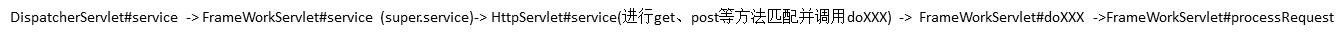接触Web时间比较久,虽然知道Servlet的生命周期但是理解却还是不够,今天刚好debug代码涉及这块就利用余下时间研究了一下。
Servlet的生命周期以及处理浏览器请求的过程。Servlet接口中定义的方法有:
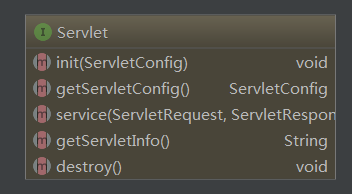
而init -> service -> destory刚好就是servlet的生命周期。通常当web容器(即web服务器,例如tomct等)启动时候回根据配置文件进行加载servlet,加载servlet过程就是初始化servlet的过程。
由web容器进行调用生命周期init方法进行初始化。初始化完成便可以进行处理浏览器发送的请求了。
当浏览器向Web容器发送请求时候便由Web容器调用Servelt的service方法(此处实现是HttpServlet的service方法)进行处理浏览器请求。HttpService的service方法关键源码实现如下:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
//判断客户端的请求是get、post、...
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);//处理post请求
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
本例以post请求进行源码跟踪,处理post请求调用doPost方法。此处回顾一下我们一般写一个servlet时候需要的步骤了,我们都是自己定义一个Servlet类然后一般都是实现doPost和doGet方法,回顾到此就可以回到本文了,本例中调用的doPost方法就是调用我们自己实现的doPost方法,这个流程下来就完成了浏览器的请求。而对于Servlet的销毁由Web容器调用destory方法进行销毁。
Spring MVC中DispatherServlet的继承结构:

在使用Spring MVC进行开发时候,在web.xml中需要配置DispatherServlet,让Web容器启动时候加载Servlet。通过继承结构可以发现DispatherServlet是HttpServlet的子类。
当浏览器进行请求时候Web容器会调用DispatherServlet的service方法,DispatherServlet的service方法在父类FrameWorkServlet中实现;FrameWorkServlet#service方法源码如下:
/**
* Override the parent class implementation in order to intercept PATCH requests.
*/
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (HttpMethod.PATCH == httpMethod || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
最后调用super.service调用HttpServlet#service方法,进行判断请求的方法是get、post还是...然后调用对应的doXXX方法,此处的doXXX方法在FrameWorkServlet中实现(FrameWorkServlet是框架实现的一个Servlet,与正常Servlet开发的servlet类似)。
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#doServiceorg.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#doPost源码如下:
@Override protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response); }
org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#processRequest源码如下:
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) //DispatcherServlet的processRequst方法在FrameWork中实现
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response); //重点
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doService源码:
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response); //重点
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
最后调用doDispatch(request, response)方法完成处理(后续代码有时间在跟踪)。
过程总结: