原地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/easymind223/archive/2012/07/04/2576964.html
ps里面的魔棒工具非常好用,是图像处理中非常常用的一个工具,它现在已经是我的c++工具箱中很重要的一员了,我会在以后的时间里把我的工具箱逐渐介绍给大家。
魔棒工具的核心算法是RegionGrow区域成长法,它的概念很简单,首先在要处理的图片上选取一个种子点,然后以此点为起点,向四周辐射形成一个区域。最初成长区域只有种子点这一个点,然后不断把周围的点归并入该成长区域,条件是该点的值与成长区域边界点的值之差小于阈值。当成长区域不能再继续扩大时,算法停止。
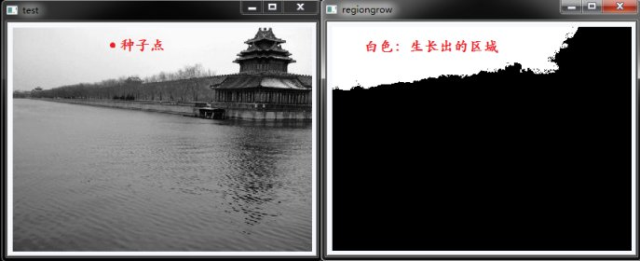
算法说明:
区域成长法的思想很好理解,代码实现对于初学者有一定难度。对于满足条件的像素点,函数会把它们一个个的压入队列的尾部,然后从队列的头部一个个的取出来,形成成长区域。M是一个点名册,用来记录每一个像素是否被处理过。start和end用来记录队列的头和尾,当start==end时,说明所有所有像素已经处理完,函数结束。
参数说明:
src: 输入的单通道图像。
dst: 输出的单通道图像,与输入同大小,必须提前开空间。
seedx, seedy: 种子点坐标
threshold: 容差
flag: 0/1 表示搜索方式是 8/4 邻域
struct Node
{
int x;
int y;
Node* next;
};
void MyTreasureBox::RegionGrow(const IplImage* src, IplImage* dst, int seedx, int seedy, int threshold, bool flag)
{
if(!src || src->nChannels != 1)return ;
int width = src->width;
int height = src->height;
int srcwidthstep = src->widthStep;
uchar* img = (uchar*)src->imageData;
//成长区域
cvZero(dst);
//标记每个像素点是否被计算过
IplImage* M = cvCreateImage(cvSize(width, height), 8, 1);
int Mwidthstep = M->widthStep;
cvZero(M);
M->imageData[seedy * Mwidthstep + seedx] = 1; //种子点位置为1,其它位置为0
CvScalar cur = CV_RGB(255,255,255);
cvSet2D(dst, seedy, seedx, cur);
//队列的两端
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
Node *queue = new Node;
queue->x = seedx;
queue->y = seedy;
queue->next = NULL;
Node *first = queue;
Node *last = queue;
while (end - start > 0)
{
int x = first->x;
int y = first->y;
uchar pixel = (uchar)img[y * srcwidthstep + x];
for (int yy = -1; yy<=1; yy++)
{
for (int xx = -1; xx<=1; xx++)
{
if(flag)
if ( abs(yy) && abs(xx))
continue;
int cx = x + xx;
int cy = y + yy;
if (cx >= 0 && cx <width && cy >=0 && cy < height)
{
if (abs(img[cy * srcwidthstep + cx] - pixel) <= threshold && M->imageData[cy * Mwidthstep + cx] != 1)
{
Node *node = new Node;
node->x = cx;
node->y = cy;
node->next = NULL;
end++;
last->next = node;
last = node;
M->imageData[cy * Mwidthstep + cx] = 1;
cvSet2D(dst, cy, cx, cur);
}
}
}
}
Node* temp = first;
first = first->next;
delete temp;
start++;
}
cvReleaseImage(&M);
}