一、简介
Ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
二、安装
yum -y install ansible
三、配置ssh-key(可选)
ssh-keygen //生成秘钥 # 将秘钥拷贝到被管理服务器上 ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub -p 22 root@192.168.182.129
四、ansible基础
4.1、ansibel主配置文件(/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg)
4.2、主要的默认配置

[defaults] # some basic default values... #inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts #library = /usr/share/my_modules/ #module_utils = /usr/share/my_module_utils/ #remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp #plugin_filters_cfg = /etc/ansible/plugin_filters.yml #forks = 5 #poll_interval = 15 #sudo_user = root #ask_sudo_pass = True #ask_pass = True #transport = smart #remote_port = 22 #module_lang = C #module_set_locale = False
4.3、开启记录日志
# 去掉前面的'#'号 #log_path = /var/log/ansible.log ==> log_path = /var/log/ansible.log
4.4、去掉第一次连接ssh ask确认(两种方法)
# 第一种(推荐) vi /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg # 其实就是把#去掉 # host_key_checking = False ==> host_key_checking = False # 第二种 vi /etc/ssh/ssh_config StrictHostKeyChecking ask ==> StrictHostKeyChecking no
4.5、以配置文件中配置的:#sudo_user = root,去执行命令
# -u:当前执行的用户,-k(小k):与-u用户对应的密码口令,-b 与配置文件的sudo_user对应,sudo提权到这个用户去执行,-K(大k):sudo_user用户的密码口令 # 前提是要在被控制端主机上配置'liuguoping'这个用户的sudo权限(但是如果输入sudo用户的密码,这个可以不用配置了sudo),可以把用户加到【%wheel ALL=(ALL) ALL】组里,即 [root@centos7-3 ~]# usermod -aG wheel liuguoping [root@centos7-3 ~]# id liuguoping uid=1000(liuguoping) gid=1000(liuguoping) groups=1000(liuguoping),10(wheel) ansible web -m command -a 'ls /root' -u liuguoping -k -b -K
4.6、列出某个分组下的清单
ansible web --list-host ansible web --list-hosts ansible web --list
4.7、常用执行操作
# 1、通配符 ansible 192.168.182.* -m ping # 2、逻辑或(:) ansible web:mysql -m ping # 3、逻辑与(用':&'号),并且关系,注意需要加单引号,双引号可能有问题,因为'&'符号在命令行是后台执行。 ansible 'web:&mysql' -m ping # 4、逻辑非,注意需要加单引号 ansible 'nfs:!mysql' -m ping # 5、综合逻辑 ansible 'nfs:!mysql:&web' -m ping # 6、正则表达式,必须使用'~'开头 ansible "~(web|my).*sql" -m ping
4.8、指定主机清单文件(-i)
ansible -i ~/hosts 192.168.182.129 -m ping
4.9、命令执行过程
步骤一、加载自己的配置文件,默认/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 步骤二、加载自己对应的模块文件(默认为command) 步骤三、通过ansible将模块或命令生成临时py文件,将该文件传输至远程服务器的对应执行用户$HOME/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-数字/xxx.py文件 步骤四、给文件+x执行权限 步骤五、执行并返回结果 步骤六、删除临时文件xxx.py文件,sleep 0退出
4.10、执行状态
绿色:执行成功并且不需要做改变的操作
黄色:执行成功并且对目标主机做变更
红色:执行失败
5、Inventory-主机清单
5.1、含义
主机清单配置(默认配置文件:/etc/ansible/hosts)
5.2、增加主机组
# 定义webservers组 [webservers] 192.168.182.130 192.168.182.128 192.168.182.129
5.3、增加用户名密码
[webservers] 192.168.182.130 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116
5.4、增加端口
[webservers] 192.168.182.130 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116 ansible_ssh_port=22
5.5、变量

