1基本原理:
模拟退火算法源于固体的退火过程,当把一个固体的加热使其升温,其内部分子出现无序状态,内能增大
而降温时,所有粒子趋于有序,冷却到最低温度时内能达到最少。当某一状态下系统内能减少,则完全
接受这一新的状态,否则对于这一状态采样概率接受,温度越高,接受的概率越大。当温度由初始值逐渐
降到最低温度时,即可得到最低的内能,也就是算法的最优解。
2算法步骤:
(1)设置算法的参数:初始温度,结束温度,温度衰减系数,每个温度下的扰动次数,初始状态,初始解
(2)对状态产生扰动,计算新状态下的解,比较两个解的大小,判断是否接受新的状态
(3)在此温度下,对步骤(2)按设置的扰动次数重复进行扰动
(4)对温度进行衰减,并在新的温度下重复(2)(3),直到结束温度
(5)输出记录最优状态和最优解,算法结束
3实例计算:
采用TSP问题中的eil51数据,官方的最优解为426,编写Matlab程序,进行计算
4Matlab代码:
clc,clear %清空环境中的变量 tic iter = 1; % 迭代次数初值 a=0.99; %温度衰减系数 t0=120; %初始温度 tf=1; %最后温度 t=t0; Markov=10000; %Markov链长度 load data1.txt %读入城市的坐标 city=data1; n = size(city,1); %城市距离初始化 D = zeros(n,n); for i = 1:n for j = 1:n D(i,j) = sqrt(sum((city(i,:) - city(j,:)).^2)); end end route=1:n; route_new=route; best_length=Inf; Length=Inf; best_route=route; %% while t>=tf for j=1:Markov %进行扰动,长生新的序列route_new; if (rand<0.7) %交换两个数的顺序 ind1=0;ind2=0; while(ind1==ind2&&ind1>=ind2) ind1=ceil(rand*n); ind2=ceil(rand*n); end temp=route_new(ind1); route_new(ind1)=route_new(ind2); route_new(ind2)=temp; else ind=zeros(3,1); L_ind=length(unique(ind)); while (L_ind<3) ind=ceil([rand*n rand*n rand*n]); L_ind=length(unique(ind)); end ind0=sort(ind); a1=ind0(1);b1=ind0(2);c1=ind0(3); route0=route_new; route0(a1:a1+c1-b1-1)=route_new(b1+1:c1); route0(a1+c1-b1:c1)=route_new(a1:b1); route_new=route0; end %计算路径的距离,Length_new length_new = 0; Route=[route_new route_new(1)]; for j = 1:n length_new = length_new+ D(Route(j),Route(j + 1)); end if length_new<Length Length=length_new; route=route_new; %对最优路线和距离更新 if length_new<best_length iter = iter + 1; best_length=length_new; best_route=route_new; end else if rand<exp(-(length_new-Length)/t) route=route_new; Length=length_new; end end route_new=route; end t=t*a; end %-------------------------------------------------------------------------- %% 结果显示 toc Route=[best_route best_route(1)]; plot([city(Route ,1)], [city(Route ,2)],'o-'); disp('最优解为:') disp(best_route) disp('最短距离:') disp(best_length) disp('最优解迭代次数:') disp(iter) for i = 1:n %对每个城市进行标号 text(city(i,1),city(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)]); end xlabel('城市位置横坐标') ylabel('城市位置纵坐标') title(['模拟退火算法(最短距离):' num2str(best_length) ''])
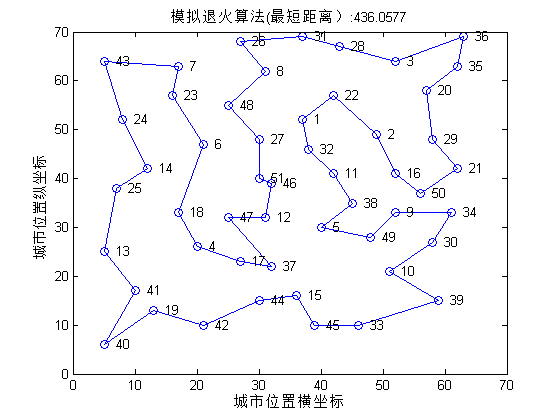
5运行结果:
最短距离:436.7146,其和最优解426接近
TSP图: