一、创建工程
在VS中新建一个Win32控制台程序,然后做一下几个操作:
1.拷贝FFmpeg的几种开发文件到项目目录下
其中包含include文件夹、lib文件夹和动态库文件(.dll)。
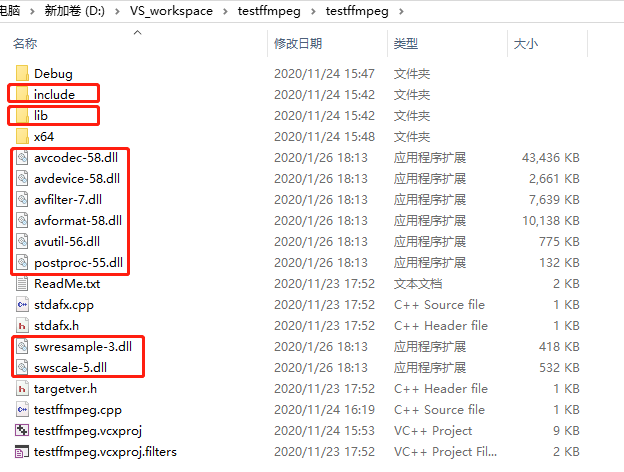
2.在VS中进行以下配置:
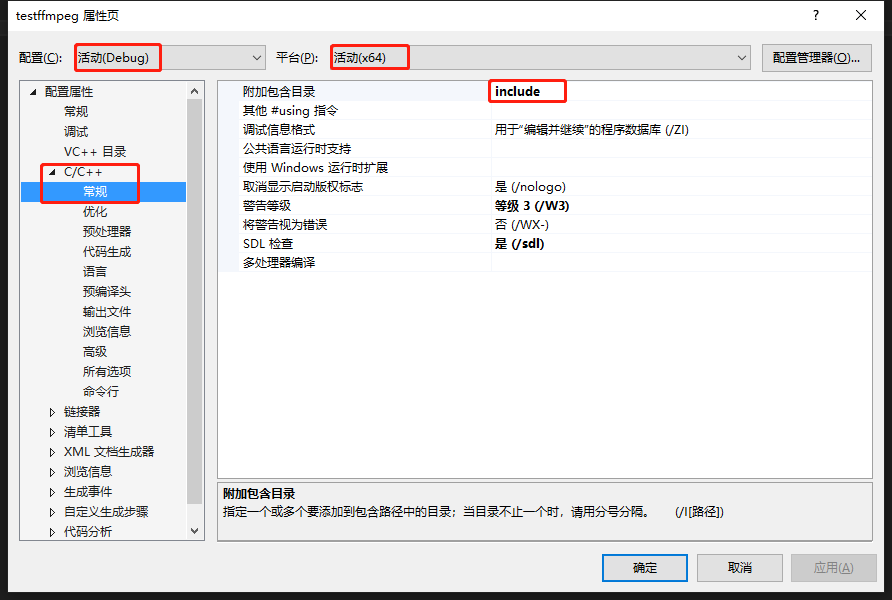
1) 配置属性-->C/C++-->常规-->附加包含目录,输入"include"(项目目录下的include)。
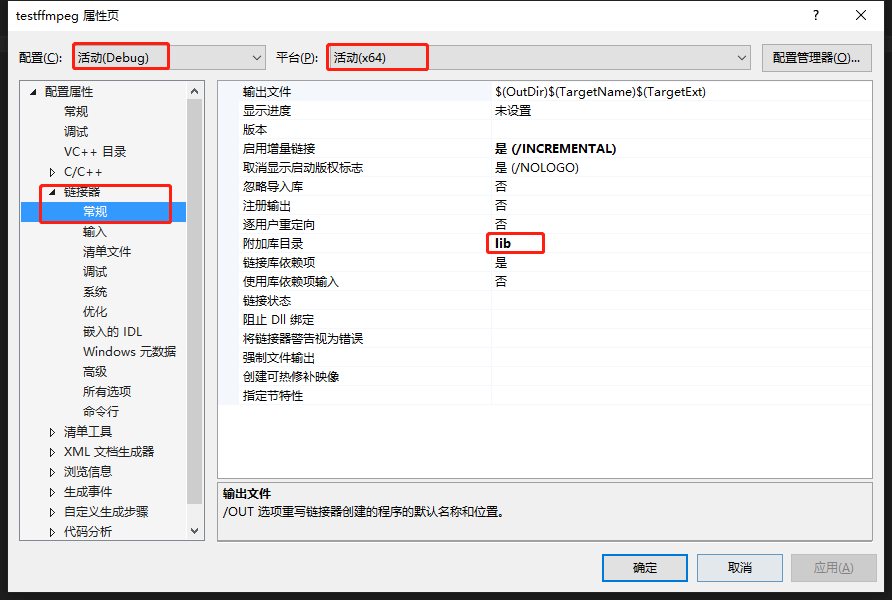
2)配置属性-->连接器-->常规-->附加库目录,输入"lib"(项目目录下的lib)
3)配置属性-->连接器-->输入-->附加依赖项,输入lib目录下所有"*.lib"文件,用分号隔开
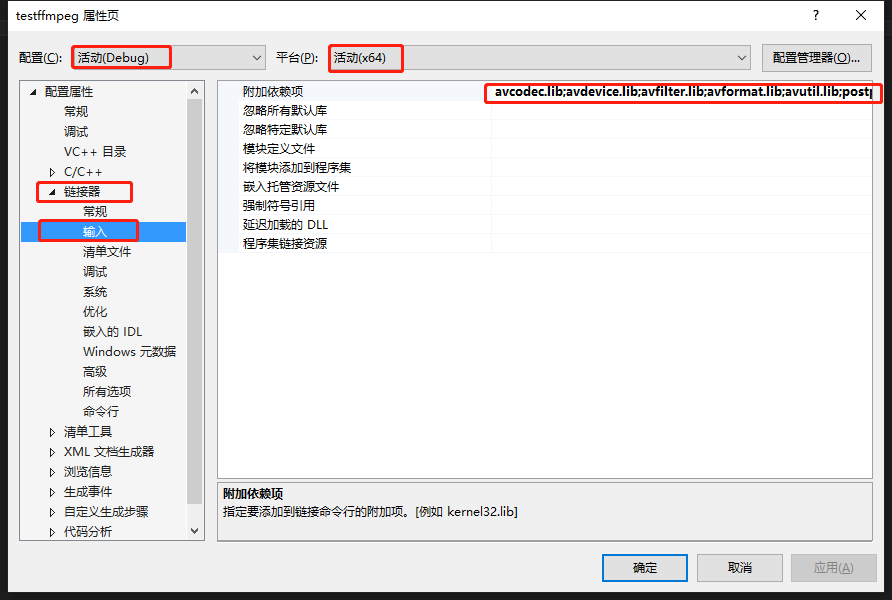
4)动态库不用配置。
3.测试是否成功
编写代码:
// testffmpeg.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS #include "stdafx.h" extern "C" { #include "libavcodecavcodec.h" } int main() { printf("%s", avcodec_configuration()); getchar(); return 0; }
可以看到运行结果:
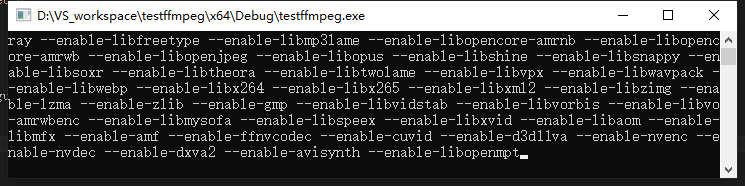
说明开发环境配置成功。
二、库和流程介绍
FFmpeg一共包含8个库:
- avcodec:编解码(最重要)。
- avformat:封装格式处理(重要)。
- avfilter:滤镜特效处理。
- avdevice:各种设备的输入输出。
- avutil:工具库(大部分库需要这个库的支持)。
- postproc:后加工。
- swresample:音频采样数据格式转换。
- swscale:视频像素数据格式转换。
1.视频读取和解码流程
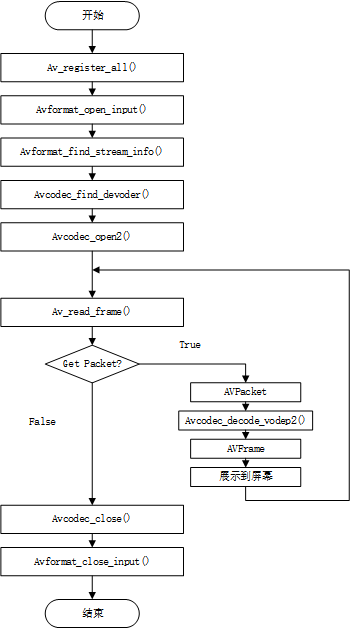
流程描述:
1.ac_register_all():注册所有组件。一般在使用ffmpeg的开始都会使用。
2.avformat_open_input():打开输入。例如文件、网络流等。
3.avformat_find_stream_info():查找流信息,例如文件中包含音频、视频等多条码流。
4.avcodec_find_devoder():查找流对应的解码器。
5.avcodec_open2():打开解码器。
6.av_read_frame():读取一帧压缩后的数据。
7.AVPacket:一个结构体,用于存放一帧压缩后的数据。这里用于存放av_read_frame读取到的数据。
8.avcodec_devode_video2():使用解码器解码AVPacket中的数据。
9.AVFrame:一个结构体,用于存放解码后的YUV数据(原始图像)。
10.显示在输出设备。
11.avcodec_close():关闭解码器。
12.avformat_close_input():关闭打开的码流。
其中6、7、8、9、10为循环过程,即每次读取一帧,解码,显示。如果没读到帧数据,说明整个码流结束。
三.数据结构介绍
FFmpeg中包含以下一些基本的数据结构:
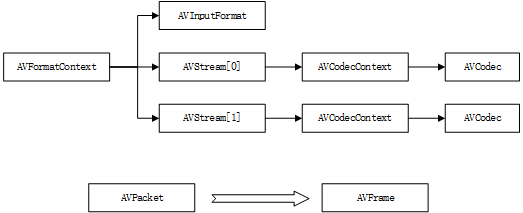
1.AVFormatConext:视频格式的上下文,其中包含封装信息,多个码流的结构体。
2.AVInputFormat:保存封装信息。
3.AVStream:这是一个数组,一般0表示视频码流,1表示音频码流。
4.AVCodecContext:解码器上下文,其中包含解码器和相关信息。
5.AVCodec:解码器
6.AVPacket:用于存放压缩后的视频数据。
7.AVFrame:用于存放解码后的数据。
1.AVFormatContext