5.6、子分组
[web] 192.168.182.130 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116 ansible_ssh_port=22 192.168.182.128 [mysql] 192.168.182.129 # 子分组 [nfs:children] web mysql # 对分组统一定义变量 [nfs:vars] ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116 ansible_ssh_port=22
5.7、自定义主机列表
# vim hostlist [web] 192.168.182.130 192.168.182.128 [mysql] 192.168.182.129 # 子分组 [nfs:children] web mysql # 对分组统一定义变量 [nfs:vars] ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass=1331301116 ansible_ssh_port=22
# ansible -i hostlist nfs -m ping -o
6、Ad-Hoc-点对点模式
6.1、简介
ad-hoc 命令是一种可以快速输入的命令,而且不需要保存起来的命令。就相当于bash中的一句话shell。这也是一个好的地方,在学习ansible playbooks时可以先了解另外一种ansible基本的快速用法,不一定非要写一个palybook文件;ad-hoc简而言之,就是"临时命令"
6.2、常用模块
6.2.1、shell模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc shell ansible-doc shell -s(推荐) # 简介 shell模块 [执行远程主机的shell/python等脚本] # 查看主机名(-o:一行显示) ansible web -m shell -a 'hostname' -o # -f:并行任务数。FORKS被指定为一个整数,默认是5 ansible web -m shell -a 'hostname' -o -f 2
# 示例
# 安装httpd ansible web -m shell -a 'yum -y install httpd' -o # 查看时间 ansible web -m shell -a 'uptime' -o
6.2.2、script模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc script -s(推荐) # 简介 script模块 [在远程主机执行主控端的shell/python等脚本 ] # 参数简介
free_form参数 :必须参数,指定需要执行的脚本,脚本位于 ansible 管理主机本地,并没有具体的一个参数名叫 free_form,具体解释请参考 command 模块。 chdir参数 : 此参数的作用就是指定一个远程主机中的目录,在执行对应的脚本之前,会先进入到 chdir 参数指定的目录中。 creates参数 :使用此参数指定一个远程主机中的文件,当指定的文件存在时,就不执行对应脚本,可参考 command 模块中的解释。 removes参数 :使用此参数指定一个远程主机中的文件,当指定的文件不存在时,就不执行对应脚本,可参考 command 模块中的解释。
# 示例
# 下面命令表示 ansible 主机中的 /testdir/testscript.sh 脚本将在 web 主机中执行,执行此脚本之前,会先进入到 web 主机中的 /opt 目录 ansible web -m script -a "chdir=/opt /testdir/testscript.sh" # 下面命令表示,web主机中的 /testdir/testfile1文件已经存在,ansible 主机中的 /testdir/testscript.sh 脚本将不会在 web 主机中执行。 ansible web -m script -a "creates=/testdir/testfile1 /testdir/testscript.sh" # 下面命令表示,web 主机中的 /testdir/testfile1 文件存在,ansible 主机中的 /testdir/testscript.sh 脚本则会在 web 主机中执行。 ansible ansible-demo3 -m script -a "removes=/testdir/testfile1 /testdir/testscript.sh"
6.2.3、command模块(默认模块)
# 帮助 ansible-doc command -s(推荐) # 简介 command模块 [执行远程命令] # 默认模块,没有shell强大,基本上shell模块都可以支持command模块的功能 # 常用参数
free_form参数 :必须参数,指定需要远程执行的命令。需要说明一点,free_form 参数与其他参数(如果想要使用一个参数,那么则需要为这个参数赋值,也就是name=value模式)并不相同。比如,当我们想要在远程主机上执行 ls 命令时,我们并不需要写成”free_form=ls” ,这样写反而是错误的,因为并没有任何参数的名字是 free_form,当我们想要在远程主机中执行 ls 命令时,直接写成 ls 即可。因为 command 模块的作用是执行命令,所以,任何一个可以在远程主机上执行的命令都可以被称为 free_form。 chdir参数 : 此参数的作用就是指定一个目录,在执行对应的命令之前,会先进入到 chdir 参数指定的目录中。 creates参数 :看到 creates,你可能会从字面上理解这个参数,但是使用这个参数并不会帮助我们创建文件,它的作用是当指定的文件存在时,就不执行对应命令,比如,如果 /testdir/test文件存在,就不执行我们指定的命令。 removes参数 :与 creates 参数的作用正好相反,它的作用是当指定的文件不存在时,就不执行对应命令,比如,如果 /testdir/tests 文件不存在,就不执行我们指定的命令,此参数并不会帮助我们删除文件。
