集合框架
1、为什么使用集合框架?
假设,一个班级有30个人,我们需要存储学员的信息,是不是我们可以用一个一维数组就解决了?
那换一个问题,一个网站每天要存储的新闻信息,我们知道新闻是可以实时发布的,我们并不知道需要多大的空间去存储,我要是去设置一个很大的数组,要是没有存满,或者不够用,都会影响我们,前者浪费空间,后者影响业务!
如果并不知道程序运行时会需要多少对象,或者需要更复杂的方式存储对象,那我们就可以使用Java的集合框架!
2、集合框架包含的内容
Java集合框架提供了一套性能优良,使用方便的接口和类,他们位于java.util包中。
【接口和具体类】

当然了,这张图只表现了一些常用的。
【算法】
Collections 类提供了对集合进行排序,遍历等多种算法实现!
【重中之重】
Collection 接口存储一组 不唯一,无序的对象
List 接口存储一组 不唯一,有序的对象。
Set 接口存储一组 唯一,无序的对象
Map 接口存储一组 键值对象,提供key到value的映射
ArrayList实现了长度可变的数组,在内存中分配连续的空间。遍历元素和随机访问元素的效率比较高
LinkedList采用链表存储方式。插入、删除元素时效率比较高
HashSet:采用哈希算法实现的Set
HashSet的底层是用HashMap实现的,因此查询效率较高,由于采用hashCode算法直接确定元素的内存地址,增删效率也挺高的。
ArrayList 实践
问题:我们现在有4只小狗,我们如何存储它的信息,获取总数,并能够逐条打印狗狗信息!
分析:通过List 接口的实现类ArrayList 实现该需求.
元素个数不确定
要求获得元素的实际个数
按照存储顺序获取并打印元素信息
1 class Dog{ 2 private String name; 3 4 public Dog(String name) { 5 this.name = name; 6 } 7 8 public String getName() { 9 return name; 10 } 11 12 public void setName(String name) { 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 } 16 17 public class test { 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 //创建ArrayList对象 , 并存储狗狗 20 List dogs = new ArrayList(); 21 dogs.add(new Dog("小狗一号")); 22 dogs.add(new Dog("小狗二号")); 23 dogs.add(new Dog("小狗三号")); 24 dogs.add(2,new Dog("小狗四号"));// 添加到指定位置 25 // .size() : ArrayList大小 26 System.out.println("共计有" + dogs.size() + "条狗狗。"); 27 System.out.println("分别是:"); 28 // .get(i) : 逐个获取个元素 29 for (int i = 0; i < dogs.size(); i++) { 30 Dog dog = (Dog) dogs.get(i); 31 System.out.println(dog.getName()); 32 } 33 34 } 35 }
问题联想:
删除第一个狗狗 :remove(index)
删除指定位置的狗狗 :remove(object)
判断集合中是否包含指定狗狗 : contains(object)
分析:使用List接口提供的remove()、contains()方法
【常用方法】
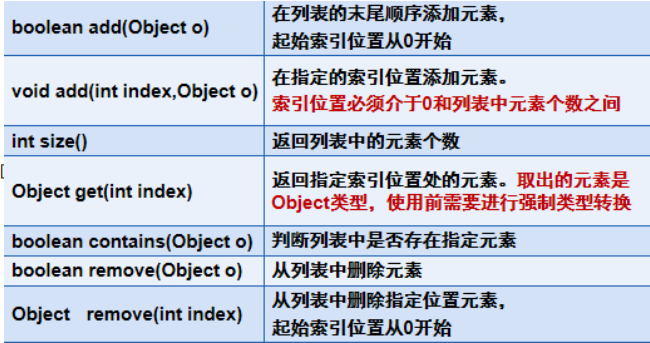
大家可以自己动手试一试
ArrayList 源码分析
1、ArrayList概述
1. ArrayList是可以动态增长和缩减的索引序列,它是基于数组实现的List类。
2. 该类封装了一个动态再分配的Object[]数组,每一个类对象都有一个capacity【容量】属性,表示它们所封装的Object[]数组的长度,当向ArrayList中添加元素时,该属性值会自动增加。如果想 ArrayList中添加大量元素,可使用ensureCapacity方法一次性增加capacity,可以减少增加重分配 的次数提高性能。
3. ArrayList的用法和Vector向类似,但是Vector是一个较老的集合,具有很多缺点,不建议使用。
另外,ArrayList和Vector的区别是:ArrayList是线程不安全的,当多条线程访问同一个ArrayList集合 时,程序需要手动保证该集合的同步性,而Vector则是线程安全的。
ArrayList和Collection的关系:

2、ArrayList的数据结构
分析一个类的时候,数据结构往往是它的灵魂所在,理解底层的数据结构其实就理解了该类的实现思 路,具体的实现细节再具体分析。
ArrayList的数据结构是:
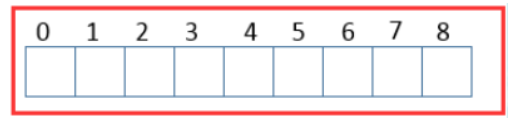
说明:底层的数据结构就是数组,数组元素类型为Object类型,即可以存放所有类型数据。我们对 ArrayList类的实例的所有的操作底层都是基于数组的。
3、ArrayList源码分析
1、继承结构和层次关系
IDEA快捷键:Ctrl+H

1 public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> 2 implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable 3 {}
我们看一下ArrayList的继承结构:
ArrayList extends AbstractList
AbstractList extends AbstractCollection
所有类都继承Object 所以ArrayList的继承结构就是上图这样。
【分析】
1. 为什么要先继承AbstractList,而让AbstractList先实现List?而不是让ArrayList直接实现List?
