20 Unix Command Line Tricks – Part I
http://www.cyberciti.biz/open-source/command-line-hacks/20-unix-command-line-tricks-part-i/
Deleting a HUGE file
I had a huge log file 200GB I need to delete on a production web server. My rm and ls command was crashed and I was afraid that the system to a crawl with huge disk I/O load. To remove a HUGE file, enter:
> /path/to/file.log # or use the following syntax : > /path/to/file.log # finally delete it rm /path/to/file.log
Want to cache console output?
Try the script command line utility to create a typescript of everything printed on your terminal.
script my.terminal.sessio
Type commands:
ls date sudo service foo stop
To exit (to end script session) type exit or logout or press control-D
exit
To view type:
more my.terminal.session less my.terminal.session cat my.terminal.session
Restoring deleted /tmp folder
As my journey continues with Linux and Unix shell, I made a few mistakes. I accidentally deleted /tmp folder. To restore it all you have to do is:
mkdir /tmp chmod 1777 /tmp chown root:root /tmp ls -ld /tmp
Locking a directory
For privacy of my data I wanted to lock down /downloads on my file server. So I ran:
chmod 0000 /downloads
The root user can still has access and ls and cd commands will not work. To go back:
chmod 0755 /downloads
Password protecting file in vim text editor
Afraid that root user or someone may snoop into your personal text files? Try password protection to a file in vim, type:
vim +X filename
Or, before quitting in vim use :X vim command to encrypt your file and vim will prompt for a password.
Clear gibberish all over the screen
Just type:
reset
Becoming human
Pass the -h or -H (and other options) command line option to GNU or BSD utilities to get output of command commands like ls, df, du, in human-understandable formats:
ls -lh # print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G) df -h df -k # show output in bytes, KB, MB, or GB free -b free -k free -m free -g # print sizes in human readable format (e.g., 1K 234M 2G) du -h # get file system perms in human readable format stat -c %A /boot # compare human readable numbers sort -h -a file # display the CPU information in human readable format on a Linux lscpu lscpu -e lscpu -e=cpu,node # Show the size of each file but in a more human readable way tree -h tree -h /boot
Show information about known users in the Linux based system
Just type:
## linux version ## lslogins ## BSD version ## logins
Sample outputs:
UID USER PWD-LOCK PWD-DENY LAST-LOGIN GECOS 0 root 0 0 22:37:59 root 1 bin 0 1 bin 2 daemon 0 1 daemon 3 adm 0 1 adm 4 lp 0 1 lp 5 sync 0 1 sync 6 shutdown 0 1 2014-Dec17 shutdown 7 halt 0 1 halt 8 mail 0 1 mail 10 uucp 0 1 uucp 11 operator 0 1 operator 12 games 0 1 games 13 gopher 0 1 gopher 14 ftp 0 1 FTP User 27 mysql 0 1 MySQL Server 38 ntp 0 1 48 apache 0 1 Apache 68 haldaemon 0 1 HAL daemon 69 vcsa 0 1 virtual console memory owner 72 tcpdump 0 1 74 sshd 0 1 Privilege-separated SSH 81 dbus 0 1 System message bus 89 postfix 0 1 99 nobody 0 1 Nobody 173 abrt 0 1 497 vnstat 0 1 vnStat user 498 nginx 0 1 nginx user 499 saslauth 0 1 "Saslauthd user"
How do I fix mess created by accidentally untarred files in the current dir?
So I accidentally untar a tarball in /var/www/html/ directory instead of /home/projects/www/current. It created mess in /var/www/html/. The easiest way to fix this mess:
cd /var/www/html/ /bin/rm -f "$(tar ztf /path/to/file.tar.gz)"
Confused on a top command output?
Seriously, you need to try out htop instead of top:
sudo htop
Want to run the same command again?
Just type !!. For example:
/myhome/dir/script/name arg1 arg2 # To run the same command again !! ## To run the last command again as root user sudo !!
The !! repeats the most recent command. To run the most recent command beginning with "foo":
!foo # Run the most recent command beginning with "service" as root sudo !service
The !$ use to run command with the last argument of the most recent command:
# Edit nginx.conf sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # Test nginx.conf for errors /sbin/nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf # After testing a file with "/sbin/nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf", you # can edit file again with vi sudo vi !$
Get a reminder you when you have to leave
If you need a reminder to leave your terminal, type the following command:
leave +hhmm
Where,
- hhmm - The time of day is in the form hhmm where hh is a time in hours (on a 12 or 24 hour clock), and mm are minutes. All times are converted to a 12 hour clock, and assumed to be in the next 12 hours.
Home sweet home
Want to go the directory you were just in? Run:cd -
Need to quickly return to your home directory? Enter:cd
The variable CDPATH defines the search path for the directory containing directories:
export CDPATH=/var/www:/nas10
Now, instead of typing cd /var/www/html/ I can simply type the following to cd into /var/www/html path:
cd html
Editing a file being viewed with less pager
To edit a file being viewed with less pager, press v. You will have the file for edit under $EDITOR:
less *.c less foo.html ## Press v to edit file ## ## Quit from editor and you would return to the less pager again ##
List all files or directories on your system
To see all of the directories on your system, run:
find / -type d | less # List all directories in your $HOME find $HOME -type d -ls | less
To see all of the files, run:
find / -type f | less # List all files in your $HOME find $HOME -type f -ls | less
Build directory trees in a single command
You can create directory trees one at a time using mkdir command by passing the -p option:
mkdir -p /jail/{dev,bin,sbin,etc,usr,lib,lib64}
ls -l /jail/
Copy file into multiple directories
Instead of running:
cp /path/to/file /usr/dir1 cp /path/to/file /var/dir2 cp /path/to/file /nas/dir3
Run the following command to copy file into multiple dirs:
echo /usr/dir1 /var/dir2 /nas/dir3 | xargs -n 1 cp -v /path/to/file
Creating a shell function is left as an exercise for the reader
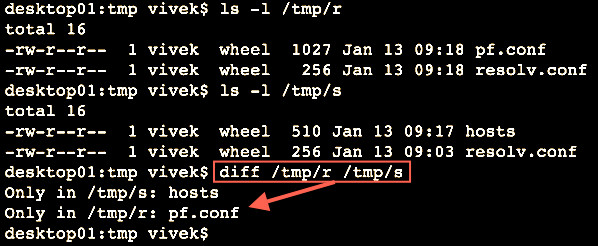
Quickly find differences between two directories
The diff command compare files line by line. It can also compare two directories:
ls -l /tmp/r ls -l /tmp/s # Compare two folders using diff ## diff /tmp/r/ /tmp/s/
Text formatting
You can reformat each paragraph with fmt command. In this example, I'm going to reformat file by wrapping overlong lines and filling short lines:
fmt file.txt
You can also split long lines, but do not refill i.e. wrap overlong lines, but do not fill short lines:
fmt -s file.txt
See the output and write it to a file
Use the tee command as follows to see the output on screen and also write to a log file named my.log:
mycoolapp arg1 arg2 input.file | tee my.log
The tee command ensures that you will see mycoolapp output on on the screen and to a file same time.