# 示例
# 上面命令表示在 web 主机上执行 ls 命令,因为使用的是 root 用户,所以默认情况下,ls 出的结果是 web 主机中 root 用户家目录中的文件列表。 ansible web -m command -a "ls" # chdir 参数表示执行命令之前,会先进入到指定的目录中,所以上面命令表示查看 web 主机上 /testdir 目录中的文件列表,返回显示有2个文件。 ansible web -m command -a "chdir=/testdir ls" # 下面命令表示 /testdir/testfile1 文件存在于远程主机中,则不执行对应命令。/testdir/testfile3 不存在,才执行”echo test”命令。 ansible web -m command -a "creates=/testdir/testfile1 echo test" # 下面命令表示 /testdir/testfile3 文件不存在于远程主机中,则不执行对应命令。/testdir/testfile1 存在,才执行”echo test”命令。 ansible web -m command -a "removes=/testdir/testfile1 echo test"
6.2.4、raw模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc raw -s (推荐) # 简介 raw模块 [类似于command模块、支持管道传递] # 示例 ansible web -m raw -a "ifconfig eth0 |sed -n 2p |awk '{print $2}' |awk -F: '{print $2}'"
6.2.5、copy模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc copy -s (推荐) # 示例
# -a,--args:后面接参数 ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/etc/ansible/hosts dest=/tmp/hosts owner=root group=bin mode=777' # backup=yes/no:文件存在且文件内容不一样是否备份,默认不备份 ansible web -m copy -a 'src=/etc/ansible/hosts dest=/tmp/hosts owner=root group=bin mode=777 backup=yes'
6.2.6、fetch模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc fetch -s (推荐) # 示例 # 跟copy支持的参数差不多,src:远端主机的目录,dest:主控端目录,其实真正存放的目录在:/tmp/192.168.182.129/tmp/up.sh,会按每台主机分组存放 # This `must' be a file, not a directory:只支持单个文件获取 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m fetch -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/testdir/ansible/"
6.2.7、unarchive模块(解包模块)
# 帮助 ansible-doc unarchive -s # 参数
copy:默认为yes,当copy=yes,那么拷贝的文件是从ansible主机复制到远程主机上的,如果设置为copy=no,那么会在远程主机上寻找src源文件 src:源路径,可以是ansible主机上的路径,也可以是远程主机上的路径,如果是远程主机上的路径,则需要设置copy=no dest:远程主机上的目标路径 mode:设置解压缩后的文件权限
# 示例 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m unarchive -a 'src=/testdir/ansible/data.tar.gz dest=/tmp/tmp/'
6.2.8、archive模块(打包模块)
# 帮助 ansible-doc unarchive -s # 示例 # path:主控端目录,format:压缩格式,dest:被控端目录文件' ansible 192.168.182.129 -m archive -a 'path=/tmp/ format=gz dest=/tmp/tmp/t.tar.gz'
6.2.9、user模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc user -s (推荐) # 创建用户(present:默认,可以不写) ansible web -m user -a 'name=test state=present' # 删除用户(absent) ansible web -m user -a 'name=test state=absent' # 修改密码 # 步骤一、生成加密密码 echo '777777'|openssl passwd -1 -stdin # 步骤二、修改秘密 ansible web -m user -a 'name=test password="$1$Jo5FD9Jr$2QB.BuybbtR35ga4O5o8N."' # 修改shell ansible web -m user -a 'name=test shell=/sbin/noglogin append=yes'
6.2.10、group模块
# 说明 ansible-doc group -s # 示例
# 创建 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m group -a 'name=testgroup system=yes' # 删除 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m group -a 'name=testgroup state=absent'
6.2.11、yum模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc yum -s (推荐) # 示例
# 升级所有包 ansible web -m yum -a 'name="*" state=latest' # 安装apache ansible web -m yum -a 'name="httpd" state=latest'
6.2.12、service模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc service -s (推荐) # 示例 ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started' ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes' ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=stopped' ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=restarted' ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=no'
6.2.13、file模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc file -s (推荐) # 示例
# 创建文件 ansible web -m file -a 'path=/tmp/88.txt mode=777 state=touch' # 创建目录 ansible web -m file -a 'path=/tmp/99 mode=777 state=directory' # 删除 ansible web -m file -a 'path=/tmp/99 state=absent'
6.2.14、setup模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc setup -s (推荐) # 示例 ansible web -m setup ansible web -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses'
6.2.15、cron模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc cron -s # 示例
# 创建定时任务 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m cron -a 'minute=* weekday=1,3,5,6,7 job="/usr/bin/wall FBI warning" name=warningcron' # 关闭定时任务 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m cron -a 'disabled=true job="/usr/bin/wall FBI warning" name=warningcron' # 删除定时任务 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m cron -a ' job="/usr/bin/wall FBI warning" name=warningcron state=absent'
6.2.16、hostname模块
# 帮助 ansible-doc hostname -s # 示例 ansible 192.168.182.129 -m hostname -a 'name=192.168.182.129'
6.3、ansible-galaxy
# 说明 1、ansible-galaxy命令与Ansible捆绑在一起,您可以使用它从Galaxy或直接从基于git的SCM【安装角色】 2、默认情况下,命令行工具使用服务器地址【https://galaxy.ansible.com】与Galaxy网站API通信 # 示例
# 展示已安装的角色 ansible-galaxy list # 删除角色 ansible-galaxy remove geerlingguy.nginx
6.4、ansible-vault
# 说明 管理加密解密yml文件 # 语法 ansible-vault [create|decrypt|edit|encrypt|rekey|view] # 示例
# 加密 ansible-vault encrypt hello.yml # 解密 ansible-vault decrypt hello.yml # 查看 ansible-vault view hello.yml # 编辑 ansible-vault edit hello.yml # 修改 ansible-vault rekey hello.yml # 创建 ansible-vault create hello.yml
6.5、ansible-console
# 查看帮助(?问好) root@all (4)[f:5]$ ? # 示例
# 切换操作列表 cd 192.168.182.129 cd web # 查看hostname command hostname # 修改 hostname name='test'
七、YAML-YAML Ain't Markup Language非标记语言
7.1、官方网站:https://yaml.org/
7.2、什么是playbook?
playbook 翻译过来就是"剧本"
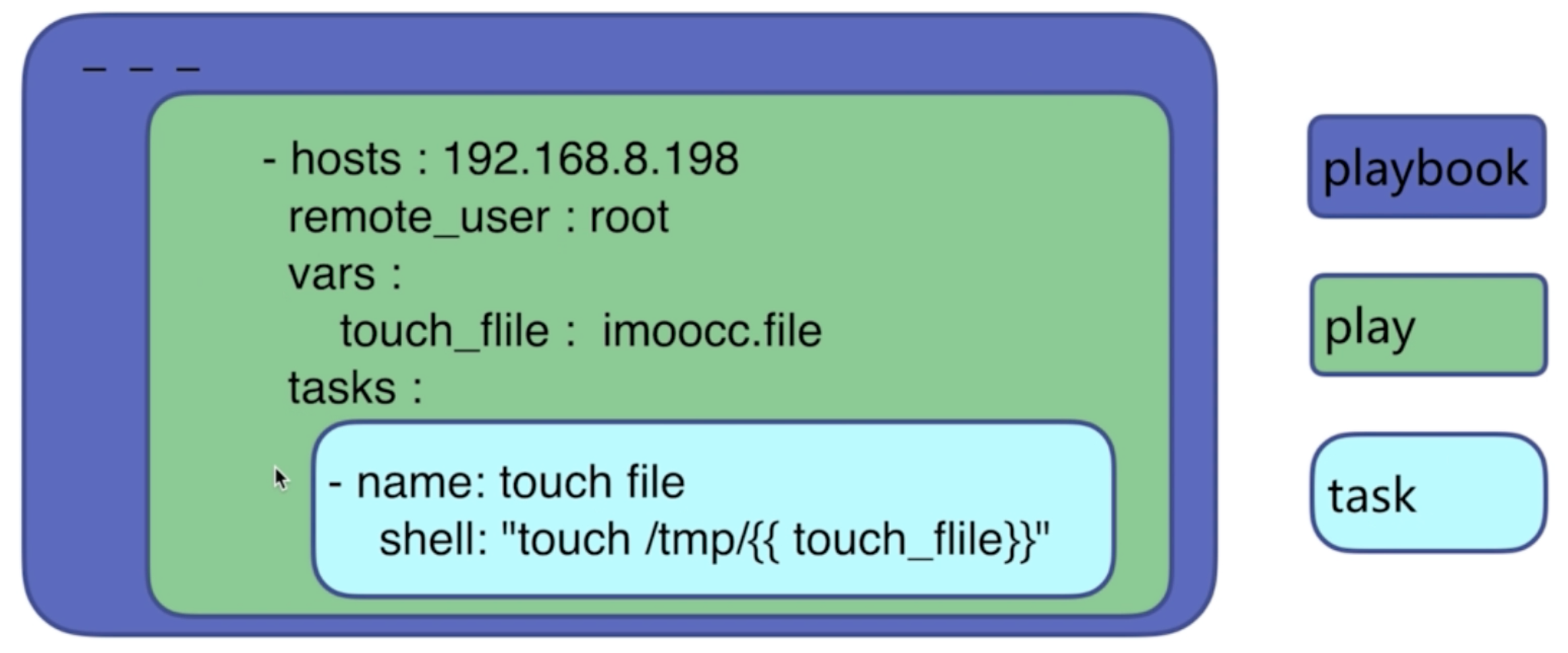
7.3、playbook的组成
play:定义的是主机的角色
task:定义的是具体执行的任务
playbook:由一个或多个play组成,一个play可以包含多个task
7.4、playbook的优势
1、功能比adhoc更全 2、控制好依赖 3、展现更直观 4、持久使用
7.5、yaml语法和变量
7.5.1、yaml语法
注意格式:
大小写敏感 使用缩进表示层级关系(只能空格不能使用tab) yaml文件"---"作为文档的开始
7.5.2、yaml支持的数据结构

