https://www.luogu.org/problem/P1002
题目描述
如图,A 点有一个过河卒,需要走到目标 B 点。卒行走规则:可以向下、或者向右。同时在棋盘上的任一点有一个对方的马(如上图的C点),该马所在的点和所有跳跃一步可达的点称为对方马的控制点。例如上图 C 点上的马可以控制 9 个点(图中的P1,P2 … P8 和 C)。卒不能通过对方马的控制点。

棋盘用坐标表示,A 点(0,0)、B 点(n,m)(n,m 为不超过 20 的整数,并由键盘输入),同样马的位置坐标是需要给出的(约定: C不等于A,同时C不等于B)。现在要求你计算出卒从 A 点能够到达 B 点的路径的条数,假设马的位置是固定不动的,并不是卒走一步马走一步。。
输入描述:
输入B点的坐标(n,m)以及对方马的坐标(X,Y){不用判错}
输出描述:
输出一个整数(路径的条数)。
示例1
输入
6 6 3 2
输出
17
说明/提示
结果可能很大!
一开始按DFS做,超时
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <math.h> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <queue> 9 #include <set> 10 #include <map> 11 #include <math.h> 12 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 13 typedef long long LL; 14 const int mod=1e9+7; 15 const double PI=acos(-1); 16 const int maxn=100010; 17 using namespace std; 18 //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 19 // cin.tie(NULL); 20 21 int n,m,x,y; 22 int ans; 23 24 bool judge(int a,int b) 25 { 26 if(a==x&&b==y) 27 return false; 28 if(a==x-1&&b==y-2) 29 return false; 30 if(a==x-2&&b==y-1) 31 return false; 32 if(a==x+1&&b==y-2) 33 return false; 34 if(a==x+2&&b==y-1) 35 return false; 36 if(a==x-2&&b==y+1) 37 return false; 38 if(a==x+2&&b==y+1) 39 return false; 40 if(a==x-1&&b==y+2) 41 return false; 42 if(a==x+1&&b==y+2) 43 return false; 44 return true; 45 } 46 47 void DFS(int a,int b) 48 { 49 if(a==n&&b==m) 50 { 51 ans++; 52 return ; 53 } 54 if(a+1<=n&&judge(a+1,b)) 55 DFS(a+1,b); 56 if(b+1<=m&&judge(a,b+1)) 57 DFS(a,b+1); 58 } 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 scanf("%d %d %d %d",&n,&m,&x,&y); 63 DFS(0,0); 64 printf("%d ",ans); 65 return 0; 66 }
后来以为if判断太多,换了种方法,依然超时
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <math.h> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <queue> 9 #include <set> 10 #include <map> 11 #include <math.h> 12 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 13 typedef long long LL; 14 const int mod=1e9+7; 15 const double PI=acos(-1); 16 const int maxn=100010; 17 using namespace std; 18 //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 19 // cin.tie(NULL); 20 21 int n,m,x,y; 22 int G[22][22]; 23 int ans; 24 25 void DFS(int a,int b) 26 { 27 if(a==n&&b==m) 28 { 29 ans++; 30 return ; 31 } 32 if(a+1<=n&&G[a+1][b]==0) 33 DFS(a+1,b); 34 if(b+1<=m&&G[a][b+1]==0) 35 DFS(a,b+1); 36 return ; 37 } 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 //freopen("testdate.in","r",stdin); 42 scanf("%d %d %d %d",&n,&m,&x,&y); 43 G[x][y]=1; 44 if(x-2>=0) 45 { 46 G[x-2][y-1]=1; 47 G[x-2][y+1]=1; 48 } 49 if(y-2>=0) 50 { 51 G[x-1][y-2]=1; 52 G[x+1][y-2]=1; 53 } 54 if(x-1>=0) 55 { 56 G[x-1][y+2]=1; 57 } 58 if(y-1>=0) 59 { 60 G[x+2][y-1]=1; 61 } 62 G[x+2][y+1]=1; 63 G[x+1][y+2]=1; 64 DFS(0,0); 65 printf("%d ",ans); 66 return 0; 67 }
最后意识到,这题没那么简单.
看过题解才明白这题是记忆化递推,或者说是DP
DP题就是要找到状态转移方程,这题的状态转移方程只用手动模拟一下就可以了,就可以得出到每一个点的方案数就是上面和左边的方案数的总和(因为只可以向右走或向下走),具体的状态转移方程是
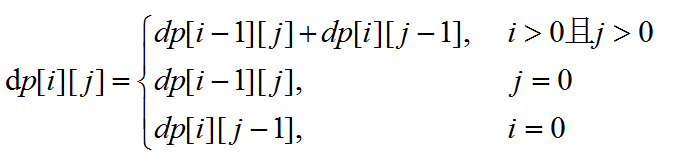
即可以写成DP[i][j]=max(DP[i][j],DP[i-1][j]+DP[i][j-1])
注意,最大的结果已经超过了int的范围,这是一个坑
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 #include <math.h> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <vector> 8 #include <queue> 9 #include <set> 10 #include <map> 11 #include <math.h> 12 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 13 typedef long long LL; 14 const int mod=1e9+7; 15 const double PI=acos(-1); 16 const int maxn=100010; 17 using namespace std; 18 //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 19 // cin.tie(NULL); 20 21 int n,m,x,y; 22 LL DP[23][23];//DP[i][j]代表从A点到(i,j)的线路条数 23 bool G[23][23];//判断这个点有没有马盯着 24 //马可以走到的位置 25 int fx[]={0,-2,-1,1,2,2,1,-1,-2}; 26 int fy[]={0,1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1}; 27 28 int main() 29 { 30 scanf("%d %d %d %d",&n,&m,&x,&y); 31 n+=2;m+=2,x+=2,y+=2;//坐标加2,防止标记马时越界 32 for(int i=0;i<=8;i++)//标记马的位置 33 { 34 G[x+fx[i]][y+fy[i]]=true; 35 } 36 DP[2][2]=1;//初始化 37 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) 38 { 39 for(int j=2;j<=m;j++) 40 { 41 if(G[i][j]) 42 continue; 43 DP[i][j]=max(DP[i][j],DP[i-1][j]+DP[i][j-1]);//状态转移方程 44 } 45 } 46 printf("%lld ",DP[n][m]); 47 return 0; 48 }
下面粘一个有意思的代码(递推):
我们可以发现一个规律:每个数都等于它上面左边的数的和
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 int n,m,my,mx; 5 long long a[25][25]; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 cin >>n >>m >>my >>mx;//输入数据 10 n=n+2;m=m+2;my=my+2;mx=mx+2; //隔出两格,当要把马可跳到的地方掷成0时不会出错 11 for(int z=2;z<=m;z++) 12 { 13 for(int y=2;y<=n;y++) 14 { 15 a[z][y]=a[z-1][y]+a[z][y-1]; //将这个数左边和上面的数相加 16 a[2][2]=1;//由于会把起点掷成0,所以要回归1 17 a[mx][my]=0;//将马的地方掷成0 18 a[mx+2][my+1]=0;a[mx+2][my-1]=0;//将马可跳到的地方掷成0 19 a[mx-2][my+1]=0;a[mx-2][my-1]=0;//将马可跳到的地方掷成0 20 a[mx+1][my+2]=0;a[mx+1][my-2]=0;//将马可跳到的地方掷成0 21 a[mx-1][my+2]=0;a[mx-1][my-2]=0;//将马可跳到的地方掷成0 22 } 23 } 24 cout <<a[m][n];//输出结果 25 return 0; 26 }