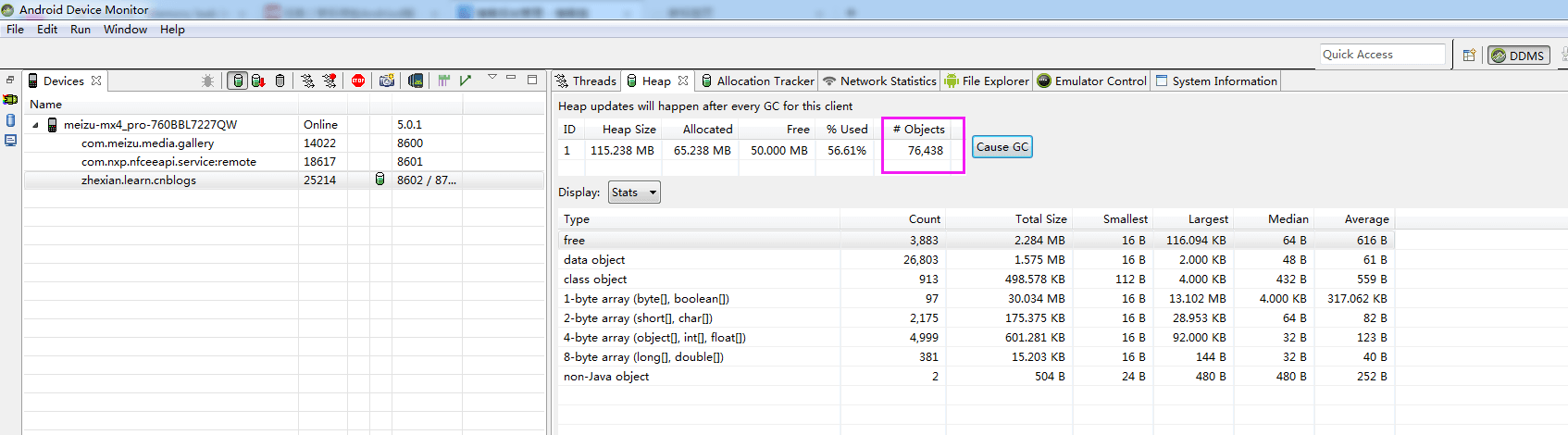
在咱的博客园app里,新闻的内容使用WebView展示的。在测试中,咱重复进入、退出某个新闻10多次,观察到
Objects一直在不断增长,反复触发GC,但是一直回收不了,占用的内存越来越高,于是警觉到这个WebView可能泄露内存了
如下:
在StackOverFlow上搜了下android webview memory leak(国内搜索结果质量太差,新手朋友推荐去这个网站搜答案)
我们在xml里面定义的WebView标签,默认这个Activity就被这个webView作为Context参数所持有了,因此,当这个Activity结束了想释掉放自己时,但是任然被webView所引用,因此GC回收不了,造成内存泄露
解决之道就是
1: 使用容器包裹WebView
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/web_container" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
2:手动创建WebView,使用ApplicationContext作为参数。在Ondestroy,调用容器的removeAllViews,同时调用webView的 destroy
public class TestActivity extends Activity { private FrameLayout mWebContainer; private WebView mWebView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.your_layout); mWebContainer = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.web_container); mWebView = new WebView(this); mWebContainer.addView(mWebView); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); mWebContainer.removeAllViews(); mWebView.destroy(); } }
修改之后,反复测试,发现gc都能正常回收webView的资源了,非常好
最后给上android如何回避内存泄露的一些建议,原文如下
- Do not keep long-lived references to a context-activity (a reference to an activity should have the same life cycle as the activity itself)
- Try using the context-activity instead of a context-application
- Avoid non-static inner classes in an activity if you don't control their life cycle, use a static inner class and make a weak reference to the activity inside. The solution to this issue is to use a static inner class with a WeakReference to the outer class, as done in ViewRoot and its W inner class for instance
大体的意思就是,内存不能被回收,很多情况下,都是因为Activity被某个元素持有引用导致GC无法回收的。
因此
1:保持activity持有对象的生命周期和activity是一致的。(特别是各种异步操作生命周期会比activity长)
2:使用Activity来代替全局对象Application,只有在你知道为啥使用Application长生命周期的时候,才去用它。 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/7298731/when-to-call-activity-context-or-application-context
3:注意Activity的内部类会持有Activity的隐式引用(不然你咋能访问外部类的变量。。),因此使用static修饰内部类消除外部类隐式引用,并用weakReference访问外部类的属性。一个例子