本文通过模拟汇编里的stack机制,构建一个自己的stack,然后将上一篇blog末尾的递归函数void bst_walk(bst_node_t *root)非递归化。
o libstack.h
1 #ifndef _LIBSTACK_H 2 #define _LIBSTACK_H 3 4 #ifdef __cplusplus 5 extern "C" { 6 #endif 7 8 typedef void * uintptr_t; /* generic pointer to any struct */ 9 10 uintptr_t *stack_init(size_t size); 11 void stack_fini(); 12 int stack_isFull(); 13 int stack_isEmpty(); 14 void push(uintptr_t e); 15 void pop(uintptr_t *e); 16 17 #ifdef __cplusplus 18 } 19 #endif 20 21 #endif /* _LIBSTACK_H */
o libstack.c
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include "libstack.h" 4 5 /** 6 * Basic Stack OPs are supported, including: 7 * 8 * 1. Construct/Destruct a stack 9 * 2. Tell stack is full or empty 10 * 3. push() and pop() 11 * 12 * == DESIGN NOTES == 13 * 14 * There are 3 static variables reserved, 15 * 16 * ss: stack segment 17 * sp: stack pointer 18 * sz: stack size 19 * 20 * And the stack looks like: 21 * 22 * | RED | ss[-1] ; SHOULD NEVER BE ACCESSED 23 * low-addr +-----+ <------------TopOfStack----------- 24 * ^ | | ss[0] 25 * | | | ss[1] 26 * | | ... | 27 * | | | 28 * | | | ss[sz-1] 29 * | +-----+ <------------BottomOfStack-------- 30 * high-addr | RED | ss[sz] ; SHOULD NEVER BE ACCESSED 31 * 32 * (1) If (sp - ss) == 0, stack is full 33 * (2) If (sp - ss) == sz, stack is empty 34 * (3) Push(E): { sp -= 1; *sp = E; } 35 * (4) Pop(&E): { *E = *sp; sp += 1; } 36 */ 37 38 static uintptr_t *ss = NULL; /* stack segment */ 39 static uintptr_t *sp = NULL; /* stack pointer */ 40 static size_t sz = 0; /* stack size */ 41 42 int stack_isFull() { return (sp == ss); } 43 int stack_isEmpty() { return (sp == ss + sz); } 44 45 uintptr_t * 46 stack_init(size_t size) 47 { 48 ss = (uintptr_t *)malloc(sizeof (uintptr_t) * size); 49 if (ss == NULL) { 50 fprintf(stderr, "failed to malloc "); 51 return NULL; 52 } 53 54 sz = size; 55 sp = ss + size; 56 return ss; 57 } 58 59 void 60 stack_fini() 61 { 62 free(ss); 63 } 64 65 void 66 push(uintptr_t e) 67 { 68 sp -= 1; 69 *sp = e; 70 } 71 72 void 73 pop(uintptr_t *e) 74 { 75 *e = *sp; 76 sp += 1; 77 }
1. 一旦栈被初始化后,栈指针sp一定是指向栈底,*sp不可访问(尤其是写操作),因为不在分配的内存有效范围内;
2. 对于入栈操作(push), 第一步是将sp-=1, 第二步是写入要入栈的元素 (*sp = E); (因为初始化后*sp的内存不可写,所以push操作一定率先改写sp)
3. 对于出栈操作(pop), 顺序与push相反,第一步取出sp指向的内存地址里的内容(E = *sp), 第二步才是将sp+=1;
o foo.c (简单测试)
