Spark2.0 MLPC(多层神经网络分类器)算法概述
MultilayerPerceptronClassifier(MLPC)这是一个基于前馈神经网络的分类器,它是一种在输入层与输出层之间含有一层或多层隐含结点的具有正向传播机制的神经网络模型。
中间的节点使用sigmoid (logistic)函数,输出层的节点使用softmax函数。输出层的节点的数目表示分类器有几类。MLPC学习过程中使用BP算法,优化问题抽象成logistic loss function并使用L-BFGS进行优化。
算法进一步剖析
Sigmoid函数
中间层使用Sigmoid函数(也叫 logistic函数),看下面的函数曲线,Zi=0时,f(Zi)=0.5,Zi<0时候,f(Zi)<0.5, Zi>0时,f(Zi)>0.5,这样就可以把f(Zi)当概率理解了,大于0.5的概率一类,小于0.5概率的一类。由此可见,Sigmoid函数通常用于二分问题。
Sigmoid函数:
Sigmoid微分:
Sigmoid函数可以连续微分,因此可以用在BP(后向传播)过程中。使用这个函数形式还有一个很重要的原因,Sigmoid函数的微分形式完全可以用自身表达出来,与函数变量x无关,使得Sigmoid的函数很容易使用链式法则。
BP
参考博文:
BP神经网络后向传播原理
http://blog.csdn.net/tingyue_/article/details/38966249
softmax函数
参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Softmax_function
假设输出层有K个节点,各节点完成训练后的拟合系数向量为:
w1,w2,...wk...wK,注意这里的wk是第k节点的拟合系数向量,wk本身也是一个向量,wk=[wk0,wk1,...],k=1∼K,
xk是最后一个隐含层向第k个节点的输出向量
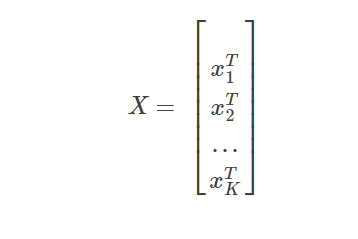
X是最后一个隐含层对所有节点的输出矩阵
softmax函数为:
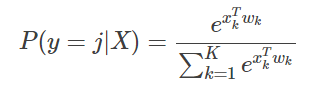
显然对所有输出节点而言,最大概率(P(y=j|X),j=1∼K)所在的位置,就是某个样本最终的分类。
Spark2.0 MLPC 代码(流程)
package my.spark.ml.practice.classification; import org.apache.log4j.Level; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.MultilayerPerceptronClassificationModel; import org.apache.spark.ml.classification.MultilayerPerceptronClassifier; import org.apache.spark.ml.evaluation.MulticlassClassificationEvaluator; import org.apache.spark.sql.Dataset; import org.apache.spark.sql.Row; import org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession; public class myMLPC { public static void main(String[] args) { SparkSession spark=SparkSession .builder() .appName("MLPC") .master("local[4]") .config("spark.sql.warehouse.dir","file///:G:/Projects/Java/Spark/spark-warehouse" ) .getOrCreate(); String path="G:/Projects/CgyWin64/home/pengjy3/softwate/spark-2.0.0-bin-hadoop2.6/" + "data/mllib/sample_multiclass_classification_data.txt"; //屏蔽日志 Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.ERROR); Logger.getLogger("org.eclipse.jetty.server").setLevel(Level.OFF); //加载数据,randomSplit时加了一个固定的种子seed=100, //是为了得到可重复的结果,方便调试算法,实际工作中不能这样设置 Dataset<Row>[] split=spark.read().format("libsvm").load(path).randomSplit(new double[]{0.6,0.4},100); Dataset<Row> training=split[0]; Dataset<Row> test=split[1]; training.show(100,false);//数据检查 //第一层树特征个数 //最后一层,即输出层是labels个数(类数) //隐藏层自己定义 int[] layer=new int[]{4,6,4,3}; int[] maxIter=new int[]{5,10,20,50,100,200}; double[] accuracy=new double[]{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}; //利用如下类似的循环可以很方便的对各种参数进行调优 for(int i=0;i<maxIter.length;i++){ MultilayerPerceptronClassifier multilayerPerceptronClassifier= new MultilayerPerceptronClassifier() .setLabelCol("label") .setFeaturesCol("features") .setLayers(layer) .setMaxIter(maxIter[i]) .setBlockSize(128) .setSeed(1000); MultilayerPerceptronClassificationModel model= multilayerPerceptronClassifier.fit(training); Dataset<Row> predictions=model.transform(test); MulticlassClassificationEvaluator evaluator= new MulticlassClassificationEvaluator() .setLabelCol("label") .setPredictionCol("prediction") .setMetricName("accuracy"); accuracy[i]=evaluator.evaluate(predictions); } //一次性输出所有评估结果 for(int j=0;j<maxIter.length;j++){ String str_accuracy=String.format(" accuracy = %.2f", accuracy[j]); String str_maxIter=String.format(" maxIter = %d", maxIter[j]); System.out.println(str_maxIter+str_accuracy); } } }
