上两篇已经讲解了SqlSessionFactory的创建和SqlSession创建过程。今天我们来分析myabtis的sql是如何一步一步走到Excutor。
还是之前的demo
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = null;
String resource = "configuration.xml";
sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource));
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(userMapper.findUserById(1));
}我们想看下基本的时序图有个大致了解
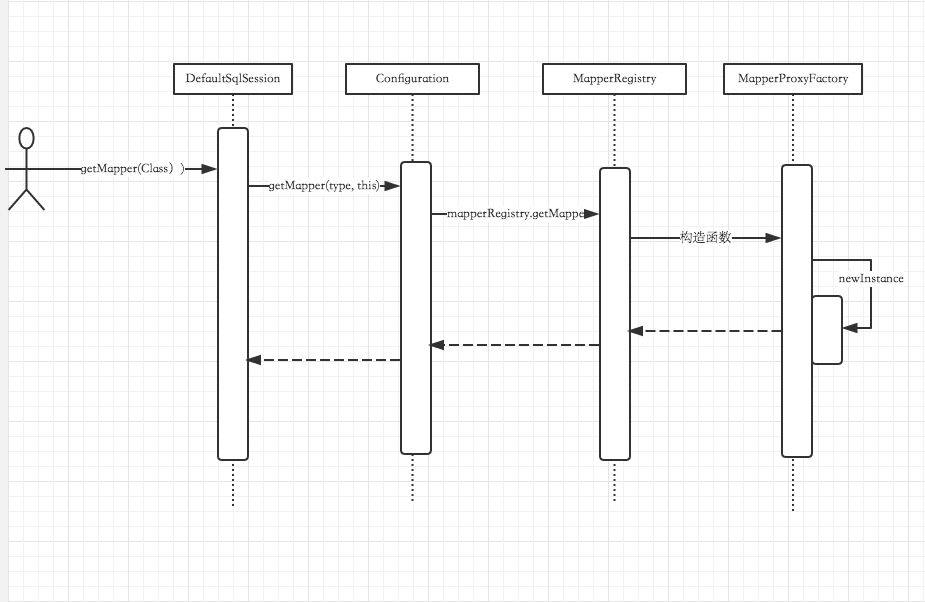
1:DefaultSqlSession获取getMapper
@Override
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
2:Configuration获取getMapper
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}Configuration和DefaultSqlSession什么都没有做,交给了MapperRegistry,我们看下MapperRegistry做了什么。
3:MapperRegistry获取getMapper
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}通过knownMappers获取一个MapperProxyFactory,后然newInstance了一下,那么newInstance得到了什么东西呢?
4:MapperProxyFactory
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
//java代理
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
} public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
通过以上的动态代理,咱们就可以方便地使用dao接口啦。到这里我们还没有看到任何执行sql有关的信息,或者说还没走到文章开始说的的Excutor, 我们看下MapperProxy代理类
MapperProxy
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}代理类交给了mapperMethod.execute进行处理,到这里我们只是看到了execute字眼了,我们继续往下看。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}上面代码先是判断CRUD类型,然后根据类型去选择到底执行sqlSession中的哪个方法,我们现在是查询那么程序应该走到sqlSession.selectOne。
@Override
public T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//终于看到我们要找的executor接口了
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}我们终于看到executor类了, 调用了query方法,接下来的事情全部交给了executor处理了,
executor底层的分析已经在上一篇已经分享了。
我们代理执行sql的基本顺序是
MapperMethod.execute() --> DefaultSqlSession.selectOne --> BaseExecutor.query --> SimpleExecutor.doQuery --> SimpleStatementHandler.query --> DefaultResultSetHandler.handleResultSets(Statement stmt) 最终得到数据。