Spring environment 和 applicationContext
Environment 表示当前应用程序正在运行的环境,表示整个 spring 应用运行的环境信息,存储各种环境变量,如 JDK 信息、磁盘信息、用户自定义的一些属性值等。
查看源码可知继承接口 PropertyResolver - 属性解析器,用来解析不同属性源 PropertySource 里的 key-value。
/**
* Interface representing the environment in which the current application is running.
* ...
*/
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
// ...
}
PropertyResolver
查看接口 PropertyResolver 的实现,它的继承为
PropertyResolver -> ConfigurablePropertyResolver -> AbstractPropertyResolver -> PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
ConfigurablePropertyResolver
可配置处理类,在 PropertyResolver 的基础上扩展定义类型转换、属性校验、分隔符等一些列的功能。
AbstractPropertyResolver
实现了 ConfigurablePropertyResolver 的接口方法,使用 PropertyPlaceholderHelper 处理占位符。
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
具体的实现以封装在 AbstractPropertyResolver 中,PropertySourcesPropertyResolver作为它的子类它只需要提供数据源 propertySources。
public class PropertySourcesPropertyResolver extends AbstractPropertyResolver {
@Nullable
private final PropertySources propertySources;
/**
* Create a new resolver against the given property sources.
* @param propertySources the set of {@link PropertySource} objects to use
*/
public PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(@Nullable PropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
}
// ...
}
Environment
Environment 的继承实现:
PropertyResolver -> Environment -> ConfigurableEnvironment -> AbstractEnvironment -> StandardEnvironment/StandardServletEnvironment/...
Environment
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* Return the set of profiles explicitly made active for this environment.
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles();
/**
* Return the set of profiles to be active by default when no active profiles have
* been set explicitly.
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
@Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* 判断传入的 profiles 是否激活
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}
ConfigurableEnvironment
扩展出了修改和配置 profiles 的一系列方法,包括用户自定义的和系统相关的属性。
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles);
void addActiveProfile(String profile);
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles);
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources();
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties();
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment();
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
}
AbstractEnvironment
抽象实现类,完成了对 active、default 等相关方法的复写处理。根据注释可知具体的子类主要区别在于它们默认添加的 PropertySource 属性源,
子类分别有 StandardEnvironment(非 web 容器运行的环境)、StandardServletEnvironment(web容器)、StandardReactiveWebEnvironment、MockEnvironment。
**
* Abstract base class for {@link Environment} implementations. Supports the notion of
* reserved default profile names and enables specifying active and default profiles
* through the {@link #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME} and
* {@link #DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME} properties.
*
* <p>Concrete subclasses differ primarily on which {@link PropertySource} objects they
* add by default. {@code AbstractEnvironment} adds none. Subclasses should contribute
* property sources through the protected {@link #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)}
* hook, while clients should customize using {@link ConfigurableEnvironment#getPropertySources()}
* and working against the {@link MutablePropertySources} API.
* See {@link ConfigurableEnvironment} javadoc for usage examples.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment
* @see StandardEnvironment
*/
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
// ...
