本篇记录一下springboot监听事件的四种方式。总体来说,springboot监听事件包含四个步骤
(1)自定义要监听的事件
(2)自定义监听器
(3)使spring容器获取到监听器,这里有三种方式,后面会依次说到
(4)发布事件
下面是详细步骤:
pom.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.edu.spring</groupId> <artifactId>springboot</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>springboot</name> <!-- FIXME change it to the project's website --> <url>http://www.example.com</url> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <scope>import</scope> <type>pom</type> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
MyApplicationEvent.java自定义事件,继承ApplicationEvent

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; public class MyApplicationEvent extends ApplicationEvent { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public MyApplicationEvent(Object source) { super(source); } }
MyAppilcationListener.java实现接口ApplicationListener,接收自定义事件的泛型

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; public class MyAppilcationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent> { public void onApplicationEvent(MyApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("接收到事件:"+event.getClass()); } }
App.java发布事件,这里添加监听器的方式是SpringApplication的addListeners方法

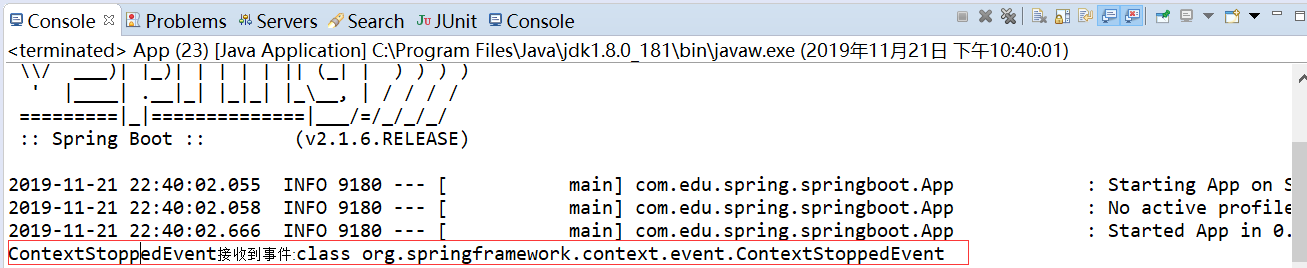
package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication app=new SpringApplication(App.class); app.addListeners(new MyAppilcationListener());//添加监听 ConfigurableApplicationContext context=app.run(args); context.publishEvent(new MyApplicationEvent(new Object()));//发布事件 context.close(); } }
运行结果如下:
第二种添加监听器的方式,在自定义的监听器上添加@Component,如下:
MyAppilcationListener.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyAppilcationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent> { public void onApplicationEvent(MyApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("接收到事件:"+event.getClass()); } }
App.java,现在不需要调用SpringApplication的addListeners方法,如下:

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication app=new SpringApplication(App.class); ConfigurableApplicationContext context=app.run(args); context.publishEvent(new MyApplicationEvent(new Object()));//发布事件 context.close(); } }
第三种添加监听器的方式,在application.properties配置文件中添加context.listener.classes属性,如下
application.properties

context.listener.classes=com.edu.spring.springboot.MyAppilcationListener
MyAppilcationListener.java,不需要添加注解,如下:

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; public class MyAppilcationListener implements ApplicationListener<MyApplicationEvent> { public void onApplicationEvent(MyApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("接收到事件:"+event.getClass()); } }
App.java,现在不需要调用SpringApplication的addListeners方法,如下:

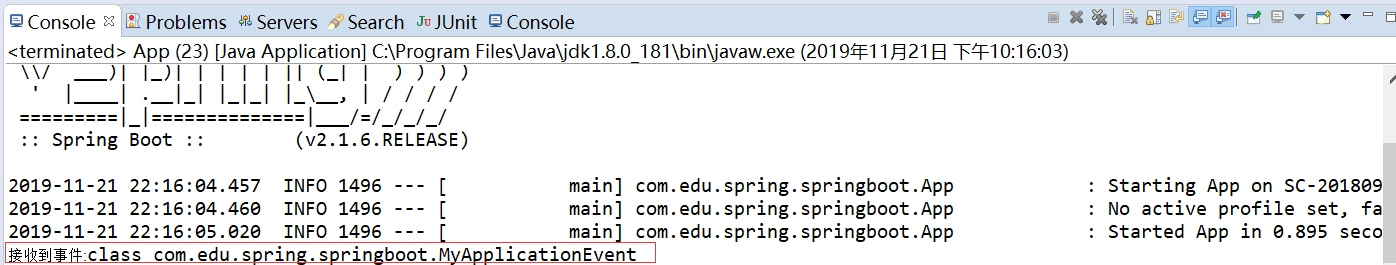
package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication app=new SpringApplication(App.class); ConfigurableApplicationContext context=app.run(args); context.publishEvent(new MyApplicationEvent(new Object()));//发布事件 context.close(); } }
运行结果如下:
第四种添加监听器的方式,使用@EventListener注解,如下:
MyEventHandle.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyEventHandle { @EventListener public void event(MyApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("MyEventHandle接收到事件:"+event.getClass()); } }
App.java

