fork()的作用就是创建一个该进程下的子进程,在其exit 或 exec之前,和他共享代码,以一个父进程的身份,完成以下工作:
1.分配标识符pid和PCB。
2.让子进程复制父进程的环境。
3.给子进程分配地址空间和资源。
4.复制父进程的地址空间信息。
有了子进程,所以才有了僵尸进程和孤儿进程——
一.僵尸进程
创建子进程后,如果子进程比父进程早结束,而且父进程迟迟没有结束,那么子进程就会进入一个Z状态——僵尸状态,此时如果父进程不去处理,那么子进程就会一直处于这个状态,它毫无作用,又占了内存,因为其PCB中还保留了很多关于它的退出信息,所以它的PCB也不会被摧毁,这就对操作系统造成了负面影响:
看下列代码:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4
5
6 #define ERR_EXIT(m)
7 do
8 {
9 perror(m);
10 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
11 } while(0)
12
13 int main()
14 {
15 pid_t id;
16
17 if((id = fork()) == -1)
18 ERR_EXIT("fork");
19 else if (id == 0)
20 {
21 printf("I am the kid,my pid : %d,my father's pid : %d!
",getpid(),getppid());
22 }
23 else
24 {
25 while(1)
26 {
27 printf("I am the father,my pid : %d!
",getpid());
28 sleep(2);
29 }
30 }
31
32 return 0;
33 }
以下为运行现象:

以及进程状态:

可以明显看到,子进程早早结束而父进程陷入死循环——子进程进入一个<defunct>状态,也就是僵尸状态,切记!僵尸状态对操作系统是有害的。所以要避免(文末最后讲两个处理方式)。
这个状态,连最无情的kill -9 也无法处理,只能等父进程来处理。
二.孤儿进程
孤儿进程,顾名思义,子进程还在世的时候父进程却结束了,要记住:孤儿进程是无害的!那么孤儿进程没了父进程,是不是就被孤立了呢?不会的,我们还需要了解到1号进程——init进程,它不是第一个进程,但是是用户端的第一个进程,它在用户机开启时开始工作,在用户机结束时终止。它有一个功能就是收养这些孤儿,在这些孤儿进程结束时第一时间回收他们的退出信息,保证他们不一直成为僵尸进程。所以init进程,也被称作为孤儿院。2333333333
看下列代码:
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<stdlib.h>
4
5
6 #define ERR_EXIT(m)
7 do
8 {
9 perror(m);
10 exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
11 } while(0)
12
13 int main()
14 {
15 pid_t id;
16
17 if((id = fork()) == -1)
18 ERR_EXIT("fork");
19 else if (id == 0)
20 {
21 while(1)
22 {
23 printf("I am the kid,my pid : %d,my father's pid : %d!
",getpid(),getppid());
24 sleep(2);
25 }
26 }
27 else
28 {
29 sleep(1);
30 printf("I am the father,my pid : %d!
",getpid());
31 }
32
33 return 0;
34 }
以下为运行结果:

以下为运行状态:
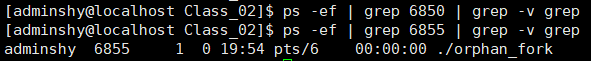
可以明显看到,在父进程未结束之前,子进程的父进程还是父进程的pid,当父进程结束后,子进程的父进程就成了init——1号进程,而且可以看到父进程是完全退出的。
ps:此时如果你用ctrl+c,是无法结束子进程的,因为他的终端已经成了1号进程,必须找到其进程号,利用“kill -15 进程号”,来结束。
三.两个处理僵尸进程的方法:
我们试想下列这种情况:父进程是一个死循环,他会定时创造一个子进程去做一个简单的任务,但是子进程任务结束时发现父进程还在工作,所以它就处于僵尸状态等待父进程回收,那么这样的情况下,僵尸进程会越来越多,父进程只创建却不回收,迟早有一天会造成大麻烦。
方法1——进程等待:
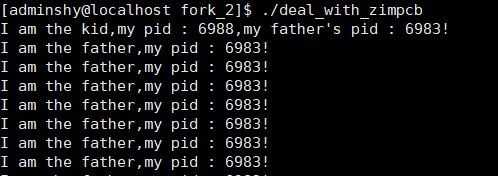
让父进程等待子进程,子进程工作完父进程再执行工作:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<unistd.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<sys/wait.h> 5 #include<sys/types.h> 6 7 8 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 9 do 10 { 11 perror(m); 12 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 13 } while(0) 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 pid_t id; 18 19 if((id = fork()) == -1) 20 ERR_EXIT("fork"); 21 else if (id == 0) 22 { 23 printf("I am the kid,my pid : %d,my father's pid : %d! ",getpid(),getppid()); 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 wait(NULL); 28 while(1) 29 { 30 printf("I am the father,my pid : %d! ",getpid()); 31 sleep(2); 32 } 33 } 34 35 return 0; 36 }
以下为运行结果:
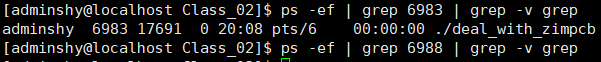
以下为进程状态:
方法2——托付给Init进程:
这个方法是用子进程再创建一个子进程,此时子进程就成了 子进程的子进程 的父进程,然后让子进程结束,那么 子进程的子进程 接受本应该子进程接受的任务,而且 子进程的子进程 此时成了孤儿进程,他的生死父进程也不会过问,交给1号进程init来解决。
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<unistd.h> 3 #include<stdlib.h> 4 #include<sys/wait.h> 5 #include<sys/types.h> 6 7 8 #define ERR_EXIT(m) 9 do 10 { 11 perror(m); 12 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 13 } while(0) 14 15 int main() 16 { 17 pid_t id; 18 19 if((id = fork()) == -1) 20 ERR_EXIT("fork"); 21 else if (id == 0) 22 { 23 printf("I am the kid,my pid : %d,my father's pid : %d! ",getpid(),getppid()); 24 } 25 else 26 { 27 wait(NULL); 28 while(1) 29 { 30 printf("I am the father,my pid : %d! ",getpid()); 31 sleep(2); 32 } 33 } 34 35 return 0; 36 }
使用信号方式:
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <signal.h> #include <errno.h> #include <stdio.h> void sig_chld(int signo) { pid_t pid; int stat; while ( (pid = waitpid(-1, &stat, WNOHANG)) > 0) //while循环是表示处理所有待处理的信号,-1表示任意子进程,WNOHANG表示非阻塞 printf("child %d terminated ", pid); return; } int main() { signal(SIGCHLD, sig_chld); pid_t cli = fork(); if (cli > 0) { printf("I am father "); } else { printf("I am child "); _exit(0); } while (1) { sleep(1); } }
以下是运行结果:
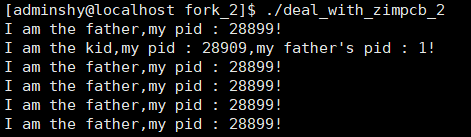
以下是进程状态:

这个方法适用于子进程执行的任务在规定时间内完成但是规定时间较长,父进程不可能永久等待,所以不如交给 子进程的子进程 来处理,这样父进程就不用在乎其任务结束与否。
当然也可以用waitpid并在第三个参数中选择非阻塞的等待方式(时间片轮转等待)。
