一、基本的读取操作:
- -read(filename) 直接读取文件内容
- -sections() 得到所有的section,并以列表的形式返回
- -options(section) 得到该section的所有option
- -items(section) 得到该section的所有键值对
- -get(section,option) 得到section中option的值,返回为string类型
- -getint(section,option) 得到section中option的值,返回为int类型,还有相应的getboolean()和getfloat() 函数
二、基本的写入操作:
- -write(fp) 将config对象写入至某个 .init 格式的文件 Write an .ini-format representation of the configuration state.
- -add_section(section) 添加一个新的section
- -set( section, option, value 对section中的option进行设置,需要调用write将内容写入配置文件
- -remove_section(section) 删除某个 section
- -remove_option(section, option)
三、代码示例
1、新建一个配置文件:config.ini,内容如下:
# 定义DATABASE分组 [DATABASE] host = 50.23.190.57 username = xxxxxx password = ****** port = 3306 database = databasename
2、在对配置文件进行读写操作前,我们需要先进行一个操作:
# 实例化ConfigParser config = configparser.ConfigParser()
3、进行配置文件的读取操作。以get为例,示例代码如下:
# 读取config.ini config.read("config.ini") # 读取 [DATABASE] 分组下的 host 的值 value = config.get("DATABASE", "host") print(value)
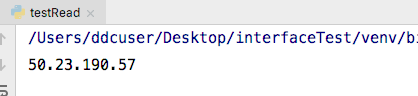
4、进行配置文件的写入操作。以set(section, option, value)为例,示例代码如下:
# 创建一个组:LILY config.add_section("LILY") # 给LILY组添加一个属性name=lily config.set("LILY", "name", "lily") # 写入 config.ini # r:读,r+:读写,w:写,w+:写读,a:追加,a+:追加读写 # 写读和读写的区别:读写,文件已经存在;读写,创建新的文件 config.write(open('config.ini', 'a'))