}
PropertySource 配置源
表示 Spring 各种的配置来源,如:
MapPropertySourcePropertiesPropertySource
CompositePropertySource:组合SystemEnvironmentPropertySource:环境变量
与 environment 的关系
Environment -> ConfigurableEnvironment: 父子层次
ConfigurableEnvironment -> MutablePropertySources: 获取可变多个配置源
MutablePropertySources -> List PropertySource : 包含多个 PropertySource
在 StandardServletEnvironment 中,构造器接受配置源 MutablePropertySources,使用 PropertySourcesPropertyResolver 进行解析,把获取的配置存在 environment 中
Java 获取配置文件的方式
1、使用
JDKproperty(只能获取String类型)2、apache 的
commons-configuration(提供大多数常见类型的Value转换 )3、Spring 的
environment
应用配置的优先级
通过文档可知不同位置的配置的加载优先级
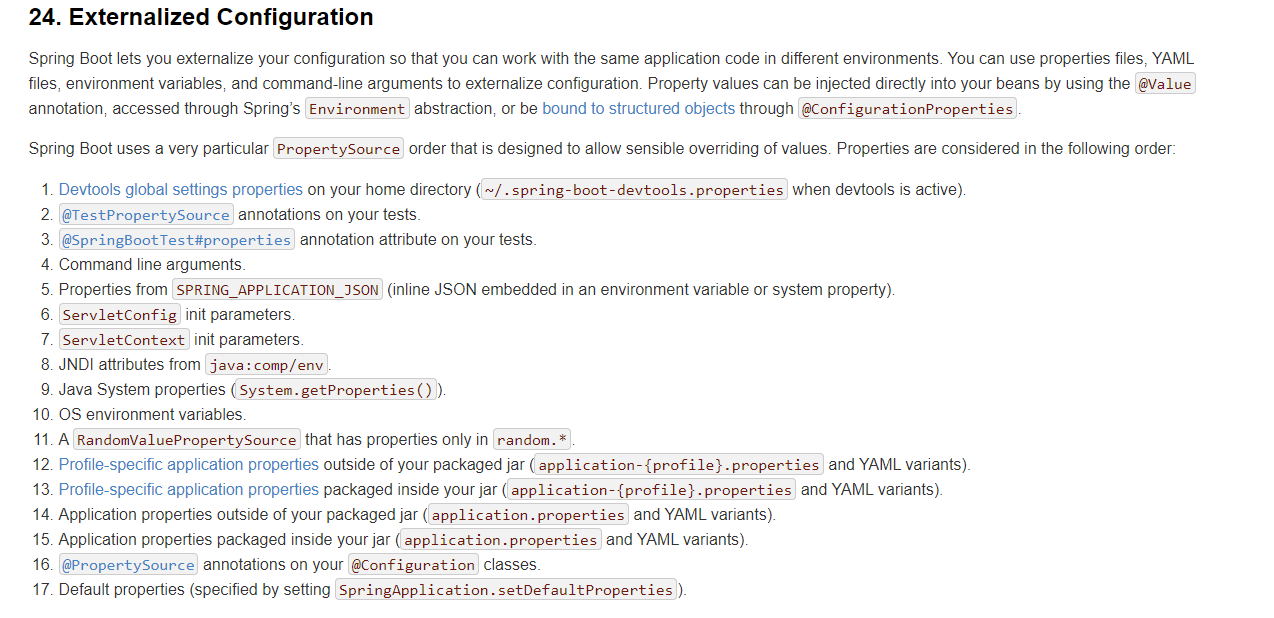
优先级的保证:
public class MutablePropertySources implements PropertySources {
// 使用 List 存储配置,保证有序性
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
// ...
}
public class PropertySourcesPropertyResolver extends AbstractPropertyResolver {
// ...
@Nullable
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" +
propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
// 顺序遍历,读取到的时候返回,优先级越高的配置越前
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
}
Spring 应用上下文 - ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 本质是一个维护 Bean 定义以及对象之间协作关系的接口,或者说为应用 application 提供配置的核心接口。
/**
* Central interface to provide configuration for an application.
* This is read-only while the application is running, but may be
* reloaded if the implementation supports this.
*/
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
}
ApplicationContext 继承 ListableBeanFactory 和 HierarchicalBeanFactory ,实现了 Bean 的生命周期管理(BeanFactoy)、有序性(ListableBeanFactory)和层次性(HierarchicalBeanFactory),并进行扩展。
Spring也为我们提供了 ApplicationContext 的多种类型的容器实现,供我们在不同的应用场景选择,例如:
-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:从一个或多个基于 Java 的配置类中加载上下文定义,适用于 Java 注解的方式 -
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext:专门为 web 应用准备的,适用于注解方式 -
等
在 Spring Boot 的启动方法 run() 我们可以看到 Spring Boot 根据当前应用环境 webApplicationType 决定创建相应的 ConfigurableApplicationContext 对象
run() 内的 prepareEnvironment 监听 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent 事件,由 listeners 处理,然后 createApplicationContext() 创建上下文
public class SpringApplicationBuilder {
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// ...
if (this.running.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
synchronized (this.running) {
// 创建 应用上下文
this.context = build().run(args);
}
}
return this.context;
}
}
public class SpringApplication {
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// ...
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// ...
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// ...
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
context = createApplicationContext();
// ...
}
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
}