大趋势下,目前很多的项目都采用了前后端分离的方式进行开发,最近我接触到的项目大多数都是采用了前后端分离的方式进行开发。既然摆脱了js和html的干扰,更优化的展示接口内容和调用是后端更多需要关注的事情。(非常重要的一点,如果你想简单上手直接使用文章中的项目框架模型,可以直接拉取项目代码:github:https://github.com/licunzhi/dream_on_sakura_rain/tree/master/springboot_swagger_demo)
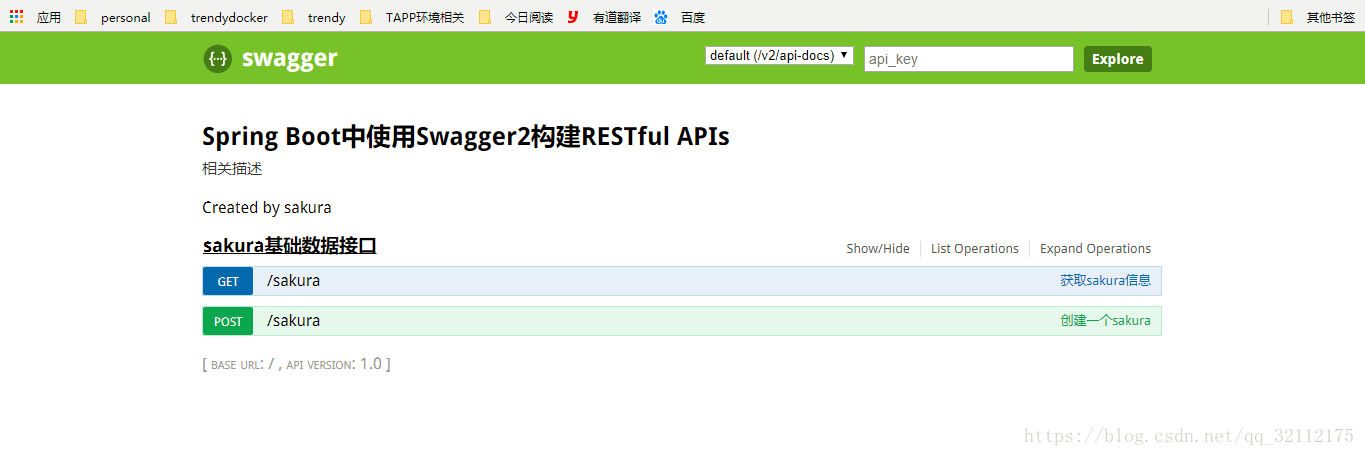
这里介绍使用swagger作为接口文档展示的配置和使用,最终的效果将会是
首先,需要搭建基础的springboot项目。