7.5.3、yaml变量的应用

7.5.4、tasks:任务列表
7.5.4.1、格式
第一种:action: module arguments # 建议使用 第二种:module: arguments
7.5.4.2、注意
1)shell和command 模块后面跟命令,而非key=value 2)某任务的状态运行后为changed时,可通过"notify"通知给相应的handlers 3)任务可以通过"tags"打标签,而后可在ansible-playbook命令上使用-t指定进行调用 4)如果命令或者脚本退出码不为零,可以使用如下方式替代
tasks: - name: run this command and ignore the result shell: /usr/bin/somecommand || /bin/true
5)或者使用ignore_errors来忽略错误信息
tasks: - name: run this command and ignore the result shell: /usr/bin/somecommand ignore_errors: True
7.5.5、运行playbook的方式
ansible-playbook <filename.yml> ... [options]
7.5.6、常见选项
--check/-C:只检查可能会发生的改变,单不真正执行操作 --list-hosts:列出运行任务的主机 --limit:主机列表,只针对主机列表中的主机执行 -v:显示过程 -vv,-vvv更详细 # 示例
ansible-playbook file.yml --check 只检测 ansible-playbook file.yml ansible-playbook file.yml --limit web
7.5.7、handlers和notify结合使用触发条件
7.5.7.1、handlers
是task列表,这些task与前述的task并没有本质上的不同,用于当关注的资源发生时,才会采取一定的操作
7.5.7.2、notify
notify此action可用于在每个play的最后被触发,这样可避免多次有改变发生时每次都执行指定的操作,仅在所有的变化发生完成后一次性地执行指定操作,在notify列出的操作称为handler,也即notify中调用handler中定义的操作
7.5.7.3、示例

--- - hosts: 192.168.182.129 remote_user: root tasks: - name: install httpd package yum: name=httpd - name: copy conf file copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/ backup=yes notify: restart servie - name: start service service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes handlers: - name: restart servie service: name=httpd state=restarted
7.5.5、tags

--- - hosts: 192.168.182.129 remote_user: root tasks: - name: install httpd package yum: name=httpd tags: inshttpd - name: copy conf file copy: src=files/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/ backup=yes notify: restart servie - name: start service service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes tags: rshttpd handlers: - name: restart servie service: name=httpd state=restarted
7.6、模板template
7.6.1、说明
文本文件,嵌套有脚本(使用模板编程语言编写)
只能通过playbook调用
7.6.2、Jinja2语言
7.6.2.1、字面量形式
字符串:使用单引号或双引号 数字:整数,浮点数 列表:[item1,item2,...] 元祖:(item1,item2,...) 字典:{key1:value1,key2:value2,...} 布尔值:true/false
7.6.2.2、算术运算
# //:除取整 +,-,*,/,//,%,**
7.6.2.3、比较操作
==,!=,>,>=,<,<=
7.6.2.4、逻辑操作
and,or,not
7.6.2.5、流表达式
1)when
# 说明
在task后添加when子句即可使用条件测试;when语句支持jinja2表达式语法
# 示例
--- - hosts: test remote_user: root tasks: - name: test when command: ls /tmp when: ansible_os_family == 'RedHat'
2)with_items
# 说明
遍历列表
# 示例
--- - hosts: test remote_user: root tasks: - name: touch file file: name=/tmp/tmp/{{ item }} state=touch with_items: - file1 - file2 - file3 - name: install software yum: name={{ item }} state=present with_items: - htop - sl - hping3
3)template for if

