背景:
基于公式1.42(Ez分量)、1.43(Hy分量)的1D FDTD实现。
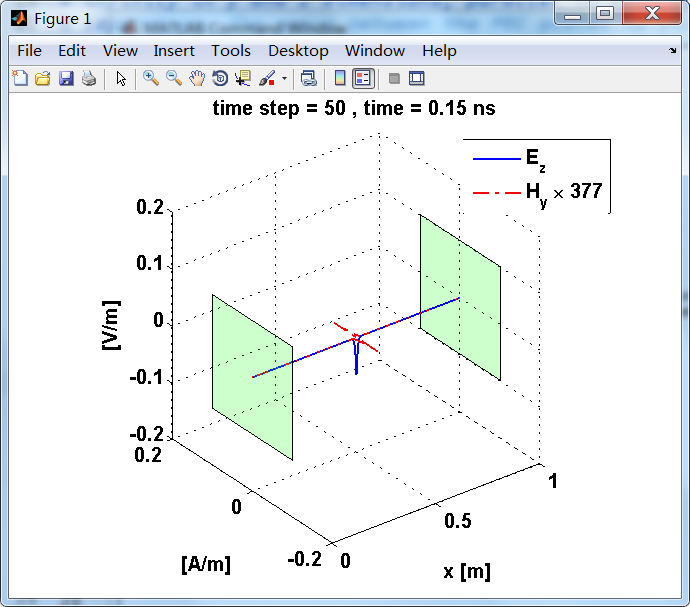
计算电场和磁场分量,该分量由z方向的电流片Jz产生,Jz位于两个理想导体极板中间,两个极板平行且向y和z方向无限延伸。
平行极板相距1m,差分网格Δx=1mm。
电流面密度导致分界面(电流薄层)磁场分量的不连续,在两侧产生Hy的波,每个强度为5×10^(-4)A/m。因为电磁波在自由空间中传播,本征阻抗为η0。
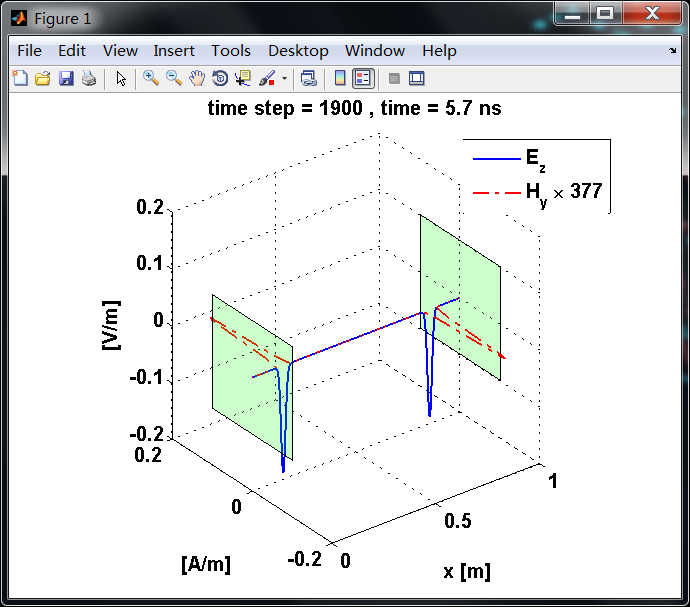
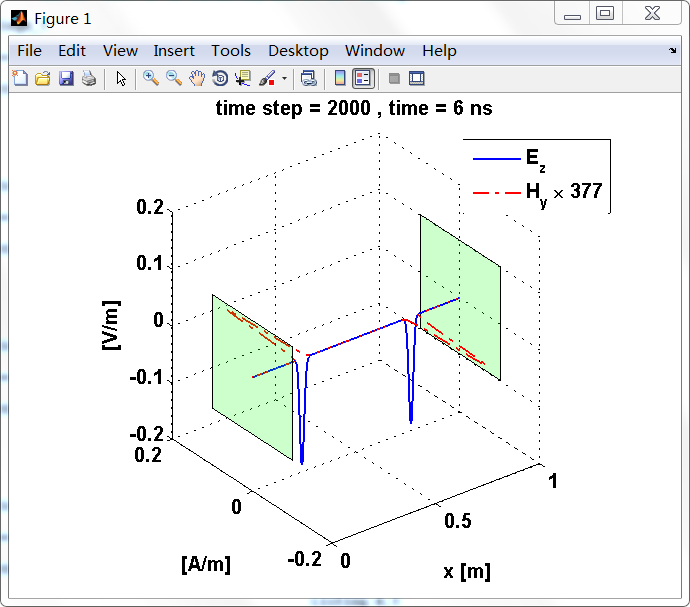
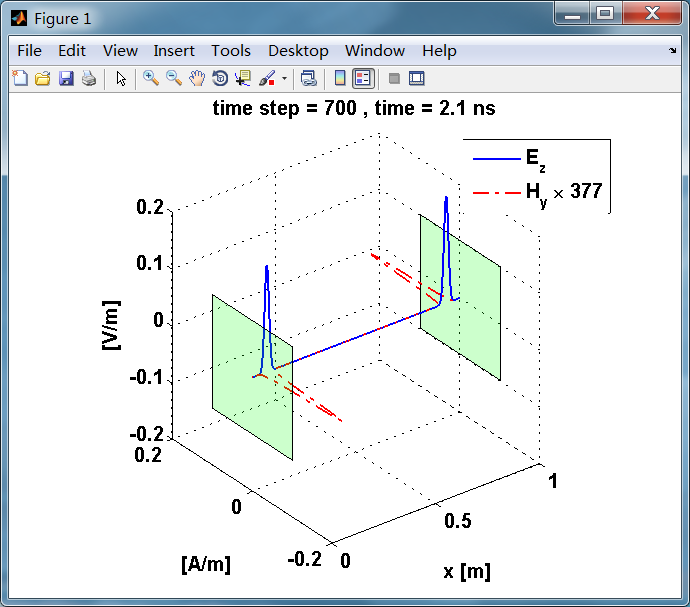
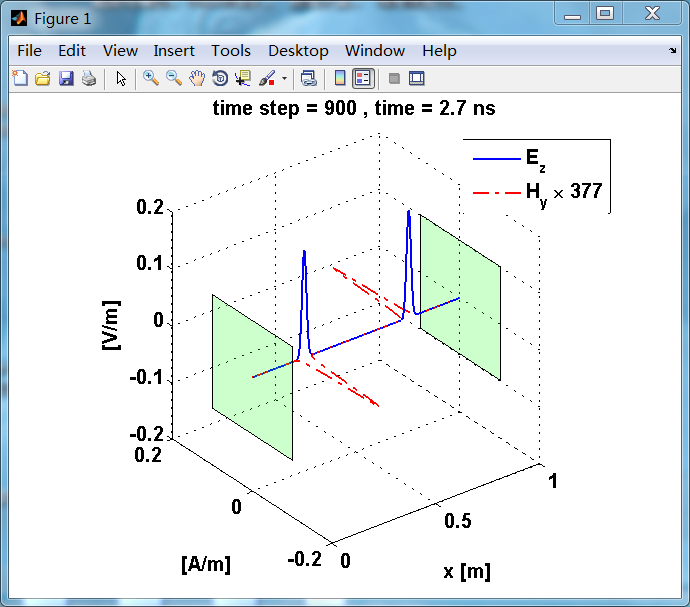
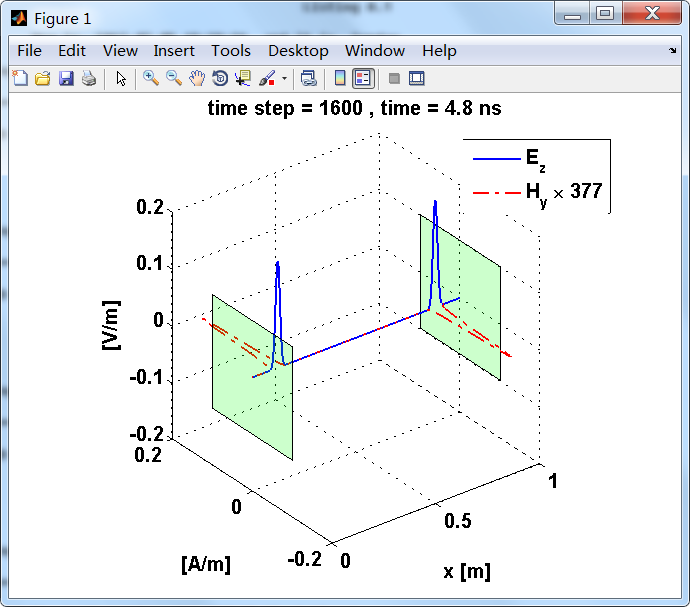
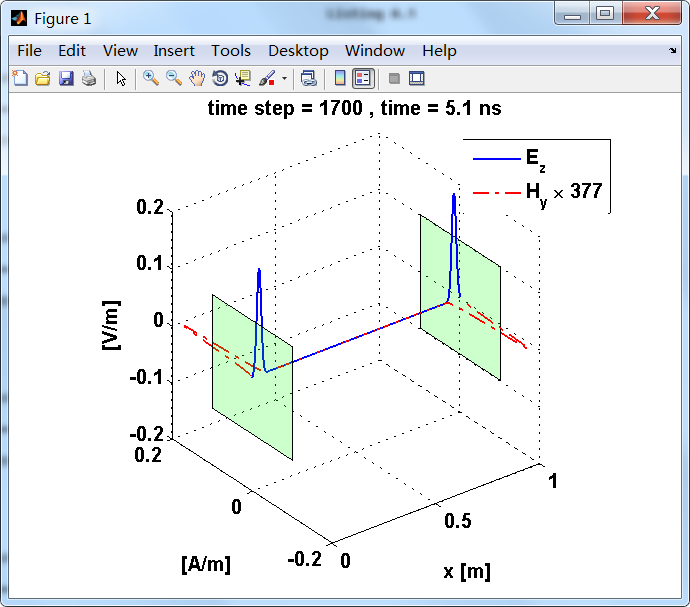
显示了从左右极板反射前后的传播过程。本例中是PEC边界,正切电场分量(Ez)在PEC表面消失。
观察图中step650到700的场的变换情况,经过PEC板的入射波和反射波的传播特征。经过PEC反射后,Ez的极性变反,这是因为反射系数等于-1;
而磁场分量Hy没有反向,反射系数等于1。
下面是书中的代码(几乎没动):
第1个是主程序:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('
****************************************************************
');
fprintf('
<FDTD 4 ElectroMagnetics with MATLAB Simulations>
');
fprintf('
Listing A.1
');
time_stamp = datestr(now, 31);
[wkd1, wkd2] = weekday(today, 'long');
fprintf(' Now is %20s, and it is %7s
', time_stamp, wkd2);
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------------
% This program demonstrates a one-dimensional FDTD simulation.
% The problem geometry is composed of two PEC plates extending to
% infinity in y and z dimensions, parallel to each other with 1 meter
% separation. The space between the PEC plates is filled with air.
% A sheet of current source paralle to the PEC plates is placed
% at the center of the problem space. The current source excites fields
% in the problem space due to a z-directed current density Jz,
% which has a Gaussian waveform in time.