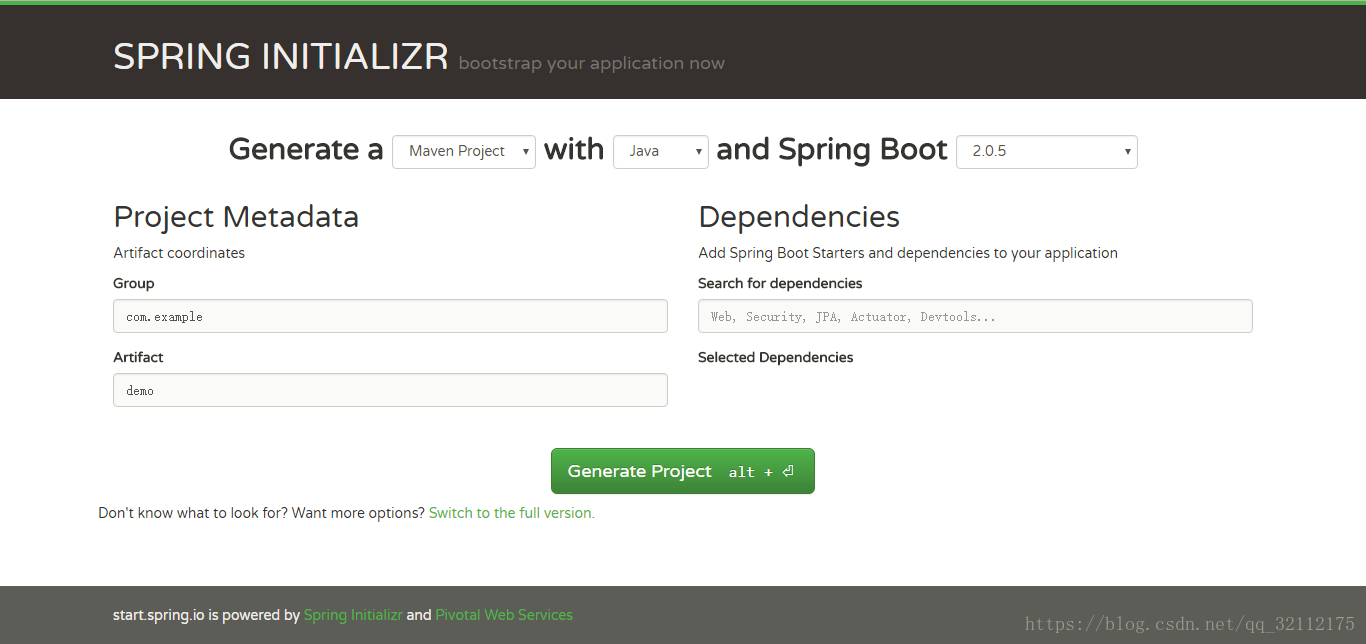
这里推荐大家可以使用 springboot官方推荐模板快速生成工具,地址为:https://start.spring.io/
页面的效果是这样的
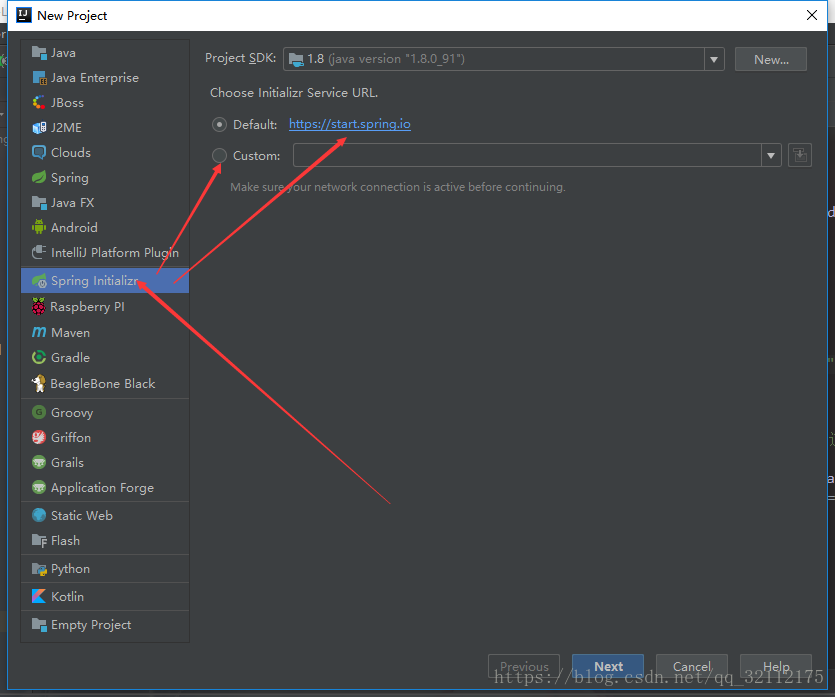
除了上面的方法支持创建简易的springboot项目的配置模板,实际上在开发工具中也有对这种方法的支持。
开发中使用idea也可以进行相关的操作,其中引用的地址可以是上面的地址,也可以是自己定义的,效果展示是下面的图片
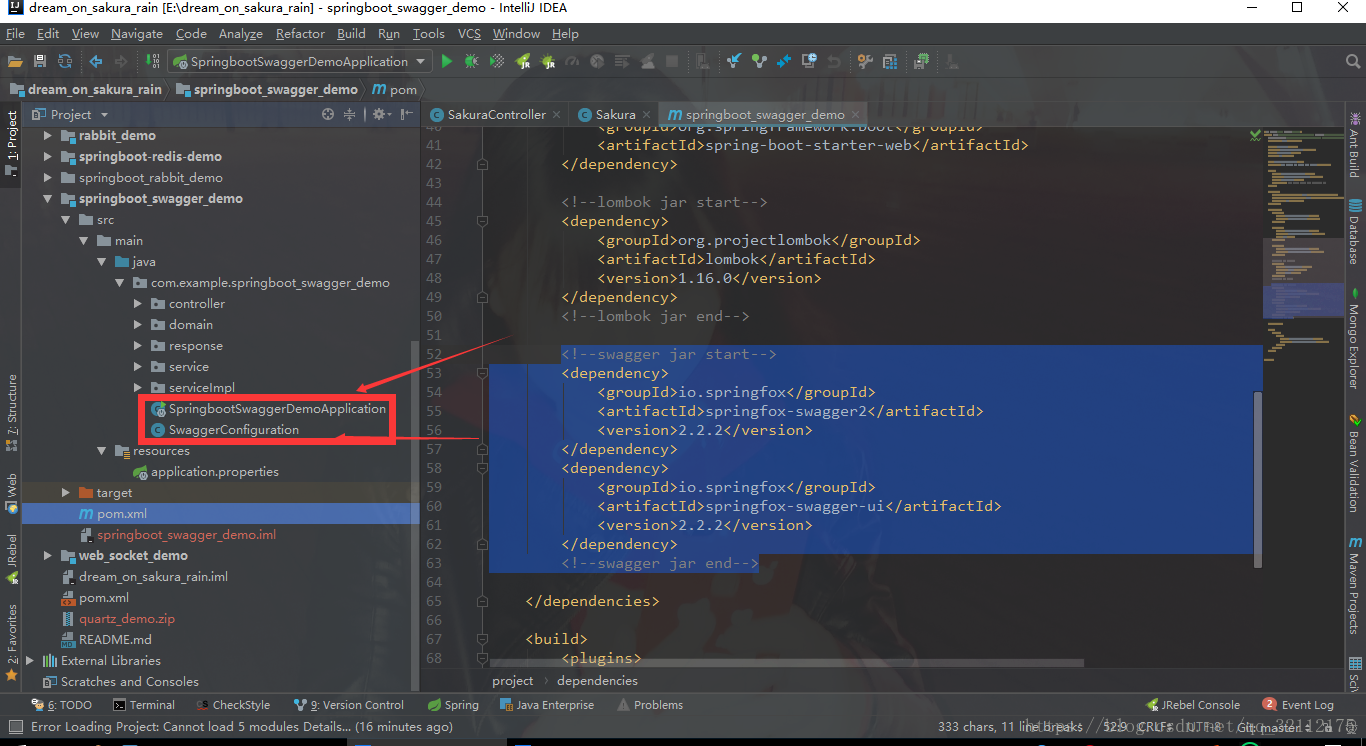
你需要引入包文件
启动类统计编写配置方法,效果图大概是这样的
配置代码
编写控制层的代码(这里面我已经吧经常会用到的注解都写上了,没有考虑到代码的规范性问题,只是为了给大家展示一下注解的含义相关用法)
那么究竟有多少注解需要我们去探究,实际上没有多少,大概。。。。。就这么多吧
具体的含义和使用的详情要不然就是网上有了很多的解释,要不然就是点进注解之后英文解释的已经非常详细了,我这里面就不做解释了。
以上项目只是个人的简单总结和使用,不足之处大神勿喷。
欢迎访问交流群:589780530
博主交流:2718272293
邮箱:2718272293@qq.com licunzhi2@gmail.com
github: https://github.com/licunzhi