# cat test_for.yml --- - hosts: test remote_user: root vars: ports: - web1: port: 80 name: web1.com rootdir: /data/website1 - web2: port: 81 #name: web2.com rootdir: /data/website2 - web3: port: 83 name: web3.com rootdir: /data/website3 tasks: - name: copy conf template: src=for1.conf.j2 dest=/tmp/tmp/for1.conf # cat templates/for1.conf.j2 {% for p in ports %} server{ listen {{ p.port }} {% if p.name is defined %} servername {{ p.name }} {% endif %} documentroot {{ p.rootdir }} } {% endfor %}
4)示例

--- - hosts: test remote_user: root tasks: - name: install package yum: name=nginx - name: copy template # src:默认会在当前目录templates template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf notify: restart service - name: start service service: name=nginx state=started handlers: - name: restart service service: name=nginx state=restarted
7.7、roles角色和场景演练
7.7.1、说明
roles就是通过分别将变量、文件、任务、模块及处理器放置于单独的目录中、并可以便捷地include他们的一种机制
例如:下面的场景演练的层次目录结构
7.7.2、为什么需要用到roles
# 什么是roles?
是一种利用在大型playbook中的剧本配置模式,有这自己特定结构
# 为什么需要用到roles?
和面向对象开发思想相似
利用大型的项目任务中,尽可能的将公共的任务、变量等内容独立
7.7.3、角色简单使用
# 1)创建roles目录,所以得角色都放在这个目录下
7.7.3.2、示例
1)安装nginx
# 目录结构
.
├── httpd
├── memcache
├── mysql
├── nginx
│ ├── tasks
│ │ ├── group.yml
│ │ ├── install.yml
│ │ ├── main.yml
│ │ ├── restart.yml
│ │ ├── start.yml
│ │ ├── templ.yml
│ │ └── user.yml
│ └── templates
│ └── nginx.conf.j2
└── nginx_role.yml
# nginx_role.yml
[root@bogon roles]# cat nginx_role.yml - hosts: test remote_user: root roles: - role: nginx
# 调用
ansible-playbook nginx_role.yml
2)综合案例
# 目录结构
[root@bogon roles]# tree app
app
├── files
│ └── hosts
├── handlers
│ └── main.yml
├── tasks
│ ├── copyfile.yml
│ ├── group.yml
│ ├── main.yml
│ ├── start.yml
│ ├── templ.yml
│ ├── user.yml
│ └── yum.yml
├── templates
│ └── httpd.conf.j2
└── vars
└── main.yml
# app_role.yml
[root@bogon roles]# cat app_role.yml - hosts: test remote_user: root roles: - role: app
# 执行
ansible-playbook app_role.yml
相关文件的代码
1)app/files/hosts就是/etc/hosts
2)app/tasks/main.yml

- name: restart service
service: name=httpd state=restarted
3)app/tasks/copyfile.yml

- name: copy file
copy: src=hosts dest=/tmp/tmp/ backup=yes
4)app/tasks/group.yml

- name: create group
group: name=app
5)app/tasks/main.yml

- include: group.yml - include: user.yml - include: yum.yml - include: templ.yml - include: copyfile.yml - include: start.yml
6)app/tasks/start.yml

- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
7)app/tasks/templ.yml

- name: copy template template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf owner={{ user }} notify: restart service
8)app/tasks/user.yml

- name: create user
user: name=app group=app system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin
10)app/tasks/yum.yml

- name: install apache
yum: name=httpd state=present
11)app/templates/httpd.conf.j2