% Define initial constants
eps_0 = 8.854187817e-12; % permittivity of free space
mu_0 = 4*pi*1e-7; % permeability of free space
c = 1/sqrt(mu_0*eps_0); % speed of light
% Define problem geometry and parameters
domain_size = 1; % 1D problem space length in meters
dx = 1e-3; % cell size in meters, Δx=0.001m
dt = 3e-12; % duration of time step in seconds
number_of_time_steps = 2000; % number of iterations
nx = round(domain_size/dx); % number of cells in 1D problem space
source_position = 0.5; % position of the current source Jz
% Initialize field and material arrays
Ceze = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Cezhy = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Cezj = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Ez = zeros(nx+1, 1);
Jz = zeros(nx+1, 1);
eps_r_z = ones (nx+1, 1); % free space
sigma_e_z = zeros(nx+1, 1); % free space
Chyh = zeros(nx, 1);
Chyez = zeros(nx, 1);
Chym = zeros(nx, 1);
Hy = zeros(nx, 1);
My = zeros(nx, 1);
mu_r_y = ones (nx, 1); % free space
sigma_m_y = zeros(nx, 1); % free space
% Calculate FDTD updating coefficients
Ceze = (2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 - dt * sigma_e_z) ...
./(2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 + dt * sigma_e_z);
Cezhy = (2 * dt / dx) ...
./(2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 + dt * sigma_e_z);
Cezj = (-2 * dt) ...
./(2 * eps_r_z * eps_0 + dt * sigma_e_z);
Chyh = (2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 - dt * sigma_m_y) ...
./(2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 + dt * sigma_m_y);
Chyez = (2 * dt / dx) ...
./(2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 + dt * sigma_m_y);
Chym = (-2 *dt) ...
./(2 * mu_r_y * mu_0 + dt * sigma_m_y);
% Define the Gaussian source waveform
time = dt * [0:number_of_time_steps-1].';
Jz_waveform = exp(-((time-2e-10)/5e-11).^2)*1e-3/dx;
source_position_index = round(nx * source_position/domain_size)+1;
% Subroutine to initialize plotting
initialize_plotting_parameters;
% FDTD loop
for time_step = 1:number_of_time_steps
% Update Jz for the current time step
Jz(source_position_index) = Jz_waveform(time_step);
% Update magnetic field
Hy(1:nx) = Chyh(1:nx) .* Hy(1:nx) ...
+ Chyez(1:nx) .* (Ez(2:nx+1) - Ez(1:nx)) ...
+ Chym(1:nx) .* My(1:nx);
% Update electric field
Ez(2:nx) = Ceze (2:nx) .* Ez(2:nx) ...
+ Cezhy(2:nx) .* (Hy(2:nx) - Hy(1:nx-1)) ...
+ Cezj (2:nx) .* Jz(2:nx);
Ez(1) = 0; % Apply PEC boundary condition at x = 0 m
Ez(nx+1) = 0; % Apply PEC boundary condition at x = 1 m
% Subroutine to plot the current state of the fields
plot_fields;
end
第2个是initialize_plotting_parameters,看名字就知道是初始化参数:
% Subroutine used to initialize 1D plot
Ez_positions = [0:nx]*dx;
Hy_positions = ([0:nx-1]+0.5)*dx;
v = [0 -0.1 -0.1; 0 -0.1 0.1; 0 0.1 0.1; 0 0.1 -0.1; ...
1 -0.1 -0.1; 1 -0.1 0.1; 1 0.1 0.1; 1 0.1 -0.1];
f = [1 2 3 4; 5 6 7 8];
axis([0 1 -0.2 0.2 -0.2 0.2]);
lez = line(Ez_positions, Ez*0, Ez, 'Color', 'b', 'linewidth', 1.5);
lhy = line(Hy_positions, 377*Hy, Hy*0, 'Color', 'r', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'LineStyle','-.');
set(gca, 'fontsize', 12, 'fontweight', 'bold');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
axis square;
legend('E_{z}', 'H_{y} imes 377', 'location', 'northeast');
xlabel('x [m]');
ylabel('[A/m]');
zlabel('[V/m]');
grid on;
p = patch('vertices', v, 'faces', f, 'facecolor', 'g', 'facealpha', 0.2);
text(0, 1, 1.1, 'PEC', 'horizontalalignment', 'center', 'fontweight', 'bold');
text(1, 1, 1.1, 'PEC', 'horizontalalignment', 'center', 'fontweight', 'bold');
第3个就是画图:
% Subroutine used to plot 1D transient field delete(lez); delete(lhy); lez = line(Ez_positions, Ez*0, Ez, 'Color', 'b', 'LineWidth', 1.5); lhy = line(Hy_positions, 377*Hy, Hy*0, 'Color', 'r', 'LineWidth', 1.5, 'LineStyle', '-.'); ts = num2str(time_step); ti = num2str(dt*time_step*1e9); title(['time step = ' ts ' , time = ' ti ' ns']); drawnow;
运行结果:
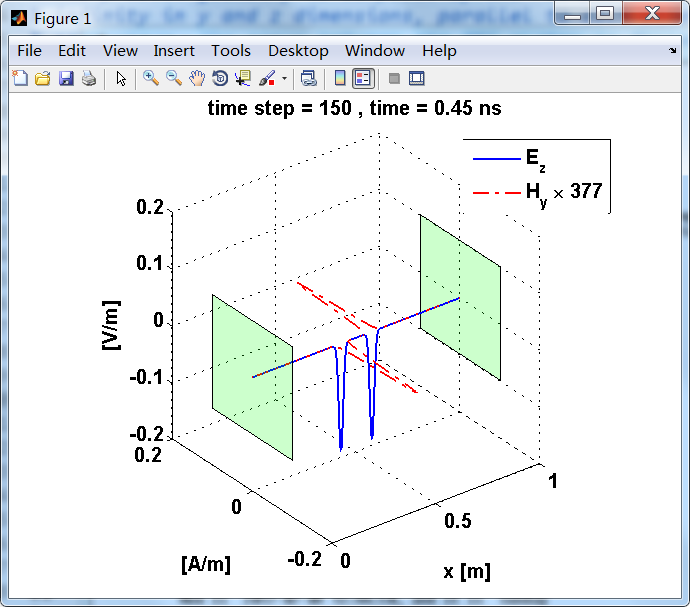
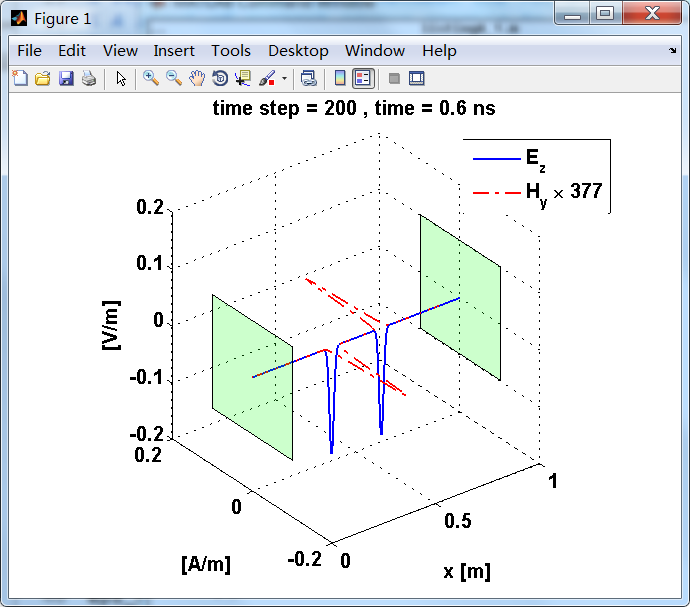
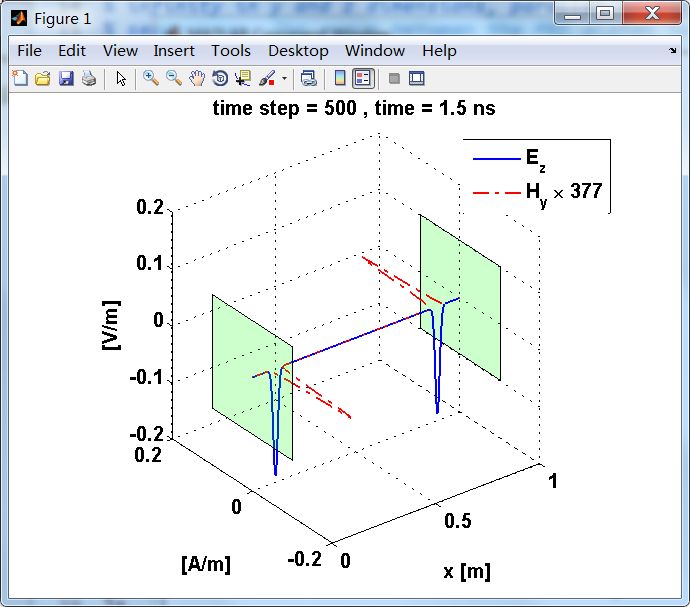
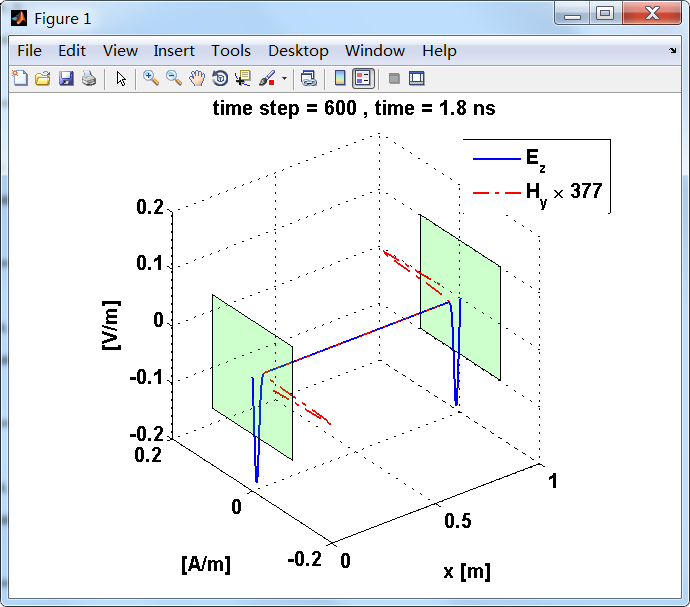
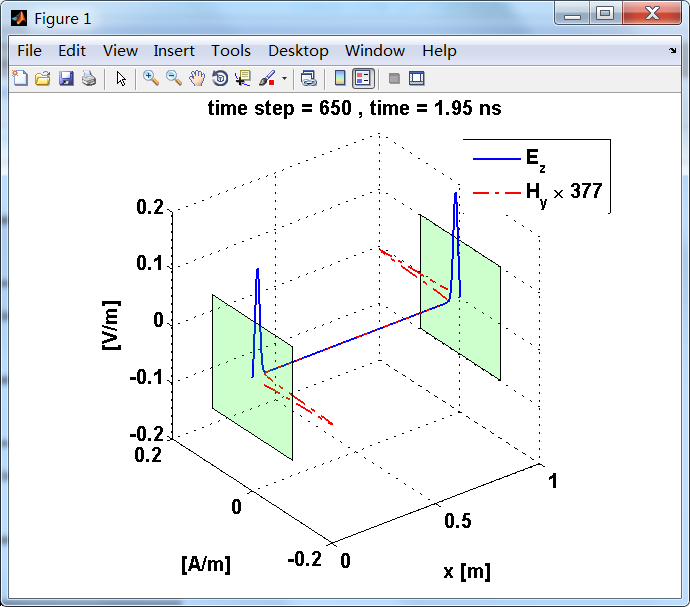
上图,从PEC板反射后,电场分量极性变反,磁场分量极性不变。
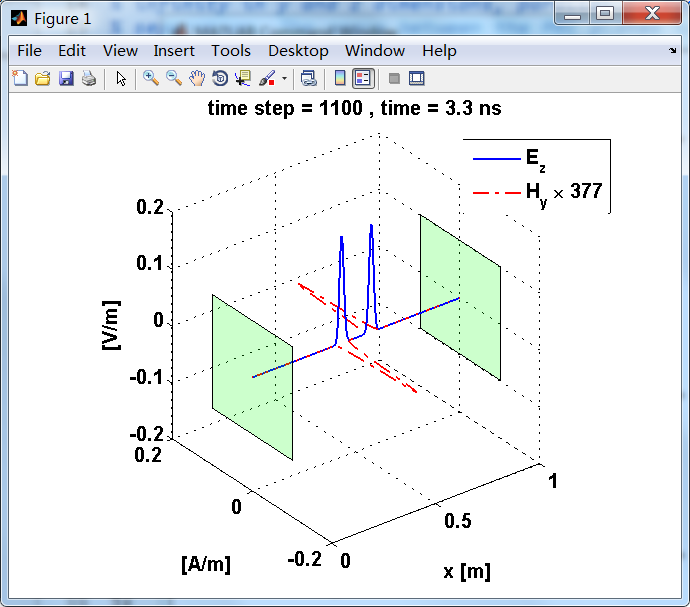

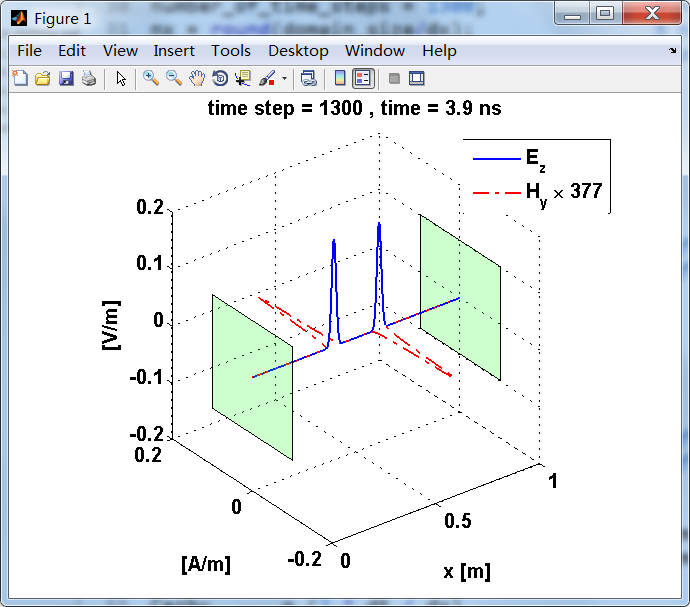
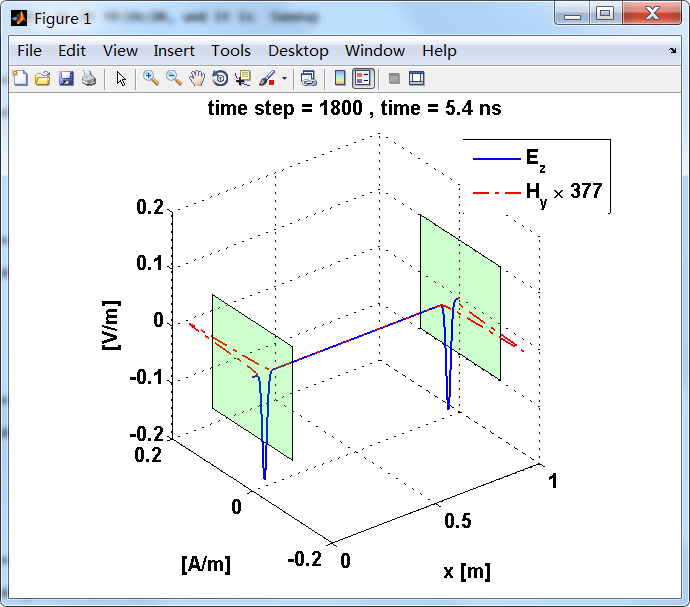
反射后,电场分量极性再次改变;