathMatcher
*/
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingFileResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
File rootDir;
try {
//获取绝对路径对应的文件目录
rootDir = rootDirResource.getFile().getAbsoluteFile();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Cannot search for matching files underneath " + rootDirResource +
" in the file system: " + ex.getMessage());
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Failed to resolve " + rootDirResource + " in the file system: " + ex);
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
//调用真真处理方法
return doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(rootDir, subPattern);
}
- 上面方法中主要调用了核心流程
#doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(...), 代码如下:
/**
* 通过ant通配符的subPattern与已经获取的根目录rootDir来组合获取所有在文件系统中的资源
* 如:我们本来的 url: 'classpath*:/test/aa/app-*.xml'
* 那么这里rootDir:classpath*:/test/aa/ subPattern :app-*.xml
* Find all resources in the file system that match the given location pattern
* via the Ant-style PathMatcher.
* @param rootDir the root directory in the file system
* @param subPattern the sub pattern to match (below the root directory)
* @return a mutable Set of matching Resource instances
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @see #retrieveMatchingFiles
* @see org.springframework.util.PathMatcher
*/
protected Set<Resource> doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(File rootDir, String subPattern) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Looking for matching resources in directory tree [" + rootDir.getPath() + "]");
}
//调用真实处理方法,获取set集合的File
Set<File> matchingFiles = retrieveMatchingFiles(rootDir, subPattern);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(matchingFiles.size());
//将获取的File转换为 FileSystemResource 同时添加到result结果集中
for (File file : matchingFiles) {
result.add(new FileSystemResource(file));
}
return result;
}
上面方法主要是将获取的 Set<File> 的结果进行转换,将资源类型转换为 FileSystemResource , 上面方法的核心方法是 #retrieveMatchingFiles(...)
#retrieveMatchingFiles(...)代码如下:
/**
*
* Retrieve files that match the given path pattern,
* checking the given directory and its subdirectories.
* @param rootDir the directory to start from
* @param pattern the pattern to match against,
* relative to the root directory
* @return a mutable Set of matching Resource instances
* @throws IOException if directory contents could not be retrieved
*/
protected Set<File> retrieveMatchingFiles(File rootDir, String pattern) throws IOException {
//1.不存在直接返回空集合
if (!rootDir.exists()) {
// Silently skip non-existing directories.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because it does not exist");
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
//2.不是目录直接返回空
if (!rootDir.isDirectory()) {
// Complain louder if it exists but is no directory.
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipping [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() + "] because it does not denote a directory");
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
//3/判断是否可读
if (!rootDir.canRead()) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipping search for matching files underneath directory [" + rootDir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
//4.将所有的系统分割器转换为 /
String fullPattern = StringUtils.replace(rootDir.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
//5.若子路径开头没有 / 则父路径要最后添加 /
if (!pattern.startsWith("/")) {
fullPattern += "/";
}
fullPattern = fullPattern + StringUtils.replace(pattern, File.separator, "/");
Set<File> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
//真真处理的方法
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, rootDir, result);
return result;
}
我们可以看到方法中主要是做了一些校验和转换,真真的处理是调用了 #doRetrieveMatchingFiles(...) 方法,
#doRetrieveMatchingFiles(...)方法定义:
/**
* 递归遍历 dir 目录 结合fullpattern 进行路径匹配,将符合的资源全部放入result中
* Recursively retrieve files that match the given pattern,
* adding them to the given result list.
* @param fullPattern the pattern to match against,
* with prepended root directory path
* @param dir the current directory
* @param result the Set of matching File instances to add to
* @throws IOException if directory contents could not be retrieved
*/
protected void doRetrieveMatchingFiles(String fullPattern, File dir, Set<File> result) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching directory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] for files matching pattern [" + fullPattern + "]");
}
//遍历目录
for (File content : listDirectory(dir)) {
//获取当前文件/目录的路径同时分隔符全部替换为 /
String currPath = StringUtils.replace(content.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
//如果是目录 同时和 fullPattern匹配 则进递归
if (content.isDirectory() && getPathMatcher().matchStart(fullPattern, currPath + "/")) {
if (!content.canRead()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipping subdirectory [" + dir.getAbsolutePath() +
"] because the application is not allowed to read the directory");
}
}
else {
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, content, result);
}
}
//如果是文件则进行匹配
if (getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
result.add(content);
}
}
}
3.5.5 findAllClassPathResources
上面分析了当有通配符时的方法调用过程,那么这里我们来分析当没有通配符时的方法调用
#findAllClassPathResources(...)方法代码:
/**
* 通过ClassLoader 来 加载所有的 class location
* Find all class location resources with the given location via the ClassLoader.
* Delegates to {@link #doFindAllClassPathResources(String)}.
* @param location the absolute path within the classpath
* @return the result as Resource array
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
* @see java.lang.ClassLoader#getResources
* @see #convertClassLoaderURL
*/
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
//真实处理方法, 得到资源结果集
Set<Resource> result = doFindAllClassPathResources(path);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result);
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[0]);
}
#doFindAllClassPathResources(...)方法代码:
/**
* Find all class location resources with the given path via the ClassLoader.
* Called by {@link #findAllClassPathResources(String)}.
* @param path the absolute path within the classpath (never a leading slash)
* @return a mutable Set of matching Resource instances
* @since 4.1.1
*/
protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException {
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
//1.通过ClassLoader获取所有的URl
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path));
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
//将URl转换为 UrlResource
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
if ("".equals(path)) {
// The above result is likely to be incomplete, i.e. only containing file system references.
// We need to have pointers to each of the jar files on the classpath as well...
//添加所有的jar包
addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result);
}
return result;
}
方法内相对简单,主要是通过ClassLoader来加载目录下的jar资源,详细不再贴出来,可以自行查看
本文由AnonyStar 发布,可转载但需声明原文出处。
仰慕「优雅编码的艺术」 坚信熟能生巧,努力改变人生
欢迎关注微信公账号 :coder简码 获取更多优质文章
更多文章关注笔者博客 :IT简码