# # This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the # configuration directives that give the server its instructions. # See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information. # In particular, see # <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html> # for a discussion of each configuration directive. # # Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding # what they do. They're here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure # consult the online docs. You have been warned. # # Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many # of the server's control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the # server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin # with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so 'log/access_log' # with ServerRoot set to '/www' will be interpreted by the # server as '/www/log/access_log', where as '/log/access_log' will be # interpreted as '/log/access_log'. # # ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server's # configuration, error, and log files are kept. # # Do not add a slash at the end of the directory path. If you point # ServerRoot at a non-local disk, be sure to specify a local disk on the # Mutex directive, if file-based mutexes are used. If you wish to share the # same ServerRoot for multiple httpd daemons, you will need to change at # least PidFile. # ServerRoot "/etc/httpd" # # Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or # ports, instead of the default. See also the <VirtualHost> # directive. # # Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to # prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses. # #Listen 12.34.56.78:80 Listen {{ port_number }} # # Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support # # To be able to use the functionality of a module which was built as a DSO you # have to place corresponding `LoadModule' lines at this location so the # directives contained in it are actually available _before_ they are used. # Statically compiled modules (those listed by `httpd -l') do not need # to be loaded here. # # Example: # LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so # Include conf.modules.d/*.conf # # If you wish httpd to run as a different user or group, you must run # httpd as root initially and it will switch. # # User/Group: The name (or #number) of the user/group to run httpd as. # It is usually good practice to create a dedicated user and group for # running httpd, as with most system services. # User {{ user }} Group {{ group}} # 'Main' server configuration # # The directives in this section set up the values used by the 'main' # server, which responds to any requests that aren't handled by a # <VirtualHost> definition. These values also provide defaults for # any <VirtualHost> containers you may define later in the file. # # All of these directives may appear inside <VirtualHost> containers, # in which case these default settings will be overridden for the # virtual host being defined. # # # ServerAdmin: Your address, where problems with the server should be # e-mailed. This address appears on some server-generated pages, such # as error documents. e.g. admin@your-domain.com # ServerAdmin root@localhost # # ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself. # This can often be determined automatically, but we recommend you specify # it explicitly to prevent problems during startup. # # If your host doesn't have a registered DNS name, enter its IP address here. # #ServerName www.example.com:80 # # Deny access to the entirety of your server's filesystem. You must # explicitly permit access to web content directories in other # <Directory> blocks below. # <Directory /> AllowOverride none Require all denied </Directory> # # Note that from this point forward you must specifically allow # particular features to be enabled - so if something's not working as # you might expect, make sure that you have specifically enabled it # below. # # # DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your # documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but # symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations. # DocumentRoot "/var/www/html" # # Relax access to content within /var/www. # <Directory "/var/www"> AllowOverride None # Allow open access: Require all granted </Directory> # Further relax access to the default document root: <Directory "/var/www/html"> # # Possible values for the Options directive are "None", "All", # or any combination of: # Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews # # Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All" # doesn't give it to you. # # The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see # http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options # for more information. # Options Indexes FollowSymLinks # # AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files. # It can be "All", "None", or any combination of the keywords: # Options FileInfo AuthConfig Limit # AllowOverride None # # Controls who can get stuff from this server. # Require all granted </Directory> # # DirectoryIndex: sets the file that Apache will serve if a directory # is requested. # <IfModule dir_module> DirectoryIndex index.html </IfModule> # # The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being # viewed by Web clients. # <Files ".ht*"> Require all denied </Files> # # ErrorLog: The location of the error log file. # If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost> # container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be # logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost> # container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here. # ErrorLog "logs/error_log" # # LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log. # Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, # alert, emerg. # LogLevel warn <IfModule log_config_module> # # The following directives define some format nicknames for use with # a CustomLog directive (see below). # LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %b "%{Referer}i" "%{User-Agent}i"" combined LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %b" common <IfModule logio_module> # You need to enable mod_logio.c to use %I and %O LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %b "%{Referer}i" "%{User-Agent}i" %I %O" combinedio </IfModule> # # The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format). # If you do not define any access logfiles within a <VirtualHost> # container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do* # define per-<VirtualHost> access logfiles, transactions will be # logged therein and *not* in this file. # #CustomLog "logs/access_log" common # # If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information # (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive. # CustomLog "logs/access_log" combined </IfModule> <IfModule alias_module> # # Redirect: Allows you to tell clients about documents that used to # exist in your server's namespace, but do not anymore. The client # will make a new request for the document at its new location. # Example: # Redirect permanent /foo http://www.example.com/bar # # Alias: Maps web paths into filesystem paths and is used to # access content that does not live under the DocumentRoot. # Example: # Alias /webpath /full/filesystem/path # # If you include a trailing / on /webpath then the server will # require it to be present in the URL. You will also likely # need to provide a <Directory> section to allow access to # the filesystem path. # # ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts. # ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that # documents in the target directory are treated as applications and # run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the # client. The same rules about trailing "/" apply to ScriptAlias # directives as to Alias. # ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/var/www/cgi-bin/" </IfModule> # # "/var/www/cgi-bin" should be changed to whatever your ScriptAliased # CGI directory exists, if you have that configured. # <Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin"> AllowOverride None Options None Require all granted </Directory> <IfModule mime_module> # # TypesConfig points to the file containing the list of mappings from # filename extension to MIME-type. # TypesConfig /etc/mime.types # # AddType allows you to add to or override the MIME configuration # file specified in TypesConfig for specific file types. # #AddType application/x-gzip .tgz # # AddEncoding allows you to have certain browsers uncompress # information on the fly. Note: Not all browsers support this. # #AddEncoding x-compress .Z #AddEncoding x-gzip .gz .tgz # # If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you # probably should define those extensions to indicate media types: # AddType application/x-compress .Z AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz # # AddHandler allows you to map certain file extensions to "handlers": # actions unrelated to filetype. These can be either built into the server # or added with the Action directive (see below) # # To use CGI scripts outside of ScriptAliased directories: # (You will also need to add "ExecCGI" to the "Options" directive.) # #AddHandler cgi-script .cgi # For type maps (negotiated resources): #AddHandler type-map var # # Filters allow you to process content before it is sent to the client. # # To parse .shtml files for server-side includes (SSI): # (You will also need to add "Includes" to the "Options" directive.) # AddType text/html .shtml AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml </IfModule> # # Specify a default charset for all content served; this enables # interpretation of all content as UTF-8 by default. To use the # default browser choice (ISO-8859-1), or to allow the META tags # in HTML content to override this choice, comment out this # directive: # AddDefaultCharset UTF-8 <IfModule mime_magic_module> # # The mod_mime_magic module allows the server to use various hints from the # contents of the file itself to determine its type. The MIMEMagicFile # directive tells the module where the hint definitions are located. # MIMEMagicFile conf/magic </IfModule> # # Customizable error responses come in three flavors: # 1) plain text 2) local redirects 3) external redirects # # Some examples: #ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo." #ErrorDocument 404 /missing.html #ErrorDocument 404 "/cgi-bin/missing_handler.pl" #ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html # # # EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile: On systems that support it, # memory-mapping or the sendfile syscall may be used to deliver # files. This usually improves server performance, but must # be turned off when serving from networked-mounted # filesystems or if support for these functions is otherwise # broken on your system. # Defaults if commented: EnableMMAP On, EnableSendfile Off # #EnableMMAP off EnableSendfile on # Supplemental configuration # # Load config files in the "/etc/httpd/conf.d" directory, if any. IncludeOptional conf.d/*.conf
12)app/vars/main.yml

