Levko and Array
Levko has an array that consists of integers: a1, a2, ... , an. But he doesn’t like this array at all.
Levko thinks that the beauty of the array a directly depends on value c(a), which can be calculated by the formula:
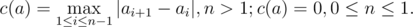
It’s time to change the world and Levko is going to change his array for the better. To be exact, Levko wants to change the values of at most k array elements (it is allowed to replace the values by any integers). Of course, the changes should make the array as beautiful as possible.
Help Levko and calculate what minimum number c(a) he can reach.
The first line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 2000). The second line contains space-separated integers a1, a2, ... , an ( - 109 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
A single number — the minimum value of c(a) Levko can get.
5 2
4 7 4 7 4
0
3 1
-100 0 100
100
6 3
1 2 3 7 8 9
1
In the first sample Levko can change the second and fourth elements and get array: 4, 4, 4, 4, 4.
In the third sample he can get array: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
【分析】题意很简单,就是给你一个数组,定义V为max(abs(a[i+1]-a[i])),给你K次改动机会,就是最多可以改动数组中的K个数,使得V最小。求最小的V。
这题思路好漂亮啊(可能是我很菜没见过吧)。先二分答案,然后看看满足这个答案的情况下需要改动多少数,如果需要改动的数的个数<=K,则保存答案继续二分。
强无敌。。。
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <string> #include <map> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <vector> #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define met(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof a) #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const int N = 3e5+10; const int M = 1e6+10; ll dp[2005]; ll a[2005]; ll n,k; ll Dp_Slove(ll mid) { memset(dp,0x3f3f3f3f,sizeof(dp)); dp[1]=0; for(ll i=2; i<=n; i++) { dp[i]=i-1; for(ll j=i-1; j>=1; j--) { if(abs(a[i]-a[j])<=mid*(i-j)) { dp[i]=min(dp[i],dp[j]+i-j-1); } } if(dp[i]+n-i<=k)return 1; } if(dp[n]<=k)return 1; else return 0; } int main() { while(~scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&k)) { for(ll i=1; i<=n; i++) { scanf("%lld",&a[i]); } ll l=0,r=2000000050; ll ans=0; while(r>=l) { ll mid=(l+r)/2; if(Dp_Slove(mid)) { r=mid-1; ans=mid; } else l=mid+1; } printf("%lld ",ans); } }