该结构体包含以下几个变量:
- iformat:输入视频的AVInputFormat结构体指针。
- nb_streams:输入视频的AVStream个数。
- streams:输入视频的AVStream[]数组,其中包含视频和音频码流等。
- duration:输入视频的时长(以毫秒为单位)。
- bit_rate:输入视频的码率。
- 等等。
2.AVInputFormat
该结构体包含以下几个变量:
- name:封装格式名称,例如FLV等。
- long_name:封装格式长名称,例如FLV<FLASH VIDEO>。
- extensions:封装格式的扩展名。
- id:封装格式ID。
- 一些封装格式处理的接口函数指针。
3.AVStream
- id:序号
- codec:该流对应的AVCodecContext结构体指针。
- time_base:该流的时基。用来计算每一帧播放时间的时基(乘数)。
- r_frame_rate:该流的帧率。一秒有多少帧画面。
- 等等。
4.AVCodecContext
- codec:编解码器的AVCodec结构体指针。
- width,height:图像的宽高(只针对视频)。
- pix_fmt:像素格式(只针对视频)。
- sample_rate:采样率(只针对音频)。
- channels:声道数(只针对音频)。
- sample_fmt:采样格式(只针对音频)。
- 等等。
5.AVCodec
- name:编解码器名称。
- long_name:编解码器长名称。
- type:编解码器类型,音频&视频。
- id:编解码器ID。
- 一些编解码的接口函数指针。
6.AVPacket
- pts:显示时间戳,通过与时基一起计算出具体时间。(由于解码顺序和显示顺序是不同的,所以有pts和dts两个时间戳,后面详细解释)
- dts:解码时间戳。
- data:压缩编码数据。
- size:压缩编码数据大小。
- stream_index:所属的AVStream。
7.AVFrame
- data:解码后的图像像素数据(音频采样数据)。
- linesize:对视频来说就是图像中一行像素的大小;对音频来说就是整个音频帧的大小。
- width,height:图像的高宽(只针对视频)。
- key_frame:是否为关键帧(只针对视频)。
- pict_type:帧类型(只针对视频)。例如I,P,B。
四、实例
打开一个视频文件,将其内容读取出来,写入h264文件,yuv文件:
#include <stdio.h> #define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS #include "stdafx.h" extern "C" { #include "libavcodec/avcodec.h" #include "libavformat/avformat.h" #include "libswscale/swscale.h" }; #define SWS_BICUBIC 4 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx; int i, videoindex; AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx; AVCodec *pCodec; AVFrame *pFrame, *pFrameYUV; uint8_t *out_buffer; AVPacket *packet; int y_size; int ret, got_picture; struct SwsContext *img_convert_ctx; //输入文件路径 char filepath[] = "output.mp4"; // 需要处理的视频文件名,在当前目录下 int frame_cnt; av_register_all(); // 注册所有组件 avformat_network_init(); // 初始化网络,例如可以读取rtsp的视频流 pFormatCtx = avformat_alloc_context(); // 分配一个AVFormatContext空间 if (avformat_open_input(&pFormatCtx, filepath, NULL, NULL) != 0) { // 打开视频文件 printf("Couldn't open input stream. "); return -1; } if (avformat_find_stream_info(pFormatCtx, NULL)<0) { // 查找流信息 printf("Couldn't find stream information. "); return -1; } videoindex = -1; for (i = 0; i<pFormatCtx->nb_streams; i++) // 找到视频码流,并记录其编号,默认一般为0(在不确定的情况下,要进行判断) if (pFormatCtx->streams[i]->codec->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) { // AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO 是枚举值,代表视频码流 videoindex = i; // 获取到视频码流的编号 break; } if (videoindex == -1) { printf("Didn't find a video stream. "); return -1; } pCodecCtx = pFormatCtx->streams[videoindex]->codec; // 获取视频码流的编解码器上下文结构体 pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id); // 获取编解码器 if (pCodec == NULL) { printf("Codec not found. "); return -1; } if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, NULL)<0) { // 打开编解码器 printf("Could not open codec. "); return -1; } /* * 在此处添加输出视频信息的代码 * 取自于pFormatCtx,使用fprintf() */ pFrame = av_frame_alloc(); // 分配一个AVFrame内存空间,用于存放解码后的YUV数据 pFrameYUV = av_frame_alloc(); // 另外再分配一个AVFrame空间,用于存放sws_scale处理后的数据(剪裁掉无数据部分) out_buffer = (uint8_t *)av_malloc(avpicture_get_size(AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height)); avpicture_fill((AVPicture *)pFrameYUV, out_buffer, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); packet = (AVPacket *)av_malloc(sizeof(AVPacket)); // 分配AVPacket内存空间,用于存放解码前的帧数据 //Output Info----------------------------- printf("--------------- File Information ---------------- "); av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, 0, filepath, 0); printf("------------------------------------------------- "); img_convert_ctx = sws_getContext(pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height, AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, SWS_BICUBIC, NULL, NULL, NULL); // 打开一个用于存放h264数据的文件 FILE * fp_264 = fopen("test264.h264", "wb+"); // 打开一个用于存放YUV数据的文件 FILE * fp_yuv = fopen("testyuv.yuv", "wb+"); frame_cnt = 0; // 帧计数 while (av_read_frame(pFormatCtx, packet) >= 0) { // 循环读取帧数据 if (packet->stream_index == videoindex) { // 判断读取到的帧是否为视频帧 /* * 在此处添加输出H264码流的代码 * 取自于packet,使用fwrite() */ // 将每一帧的未解码数据(h264数据)写入文件中,第一个参数是需要写入文件的数据,第二个参数是每次写入的字节,第三个参数是写入次数,第四个参数是文件句柄 fwrite(packet->data, 1, packet->size, fp_264); ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, pFrame, &got_picture, packet); // 使用解码器进行解码 if (ret < 0) { printf("Decode Error. "); return -1; } if (got_picture) { sws_scale(img_convert_ctx, (const uint8_t* const*)pFrame->data, pFrame->linesize, 0, pCodecCtx->height, pFrameYUV->data, pFrameYUV->linesize); // 对解码后的YUV数据进行剪裁(直接解码得到的YUV,可能存在空白部分) //printf("Decoded frame index: %d ", frame_cnt); // 打印当前是第多少帧 /* * 在此处添加输出YUV的代码 * 取自于pFrameYUV,使用fwrite() */ fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[0], 1, pCodecCtx->width*pCodecCtx->height, fp_yuv); // 写入Y数据,大小是宽*高 fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[1], 1, pCodecCtx->width*pCodecCtx->height/4, fp_yuv); // 写入U数据,注意U数据只有1/4大小 fwrite(pFrameYUV->data[2], 1, pCodecCtx->width*pCodecCtx->height/4, fp_yuv); // 写入V数据,注意V数据只有1/4大小 frame_cnt++; } } av_free_packet(packet); // 释放AVPacket空间?还是清除其中的数据?调用位置可能有问题 } fclose(fp_264); fclose(fp_yuv); sws_freeContext(img_convert_ctx); // 释放sws context对象 av_frame_free(&pFrameYUV); // 释放AVFrame空间 av_frame_free(&pFrame); // 释放AVFrame空间 avcodec_close(pCodecCtx); // 关闭解编码器 avformat_close_input(&pFormatCtx); // 关闭AVFormatContext return 0; }
= =!