我们看xml配置文件的属性
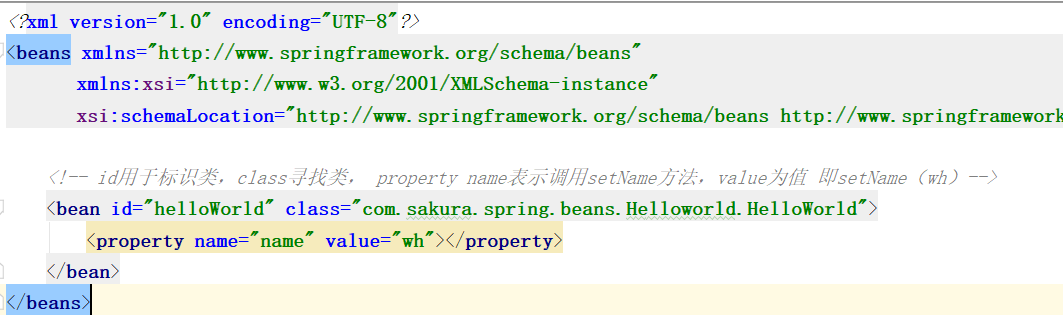
在一个< bean >标签下有以下属性
-id
-class
Id:标识容器中的bean,id唯一。

我们知道程序是通过id来识别到对应的bean。
Class:bean的全类名,通过反射的方式在IOC容器中创建bean,所以要求bean中必须有无参的构造器。
我们知道在配置xml文件时,class是类的包名加类名,所以是利用反射机制来创建类。
当我们的类中没有无参的构造方法时,就会提示没有构造器

如果没有构造方法,默认调用无参构造方法。
2.IOC容器
ApplicationContext代表IOC容器,Spring提供了两种类型的IOC容器基本实现。
-BeanFactory:IOC容器的基本实现
-ApplicationContext:提供更多的高级特性,是BeanFactory的子接口。
区别:
BeanFactoty是Spring架构的基础设施,面向Spring本身,而ApplicationContext则是面向Spring框架的开发者,大多数使用ApplicationContext而不是底层的BeanFactory。(教学说的)
相同:
配置文件时是相同的。
ApplicationContext :
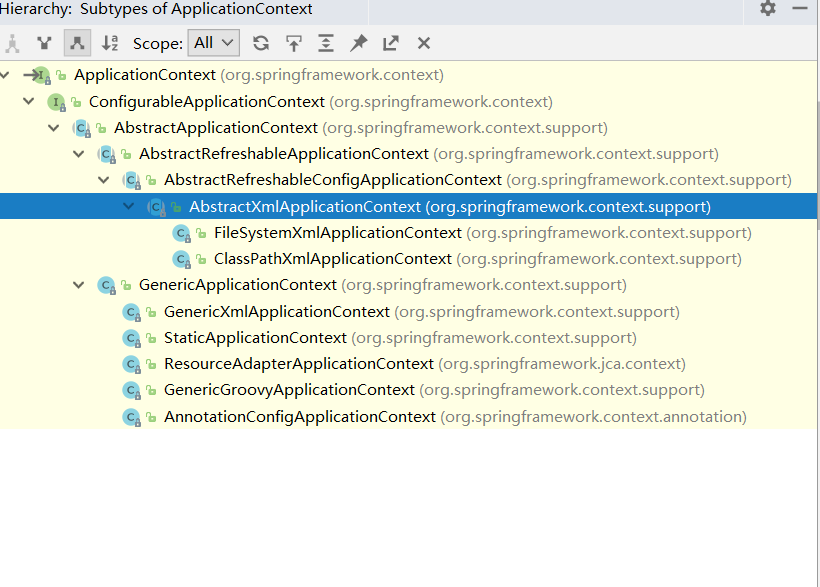
通过查看其实现及接口我们可以看到其层次结构(IDEA选中后按Ctrl+H)
ApplicationContext的主要实现类:
-ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:从类路径下加载配置文件
-FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统中加载配置文件
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");实现了容器的加载及bean中对线的创建
3.Spring常用2种依赖注入的方式
-构造器注入
-setter注入
首先声明两个测试对象
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Integer hight;
//构造,set、get方法略
}
public class Man {
private Person person;
//构造,set、get方法略
}构造器注入
构造器注入就是基于构造方法实现的 容器调用带有一组参数实现类的构造方法完成依赖注入,使用的是〈 bean 〉标签中的〈 constructor-arg 〉元素
在xml中添加bean,使用构造器注入属性值,使用value属性进行参数值的注入
对应xml文件
<bean id="person" class="com.sakura.spring.beans.constructor.Person">
<constructor-arg value="二狗" index="0" type="java.lang.String"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="170" name="age"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="12" name="hight"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="man" class="com.sakura.spring.beans.constructor.Man">
<construc 大专栏 Spring学习笔记:Bean的配置及其细节tor-arg ref="person"/>
</bean>其中
其中要注意:
1.在只指定了value的情况下,即
<constructor-arg value="二狗" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="170" ></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg value="12"></constructor-arg>容器默认根据类中属性的先后顺序进行赋值,类型自动转换
当遇到String类型对应到int类型时,编译会报错。
2.可以指定index、type值让容器根据顺序和数据类型进行对应赋值
3.可以指定 name属性,对其进行精准注入,因为本质上是调用构造方法,所以name值错误或者重复赋值都会报错
4.也可以通过ref指向其他的bean建立依赖关系
测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/sakura/spring/beans/constructor/constructor-applicationContext.xml");
Person person=ctx.getBean("person",Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
Man man=ctx.getBean("man",Man.class);
System.out.println(man);
}测试结果:
Person{name='二狗', age=170, hight=12}
Man{person=Person{name='二狗', age=170, hight=12}}实现了依赖关系。
Setter注入
当容器调用一个无参的构造函数来初始化bean,通过容器在bean 上调用setter设值函数 ,使用的是〈bean〉标签中的〈property〉元素property的name属性指定类的属性名,需要一致,其他与构造器方法相同
在xml中添加一个新的bean
<bean id="personSet" class="com.sakura.spring.beans.constructor.Person">
<property name="hight" value="170"></property>
<property name="age" value="12"></property>
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>通过在对应的set方法下添加对应输出
我们可以看到输出结果
set方法..height
set方法..age
set方法..name
Person{name='张三', age=12, hight=170}集合注入方法
除了进行单值的注入,我们有时还需要对数组或集合进行注入
< list >:注入一列值,允许重复
< set >:注入一列值,不允许重复
< map >:注入键(名)值对的集合,名称和值可以是任何类型
< props >:注入键(名)值对的集合,名称和值可以是任何类型
测试类:
public class JavaCollection {
private List list;
private Map map;
private Properties prop;
}添加bean:
<bean id="coll" class="com.sakura.spring.beans.constructor.JavaCollection">
<property name="list">
<!-- 注入集合 值可重复 set就不举例了-->
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list1</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="map">
<!-- 注入map -->
<map>
<entry key="二蛋">
<value>18</value>
</entry>
<entry key="三蛋">
<value>5</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="prop">
<!-- 注入properties -->
<props>
<prop key="二黑">男</prop>
<prop key="三黑">男</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>测试结果:
JavaCollection{list=[list1], map={二蛋=18, 三蛋=5}, prop={三黑=男, 二黑=男}}