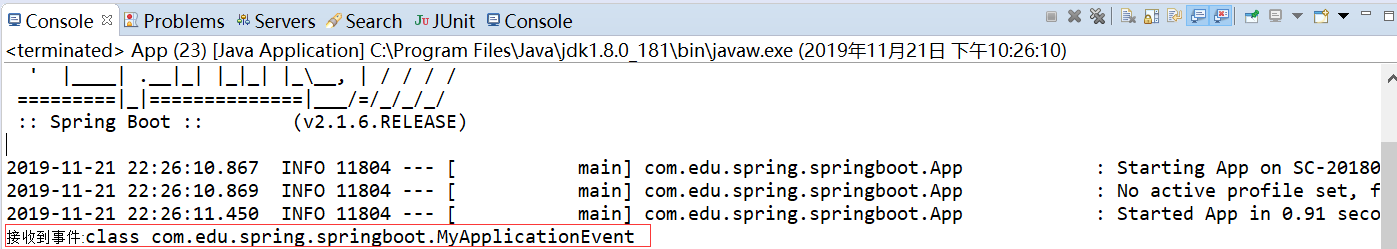
package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication app=new SpringApplication(App.class); ConfigurableApplicationContext context=app.run(args); context.publishEvent(new MyApplicationEvent(new Object()));//发布事件 context.close(); } }
运行结果如下:
很明显,第四种方式最简洁,既不用实现ApplicationListener接口,也不用调用SpringApplication的addListeners方法。
spring自定义了许多事件,如下图:
使用这些事件的时候不用发布,下面拿ContextStoppedEvent举例,该事件在调用ConfigurableApplicationContext的stop方法时触发。
MyEventHandle.java,可以写多个事件,只要在方法上添加@EventListener即可

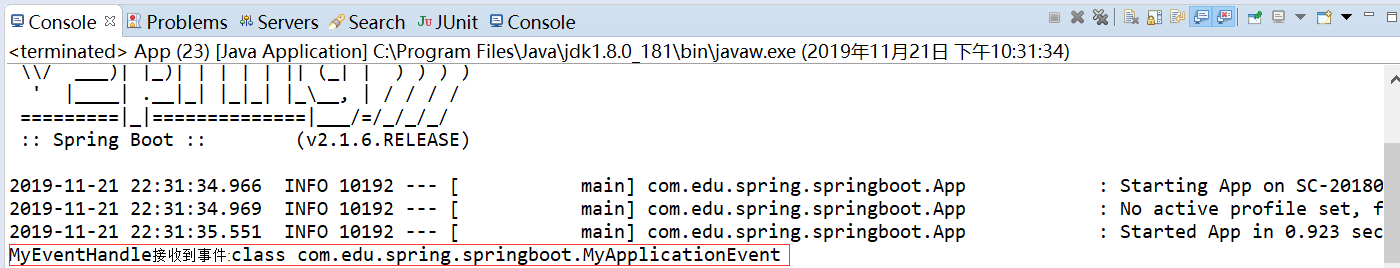
package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.context.event.ContextStoppedEvent; import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MyEventHandle { @EventListener public void test(ContextStoppedEvent event){ System.out.println("ContextStoppedEvent接收到事件:"+event.getClass()); } }
App.java

package com.edu.spring.springboot; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { SpringApplication app=new SpringApplication(App.class); ConfigurableApplicationContext context=app.run(args); context.stop(); } }
运行结果如下: