Front compression
Time Limit: 5000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 102400/102400 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 158 Accepted Submission(s): 63
Problem Description
Front compression is a type of delta encoding compression algorithm whereby common prefixes and their lengths are recorded so that they need not be duplicated. For example:
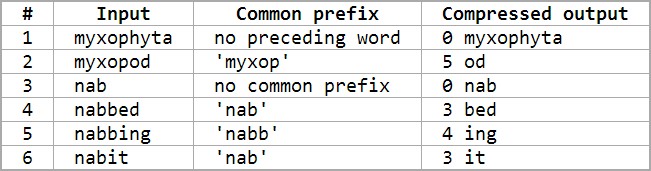
The size of the input is 43 bytes, while the size of the compressed output is 40. Here, every space and newline is also counted as 1 byte.
Given the input, each line of which is a substring of a long string, what are sizes of it and corresponding compressed output?

The size of the input is 43 bytes, while the size of the compressed output is 40. Here, every space and newline is also counted as 1 byte.
Given the input, each line of which is a substring of a long string, what are sizes of it and corresponding compressed output?
Input
There are multiple test cases. Process to the End of File.
The first line of each test case is a long string S made up of lowercase letters, whose length doesn't exceed 100,000. The second line contains a integer 1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000, which is the number of lines in the input. Each of the following N lines contains two integers 0 ≤ A < B ≤ length(S), indicating that that line of the input is substring [A, B) of S.
The first line of each test case is a long string S made up of lowercase letters, whose length doesn't exceed 100,000. The second line contains a integer 1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000, which is the number of lines in the input. Each of the following N lines contains two integers 0 ≤ A < B ≤ length(S), indicating that that line of the input is substring [A, B) of S.
Output
For each test case, output the sizes of the input and corresponding compressed output.
Sample Input
frcode
2
0 6
0 6
unitedstatesofamerica
3
0 6
0 12
0 21
myxophytamyxopodnabnabbednabbingnabit
6
0 9
9 16
16 19
19 25
25 32
32 37
Sample Output
14 12
42 31
43 40
Author
Zejun Wu (watashi)
Source
Recommend
zhuyuanchen520
后缀数组随便搞一下就可以了
1 /* *********************************************** 2 Author :kuangbin 3 Created Time :2013/8/20 13:40:03 4 File Name :F:2013ACM练习2013多校91006.cpp 5 ************************************************ */ 6 7 #include <stdio.h> 8 #include <string.h> 9 #include <iostream> 10 #include <algorithm> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <queue> 13 #include <set> 14 #include <map> 15 #include <string> 16 #include <math.h> 17 #include <stdlib.h> 18 #include <time.h> 19 using namespace std; 20 const int MAXN=100010; 21 int t1[MAXN],t2[MAXN],c[MAXN];//求SA数组需要的中间变量,不需要赋值 22 //待排序的字符串放在s数组中,从s[0]到s[n-1],长度为n,且最大值小于m, 23 //除s[n-1]外的所有s[i]都大于0,r[n-1]=0 24 //函数结束以后结果放在sa数组中 25 bool cmp(int *r,int a,int b,int l) 26 { 27 return r[a] == r[b] && r[a+l] == r[b+l]; 28 } 29 void da(int str[],int sa[],int