1 /** 2 * A simple test against stack OPs, including: 3 * o stack_init(), stack_fini() 4 * o stack_isFull(), stack_isEmpty() 5 * o push(), pop() 6 */ 7 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 #include "libstack.h" 10 11 static void 12 dump_stack(uintptr_t *ss, size_t size) 13 { 14 (void) printf("%p: ", ss); 15 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 16 if (ss[i] != NULL) 17 (void) printf("%-10p ", *(ss+i)); 18 else 19 (void) printf("0x%-8x ", 0x0); 20 } 21 printf(" "); 22 } 23 24 int 25 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 26 { 27 size_t size = 4; 28 29 uintptr_t *ss = stack_init(size); 30 dump_stack(ss, size); 31 32 for (int i = 0; !stack_isFull(); i++) { 33 push((uintptr_t)(ss+i)); 34 dump_stack(ss, size); 35 } 36 37 (void) printf(" "); 38 39 uintptr_t e = NULL; 40 for (; !stack_isEmpty();) { 41 pop(&e); 42 (void) printf(" (pop) got %-10p ", e); 43 } 44 45 stack_fini(); 46 47 return 0; 48 }
o Makefile
1 CC = gcc 2 CFLAGS = -g -Wall -std=gnu99 -m32 3 INCS = 4 5 TARGET = foo 6 7 all: ${TARGET} 8 9 foo: foo.o libstack.o 10 ${CC} ${CFLAGS} -o $@ $^ 11 12 foo.o: foo.c 13 ${CC} ${CFLAGS} -c $< ${INCS} 14 15 libstack.o: libstack.c libstack.h 16 ${CC} ${CFLAGS} -c $< 17 18 clean: 19 rm -f *.o 20 clobber: clean 21 rm -f ${TARGET}
o 编译和运行测试
$ make gcc -g -Wall -std=gnu99 -m32 -c foo.c gcc -g -Wall -std=gnu99 -m32 -c libstack.c gcc -g -Wall -std=gnu99 -m32 -o foo foo.o libstack.o $ ./foo 0x8ecc008: 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x8ecc008: 0x0 0x0 0x0 0x8ecc008 0x8ecc008: 0x0 0x0 0x8ecc00c 0x8ecc008 0x8ecc008: 0x0 0x8ecc010 0x8ecc00c 0x8ecc008 0x8ecc008: 0x8ecc014 0x8ecc010 0x8ecc00c 0x8ecc008 (pop) got 0x8ecc014 (pop) got 0x8ecc010 (pop) got 0x8ecc00c (pop) got 0x8ecc008 $
测试简单且直接,不解释。如果还不确信,可以用gdb调试。
现在对上一篇blog末尾的递归函数使用上面实现的stack进行去递归化改写,改写后的代码如下:
1 void 2 bst_walk(bst_node_t *root) 3 { 4 if (root == NULL) 5 return; 6 7 (void) stack_init(STACK_SIZE); 8 9 while (root != NULL || !stack_isEmpty()) { 10 if (root != NULL) { 11 push((uintptr_t)root); 12 root = root->left; 13 continue; 14 } 15 16 pop((uintptr_t *)(&root)); 17 printf("%d ", root->key); 18 19 root = root->right; 20 } 21 22 stack_fini(); 23 }
为方便阅读,下面给出使用meld进行diff后的截图,
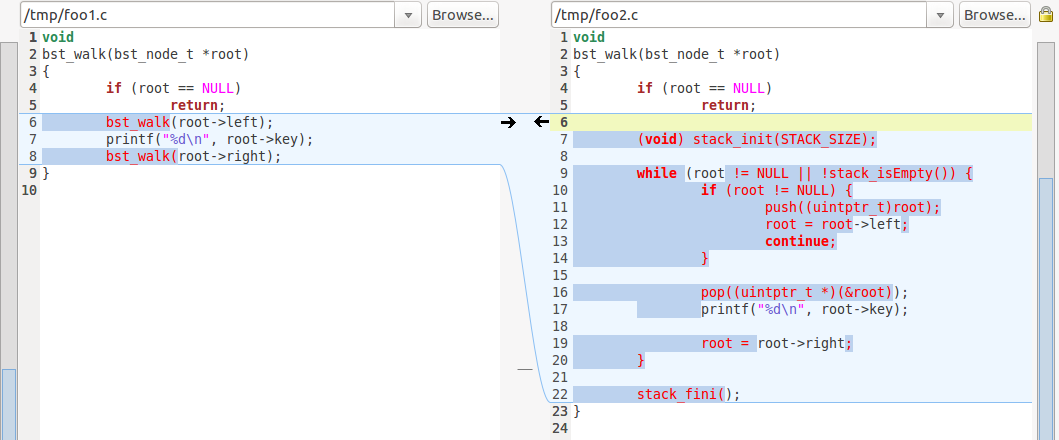
- L7: 构建一个stack, 其中STACK_SIZE是一个宏
- L22: 将stack销毁
- L9-14: 首先遍历左子树,不断将结点压入栈中,直到到达最左的叶子结点,那么则执行L16-17 (最左的叶子结点也会被压入栈中)
- L16-17: 出栈并打印结点的key
- L19: 将新的根结点设置为刚刚出栈的结点的右儿子, 重新执行L9-17, 直到所有结点都被遍历到(当然, stack为空)
注: 左图中的函数使用了两次递归,所以将其转化成非递归函数的难度相对较大。