这里是有一个思想,接口中全都是抽象的方法,而抽象类中可以有抽象方法,还可以有具体的实现方法,正是利用了这一点,让AbstractList是实现接口中一些通用的方法,而具体的类,如ArrayList就继承这个AbstractList类,拿到一些通用的方法,然后自己在实现一些自己特有的方法,这样一来,让代码更 、简洁,就继承结构最底层的类中通用的方法都抽取出来,先一起实现了,减少重复代码。所以一般看到一个类上面还有一个抽象类,应该就是这个作用。
1. ArrayList实现了哪些接口?


List接口:我们会出现这样一个疑问,在查看了ArrayList的父类 AbstractList也实现了List接口,那为什 么子类ArrayList还是去实现一遍呢?


这是想不通的地方,所以我就去查资料,有的人说是为了查看代码方便,使观看者一目了然,说法不 一,但每一个让我感觉合理的,但是在stackOverFlow中找到了答案,这里其实很有趣。
这其实是一个mistake[失误],因为他写这代码的时候觉得这个会有用处,但是其实并没什么用,但因为没什么影响,就一直留到了现在。
RandomAccess接口:这个是一个标记性接口,通过查看api文档,它的作用就是用来快速随机存取, 有关效率的问题,在实现了该接口的话,那么使用普通的for循环来遍历,性能更高,例如ArrayList。而 没有实现该接口的话,使用Iterator来迭代,这样性能更高,例如linkedList。所以这个标记性只是为了 让我们知道我们用什么样的方式去获取数据性能更好。
Cloneable接口:实现了该接口,就可以使用Object.Clone()方法了。
Serializable接口:实现该序列化接口,表明该类可以被序列化,什么是序列化?简单的说,就是能够 从类变成字节流传输,然后还能从字节流变成原来的类。
2、类中的属性
// 版本号 private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; // 缺省容量 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 空对象数组 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 缺省空对象数组 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 元素数组 transient Object[] elementData; // 实际元素大小,默认为0 private int size; // 最大数组容量 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
3、构造方法
通过IDEA查看源码,看到ArrayList有三个构造方法:
1 /** 2 * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. 3 * 构造具有指定初始容量的空列表。 4 * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list 5 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity 6 * is negative 7 */ 8 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { 9 if (initialCapacity > 0) { 10 this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 11 } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { 12 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 13 } else { 14 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ 15 initialCapacity); 16 } 17 } 18 19 /** 20 * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.这里就说明了默认会给10的大小,所以说一开始arrayList的容量是10. 21 */ 22 public ArrayList() { 23 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 24 } 25 26 /** 27 * Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified 28 * collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's 29 * iterator.按照集合迭代器返回元素的顺序构造包含指定集合的元素的列表。,这个方法不常用 30 * 31 * @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list 32 * @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null 33 */ 34 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { 35 elementData = c.toArray(); 36 if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { 37 // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652) 38 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) 39 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); 40 } else { 41 // replace with empty array. 42 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; 43 } 44 }
【总结】ArrayList的构造方法就做一件事情,就是初始化一下储存数据的容器,其实本质上就是一个数组,在其中就叫elementData。
4、核心方法-add
1 /** 2 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 3 * 添加一个特定的元素到list的末尾。 4 * @param e element to be appended to this list 5 * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 6 */ 7 public boolean add(E e) { 8 //确定内部容量是否够了,size是数组中数据的个数,因为要添加一个元素,所以size+1,先判断size+1的这个个数数组能否放得下,就在这个方法中去判断是否数组.length是否够用了。 9 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 10 elementData[size++] = e; 11 return true; 12 }
【分析:ensureCapacityInternal(xxx); 确定内部容量的方法】