port_number: 8080 user: app group: app
最后说一下ansibel的缺点:
1、ansible毕竟是基于ssh操作,所以执行效率并不高,但是对于一两百机子还是够用的,再多的机子,可以考虑用saltstack,或者puppet
2、安全性不高,所以特别注意一些危险的操作(如:rm -f 之类的命令),可以通过创建特定的用户禁用一些危险操作
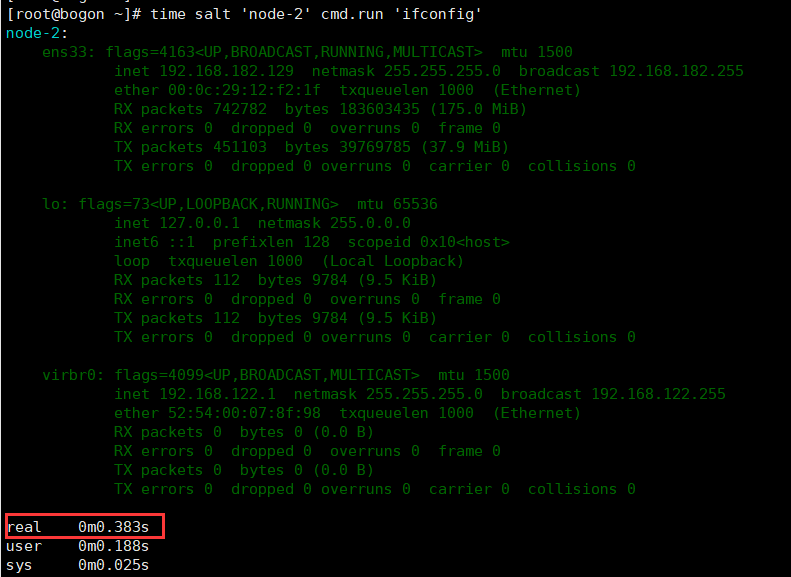
这里稍微对比一下ansible和saltstack速度,一目了然。

到此为止~~~