rank[],int height[],int n,int m) 30 { 31 n++; 32 int i, j, p, *x = t1, *y = t2; 33 //第一轮基数排序,如果s的最大值很大,可改为快速排序 34 for(i = 0;i < m;i++)c[i] = 0; 35 for(i = 0;i < n;i++)c[x[i] = str[i]]++; 36 for(i = 1;i < m;i++)c[i] += c[i-1]; 37 for(i = n-1;i >= 0;i--)sa[--c[x[i]]] = i; 38 for(j = 1;j <= n; j <<= 1) 39 { 40 p = 0; 41 //直接利用sa数组排序第二关键字 42 for(i = n-j; i < n; i++)y[p++] = i;//后面的j个数第二关键字为空的最小 43 for(i = 0; i < n; i++)if(sa[i] >= j)y[p++] = sa[i] - j; 44 //这样数组y保存的就是按照第二关键字排序的结果 45 //基数排序第一关键字 46 for(i = 0; i < m; i++)c[i] = 0; 47 for(i = 0; i < n; i++)c[x[y[i]]]++; 48 for(i = 1; i < m;i++)c[i] += c[i-1]; 49 for(i = n-1; i >= 0;i--)sa[--c[x[y[i]]]] = y[i]; 50 //根据sa和x数组计算新的x数组 51 swap(x,y); 52 p = 1; x[sa[0]] = 0; 53 for(i = 1;i < n;i++) 54 x[sa[i]] = cmp(y,sa[i-1],sa[i],j)?p-1:p++; 55 if(p >= n)break; 56 m = p;//下次基数排序的最大值 57 } 58 int k = 0; 59 n--; 60 for(i = 0;i <= n;i++)rank[sa[i]] = i; 61 for(i = 0;i < n;i++) 62 { 63 if(k)k--; 64 j = sa[rank[i]-1]; 65 while(str[i+k] == str[j+k])k++; 66 height[rank[i]] = k; 67 } 68 } 69 int rank[MAXN],height[MAXN]; 70 int RMQ[MAXN]; 71 int mm[MAXN]; 72 int best[20][MAXN]; 73 void initRMQ(int n) 74 { 75 mm[0]=-1; 76 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 77 mm[i]=((i&(i-1))==0)?mm[i-1]+1:mm[i-1]; 78 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)best[0][i]=i; 79 for(int i=1;i<=mm[n];i++) 80 for(int j=1;j+(1<<i)-1<=n;j++) 81 { 82 int a=best[i-1][j]; 83 int b=best[i-1][j+(1<<(i-1))]; 84 if(RMQ[a]<RMQ[b])best[i][j]=a; 85 else best[i][j]=b; 86 } 87 } 88 int askRMQ(int a,int b) 89 { 90 int t; 91 t=mm[b-a+1]; 92 b-=(1<<t)-1; 93 a=best[t][a];b=best[t][b]; 94 return RMQ[a]<RMQ[b]?a:b; 95 } 96 int lcp(int a,int b) 97 { 98 a=rank[a];b=rank[b]; 99 if(a>b)swap(a,b); 100 return height[askRMQ(a+1,b)]; 101 } 102 char str[MAXN]; 103 int r[MAXN]; 104 int sa[MAXN]; 105 int A[MAXN],B[MAXN]; 106 int calc(int n) 107 { 108 if(n == 0)return 1; 109 int ret = 0; 110 while(n) 111 { 112 ret++; 113 n /= 10; 114 } 115 return ret; 116 } 117 int main() 118 { 119 //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 120 //freopen("out.txt","w",stdout); 121 while(scanf("%s",str)==1) 122 { 123 int n = strlen(str); 124 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 125 r[i] = str[i]; 126 r[n] = 0; 127 da(r,sa,rank,height,n,128); 128 for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) 129 RMQ[i] = height[i]; 130 initRMQ(n); 131 int k,u,v; 132 long long ans1 = 0, ans2 = 0; 133 scanf("%d",&k); 134 for(int i = 0;i < k;i++) 135 { 136 scanf("%d%d",&A[i],&B[i]); 137 if(i == 0) 138 { 139 ans1 += B[i] - A[i] + 1; 140 ans2 += B[i] - A[i] + 3; 141 continue; 142 } 143 int tmp ; 144 if(A[i]!= A[i-1])tmp = lcp(A[i],A[i-1]); 145 else tmp = 10000000; 146 tmp = min(tmp,B[i]-A[i]); 147 tmp = min(tmp,B[i-1]-A[i-1]); 148 ans1 += B[i] - A[i] + 1; 149 ans2 += B[i] - A[i] - tmp + 1; 150 ans2 += 1; 151 ans2 += calc(tmp); 152 } 153 printf("%I64d %I64d ",ans1,ans2); 154 } 155 return 0; 156 }