1 2 3 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { 4 if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { 5 minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); 6 } 7 8 ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); 9 } 10 11 12 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { 13 modCount++; 14 15 // overflow-conscious code 16 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) 17 grow(minCapacity); 18 } 19 20 21 //arrayList核心的方法,能扩展数组大小的真正秘密。 22 /** 23 * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the 24 * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. 25 * 26 * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity 27 */ 28 private void grow(int minCapacity) { 29 // overflow-conscious code 30 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; 31 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); 32 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) 33 newCapacity = minCapacity; 34 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) 35 newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); 36 // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: 37 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); 38 }
void add(int,E)
1 /** 2 * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this 3 * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and 4 * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). 5 * 6 * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted 7 * @param element element to be inserted 8 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 9 */ 10 public void add(int index, E element) { 11 rangeCheckForAdd(index); 12 13 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! 14 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, 15 size - index); 16 elementData[index] = element; 17 size++; 18 }
【分析:rangeCheckForAdd(index)】
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) { //插入的位置肯定不能大于size 和小于0 if (index > size || index < 0) //如果是,就报这个越界异常 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
【System.arraycopy(...):就是将elementData在插入位置后的所有元素,往后面移一位.】
1 public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, 2 Object dest, int destPos, 3 int length); 4 src:源对象 5 srcPos:源对象对象的起始位置 6 dest:目标对象 7 destPost:目标对象的起始位置 8 length:从起始位置往后复制的长度。
【总结】
正常情况下会扩容1.5倍,特殊情况下(新扩展数组大小已经达到了最大值)则只取最大值。

说明:程序调用add,实际上还会进行一系列调用,可能会调用到grow,grow可能会调用 hugeCapacity。
【举例】
List<Integer> lists = new ArrayList<Integer>; lists.add(8);
说明:初始化lists大小为0,调用的ArrayList()型构造函数,那么在调用lists.add(8)方法时,会经过怎样 的步骤呢?下图给出了该程序执行过程和最初与最后的elementData的大小。
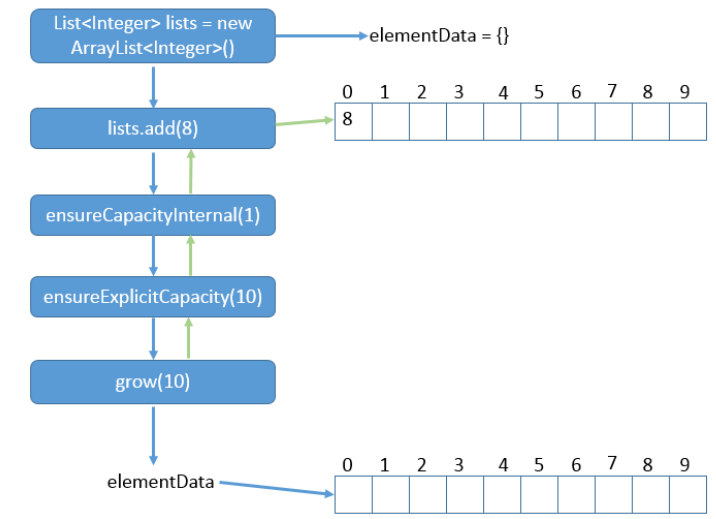
说明:我们可以看到,在add方法之前开始elementData = {};调用add方法时会继续调用,直至 grow,最后elementData的大小变为10,之后再返回到add函数,把8放在elementData[0]中。
【举例说明二】
List<Integer> lists = new ArrayList<Integer>(6); lists.add(8);
说明:调用的ArrayList(int)型构造函数,那么elementData被初始化为大小为6的Object数组,在调用 add(8)方法时,具体的步骤如下:
说明:我们可以知道,在调用add方法之前,elementData的大小已经为6,之后再进行传递,不会进行 扩容处理。
5、核心方法-remove
其实这几个删除方法都是类似的。我们选择几个讲,其中fastRemove(int)方法是private的,是提供给 remove(Object)这个方法用的。
1. remove(int):通过删除指定位置上的元素
1 /** 2 * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. 3 * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their 4 * indices). 5 * 6 * @param index the index of the element to be removed 7 * @return the element that was removed from the list 8 * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} 9 */ 10 public E remove(int index) { 11 rangeCheck(index);//检查index的合理性 12 13 modCount++;;//这个作用很多,比如用来检测快速失败的一种标志。 14 E oldValue = elementData(index);//通过索引直接找到该元素 15 16 int numMoved = size - index - 1;//计算要移动的位数。 17 if (numMoved > 0) 18 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 19 numMoved);//这个方法也已经解释过了,就是用来移动元素的。 20 elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work//将--size上的位置赋值为null,让gc(垃圾回收机制)更快的回收它。 21 22 return oldValue;//返回删除的元素。 23 }