参数设置,算法调优
Spark2.0中对于这个在1.6版本新加入的机器学习算法还没有什么文档,我们就用下面的办法吧:
//Spark中explainParams函数可以展示某个分类器有那些参数: System.out.println(multilayerPerceptronClassifier.explainParams()); //有一些不影响结果设置的我就省略了(如输入label列labelCol等等)。 (1)layers: Sizes of layers from input layer to output layer. E.g., Array(780, 100, 10) means 780 inputs, one hidden layer with 100 neurons and output layer of 10 neurons. (current: [I@158f492) (2)maxIter: maximum number of iterations (>= 0) (default: 100, current: 20) (3)tol: the convergence tolerance for iterative algorithms (default: 1.0E-4) (4)solver: The solver algorithm for optimization. Supported options: l-bfgs, gd. (Default l- bfgs) (5)stepSize: Step size to be used for each iteration of optimization (default: 0.03) (6)blockSize: Block size for stacking input data in matrices. Data is stacked within partitions. If block size is more than remaining data in a partition then it is adjusted to the size of this data. Recommended size is between 10 and 1000 (default: 128, current: 128)
可以设定的一些参数有: 神经网络结构
(1)layers:???
迭代停止条件
(2)maxIter: 需要运算到结果收敛
(3)tol: 允许误差 一般取0.001~0.00001,当迭代结果的误差小于该值时,结束迭代计算,给出结果。
优化算法-solver
Spark中的优化算法,可以参考本人的另两篇文章:
ML优化算法之一:梯度下降算法、随机梯度下降(应用于线性回归、Logistic回归等等)
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_34531825/article/details/52396165
(4)solver:有两种算法可供选择: l-bfgs和gd;
.stepSize=0.03,tol=0.0001
l-bfgs:上很快能收敛,大约20次,训练速度也更快
maxIter = 5 accuracy = 0.35 training time = 267ms
maxIter = 10 accuracy = 0.74 training time = 429ms
maxIter = 20 accuracy = 0.91 training time = 657ms
maxIter = 50 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 941ms
maxIter = 100 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 914ms
maxIter = 500 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 1052msgd算法:需要多得多的迭代次数,即使在提高学习率和提高允许误差tol的情况下,
还是慢很多,慢10以上倍左右吧。
stepsize=0.2,tol=0.001
maxIter = 100 accuracy = 0.55 training time = 4209ms
maxIter = 500 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 11216ms
maxIter = 1000 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 14540ms
maxIter = 2000 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 14708ms
maxIter = 5000 accuracy = 0.92 training time = 14669ms
由此可见,两种算法要想达到收敛,GB(梯度下降算法)慢很多,建议优先使用L-BFGS。
In general, when L-BFGS is available, we recommend using it instead of SGD since L-BFGS tends to converge faster (in fewer iterations).(Spark document)
(5)学习率stepSize,这是一个比较关键的参数
一般来说学习率越大,权重变化越大,收敛越快;但训练速率过大,会引起系统的振荡。
太高的学习率,可以减少网络训练的时间,但是容易导致网络的不稳定与训练误差的增加,
会引起系统的振荡。
太低的学习率,需要较长的训练时间。
在实际工作中,在时间可以接受的范围内,为了模型的稳定性,还是建议选择尽量选择
小一些的学习率。 
(6)blockSize:这个不很清楚究竟是什么?希望计算机牛人告诉我。



