Sample code - one pump gas station
events: arrival + departure
arrival -> departure
simulation time: unprocesed events are stored in pending list
simulation
Preview
simulate the operation of a call center that handles both incoming and outgoing telephone calls
two different kinds of agent:
service agent : 700 sales agent: 300
two different kinds of call:
incoming calls :
- service + sales both are able to handle, service first, if not available then sales, then wait in queues(0.25 probability hang up, 0.75 waits until the service)m
- incoming calls are assumed to follow a Poisson distribution, with average arrival rate A per second, time between successive calls is exponentially distributed with a mean value of 1/A.
*the time for an agent to answer an incoming call is uniformly distributed over the interval [300, 700] seconds
outgoing calls :
*only sales agent can handle. if no sales agents available, abandon the call
*every 60 seconds the dialer system places calls, then take 10 seconds to determine which calls got through, each call that got through is routed to a sales agent
parameters:
*STRUE : the probability an outgoing call is successful (success = call + go through)
*SEST + NIDLE / SEST
*SEST: the estimated probability value of success computed by the simulation program
*NIDLE: the number of idle sales agents
Simulation engine
*event list managemnt
*managinig advances in simulation time
Simulation application
*state variables
*code modeling system behavior
*I/O and user interface software
event handler procedures
arrival event{...} departure event{...}
define each structure's content.
how to use the struct? first initialize, then call them?
Background Knowledge
Structure
//learning note of struc in c
//structure
struct flightType
{
char flightNum[7];
int altitude;
double airspeed;
};
struct flightType plane; //declare a variable of this new type
struct flightType
{
char flightNum[7];
int altitude;
double airspeed;
}plane; //general syntax for a structure declaration
//access the struct using the dot "." operation
plane.airspeed = 800.00;
plane.altitude = 10000;
//typedef provide no additional functionality -> give clarity to code
typedef type name; //cause the identifier name to be synonymous with the type 'type'(both basic type of aggregate type is ok)
typedef int Color;
Color pixels[500];
//we can use typedef to create a name for the sturcture we defined
struct flightType
{
char flightNum[7];
int altitude;
double airspeed;
};
typedef struct flightType Flight;
Flight plane;
//equivalent to the declaration in the line14
//allocate contiguous region of memory to each structure
Flight planes[100]; //declare an array of structures
//calculate the average airspeed of 100 planes
int i;
double sum = 0;
double averageAirSpeed;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
sum = sum + plane[i].airspeed;
}
averageAirSpeed = sum / 100;
//
// create pointers to structures
Flight *planePtr;
planePtr = &plane[34]; //assign this variable
(*planePtr).longitude //access any of the member fields pointed to by this pointer variable
// equal
planePtr -> longitude;
Linked List
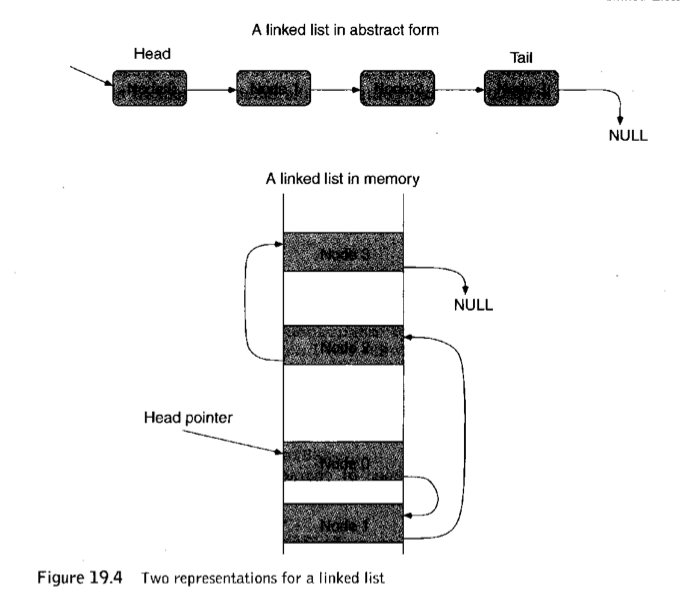
dynamic allocation
use pointer to
sample code:
Application:
EventHandler: call Arrival() and Departure() Funtion
Arrival() funtion: generate the next arrival() + determine the departure time of the arrival event if the pump is free
Departure() function: schedule the departure time, deal with the atpump type
engine:
Create an Event List: FEL
Remove
PrintList
Schedule function: insert the new event into the event list
RunSim function: to loop before the simulation time get the limit.
Binomial distribution
Generate random number
Summary:
*Application: Event handle procedures
finish three major part:
- define Event Function
- define EventHandler Function: to check which type of the event it is
- define NumberGenerator: to generate the service time and the incoming calling's time
*Engine: Event processing loop
finish the loop:
1.define the datastructure to generate FEL(Future Event List)
什么时候需要排队呢:before the first finished call, the sum_call > sum_servant