1. remove(Object):这个方法可以看出来,arrayList是可以存放null值得。
1 //感觉这个不怎么要分析吧,都看得懂,就是通过元素来删除该元素,就依次遍历,如果有这个元素, 2 就将该元素的索引传给fastRemobe(index),使用这个方法来删除该元素, 3 //fastRemove(index)方法的内部跟remove(index)的实现几乎一样,这里最主要是知道 4 arrayList可以存储null值 5 public boolean remove(Object o) { 6 if (o == null) { 7 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 8 if (elementData[index] == null) { 9 fastRemove(index); 10 return true; 11 } 12 } else { 13 for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) 14 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { 15 fastRemove(index); 16 return true; 17 } 18 } 19 return false; 20 }
1. clear():将elementData中每个元素都赋值为null,等待垃圾回收将这个给回收掉,所以叫clear
1 /** 2 * Removes all of the elements from this list. The list will 3 * be empty after this call returns. 4 */ 5 public void clear() { 6 modCount++; 7 8 // clear to let GC do its work 9 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 10 elementData[i] = null; 11 12 size = 0; 13 }
1. removeAll(collection c)
1 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { 2 Objects.requireNonNull(c); 3 return batchRemove(c, false); 4 }
1. batchRemove(xx,xx):用于两个方法,一个removeAll():它只清楚指定集合中的元素,retainAll() 用来测试两个集合是否有交集。
1 //这个方法,用于两处地方,如果complement为false,则用于removeAll如果为true,则给retainAll()用,retainAll()是用来检测两个集合是否有交集的。 2 3 private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { 4 final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; 5 int r = 0, w = 0; 6 boolean modified = false; 7 try { 8 for (; r < size; r++) 9 if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) 10 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; 11 } finally { 12 // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, 13 // even if c.contains() throws. 14 if (r != size) { 15 System.arraycopy(elementData, r, 16 elementData, w, 17 size - r); 18 w += size - r; 19 } 20 if (w != size) { 21 // clear to let GC do its work 22 for (int i = w; i < size; i++) 23 elementData[i] = null; 24 modCount += size - w; 25 size = w; 26 modified = true; 27 } 28 } 29 return modified; 30 }
总结:remove函数,用户移除指定下标的元素,此时会把指定下标到数组末尾的元素向前移动一个单 位,并且会把数组最后一个元素设置为null,这样是为了方便之后将整个数组不被使用时,会被GC,可以作为小的技巧使用。
6、其他方法
【set()方法】 说明:设定指定下标索引的元素值
1 public E set(int index, E e) { 2 rangeCheck(index); 3 checkForComodification(); 4 E oldValue = ArrayList.this.elementData(offset + index); 5 ArrayList.this.elementData[offset + index] = e; 6 return oldValue; 7 }
【indexOf()方法】 说明:从头开始查找与指定元素相等的元素,注意,是可以查找null元素的,意味着ArrayList中可以存 放null元素的。与此函数对应的lastIndexOf,表示从尾部开始查找。
public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } / 从首开始查找数组里面是否存在指定元素
【get()方法】
public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); }
说明:get函数会检查索引值是否合法(只检查是否大于size,而没有检查是否小于0),值得注意的 是,在get函数中存在element函数,element函数用于返回具体的元素,具体函数如下:
1 E elementData(int index) { 2 return (E) elementData[index]; 3 }
说明:返回的值都经过了向下转型(Object -> E),这些是对我们应用程序屏蔽的小细节
4、总结
1)arrayList可以存放null。
2)arrayList本质上就是一个elementData数组。
3)arrayList区别于数组的地方在于能够自动扩展大小,其中关键的方法就是gorw()方法。
4)arrayList中removeAll(collection c)和clear()的区别就是removeAll可以删除批量指定的元素,而 clear是全是删除集合中的元素。
5)arrayList由于本质是数组,所以它在数据的查询方面会很快,而在插入删除这些方面,性能下降很 多,有移动很多数据才能达到应有的效果
6)arrayList实现了RandomAccess,所以在遍历它的时候推荐使用for循环。