实验三进程调度模拟程序
1.实验目的
用高级语言完成一个进程调度程序,以加深对进程的概念及进程调度算法的理解。
2.实验要求
设计一个有 N个进程并发执行的进程调度模拟程序。
进程调度算法:采用最高优先级优先的调度算法(即把处理机分配给优先级最高的进程)和先来先服务(若优先级相同)算法。
(1). 每个进程有一个进程控制块(PCB)表示。进程控制块包含如下信息:进程名、优先级、到达时间、需要运行时间、已用CPU时间、进程状态等等。
(2). 进程的优先级及需要的运行时间可以事先人为地指定,进程的运行时间以时间片为单位进行计算。
(3). 每个进程的状态可以是就绪 r(ready)、运行R(Running)、或完成F(Finished)三种状态之一。
(4). 就绪进程获得 CPU后都只能运行一个时间片。用已占用CPU时间加1来表示。
(5). 如果运行一个时间片后,进程的已占用 CPU时间已达到所需要的运行时间,则撤消该进程,如果运行一个时间片后进程的已占用CPU时间还未达所需要的运行时间,也就是进程还需要继续运行,此时应将进程的优先数减1(即降低一级),然后把它插入就绪队列等待调度。
(6). 每进行一次调度程序都打印一次运行进程、就绪队列中各个进程的 PCB,以便进行检查。
(7). 重复以上过程,直到所要进程都完成为止。
3. 实验环境
vc++
4. 实验代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <windows.h>
static int id = 0;
int process_num;
int current_process;
struct pcb
{
char name[20];
int id;
char state;
int need_time;
int run_time;
struct pcb *next;
}*p, *q, *first_pcb = NULL;
typedef struct pcb PCB;
void printSort()
{
int i;
q = first_pcb;
for(i = 0; i < process_num;) {
if(i == q -> id) {
printf("|%s |%d |%c |%d |%d
", q -> name, q -> id, q -> state, q -> need_time, q -> run_time);
i++;
q = first_pcb;
}
else {
q = q -> next;
if(q == NULL) {
q = first_pcb;
i++;
}
}
}
}
void showPCB()
{
int i;
first_pcb -> run_time++;
first_pcb -> state = 'r';
if((first_pcb -> run_time) == (first_pcb -> need_time)) {
current_process--;
printf("
进程%s已经运行完毕
", first_pcb -> name);
system("pause");
first_pcb = first_pcb -> next;
if(first_pcb == NULL) {
printf("所有进程都已经运行完毕
");
system("pause");
return;
}
first_pcb -> state = 'r';
}
system("cls");
q = first_pcb -> next;
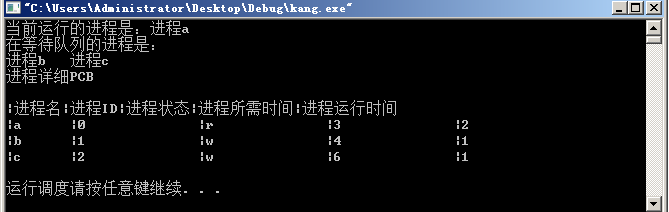
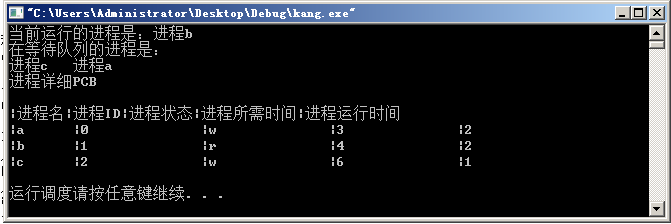
printf("当前运行的进程是:进程%s
", first_pcb -> name);
printf("在等待队列的进程是:
");
while(q != NULL) {
printf("进程%s ", q -> name);
q = q -> next;
}
printf("
进程详细PCB
");
printf("
|进程名|进程ID|进程状态|进程所需时间|进程运行时间
");
printSort();
q = first_pcb;
while(q -> next != NULL) {
q = q -> next;
}
first_pcb -> state = 'w';
q -> next = first_pcb;
first_pcb = first_pcb -> next;
q -> next -> next = NULL;
printf("
运行调度");
system("pause");
}
void pushPCB(int i)
{
q -> next = p;
q = p;
if(i == process_num - 1) q -> next = NULL;
}
void newPCB()
{
int i;
printf("请输入进程数:");
scanf("%d", &process_num);
q = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
first_pcb = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
for(i = 0; i < process_num; i++) {
system("cls");
p = (PCB*)malloc(sizeof(PCB));
printf("请输入第%d个进程名:", id + 1);
scanf("%s", p -> name);
printf("请输入进程需要的运行时间:");
scanf("%d", &p -> need_time);
p -> id = id++;
p -> run_time = 0;
p -> state = 'w';
if(i == 0) {
first_pcb = q = p;
p -> next = NULL;
}
else pushPCB(i);
}
}
void main()
{
newPCB();
current_process = process_num;
printf("按任意键开始进程调度
");
system("pause");
while(current_process) {
showPCB();
}
}
5. 实验结果
















6. 实验总结
通过今次进程调度模拟实验,不但熟悉了相关的算法、命令,也通过写代码的时候了解了时间片轮转等的调度算法。