1.字符串的内容对齐操作
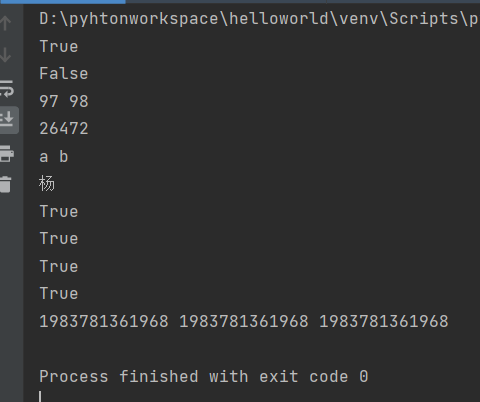
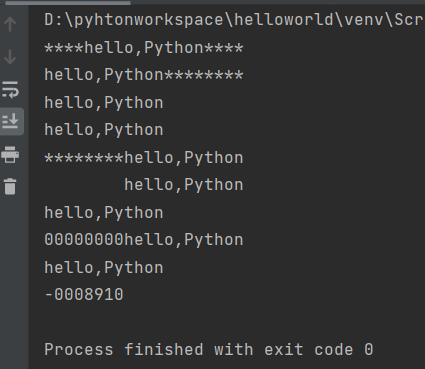
s = 'hello,Python' '''居中对齐''' print(s.center(20,'*')) '''左对齐''' print(s.ljust(20,'*')) print(s.ljust(10)) print(s.ljust(20)) '''右对齐''' print(s.rjust(20,'*')) print(s.rjust(20)) print(s.rjust(10)) '''右对齐,使用0进行填充''' print(s.zfill(20)) print(s.zfill(10)) print('-8910'.zfill(8))
2.字符串的分割
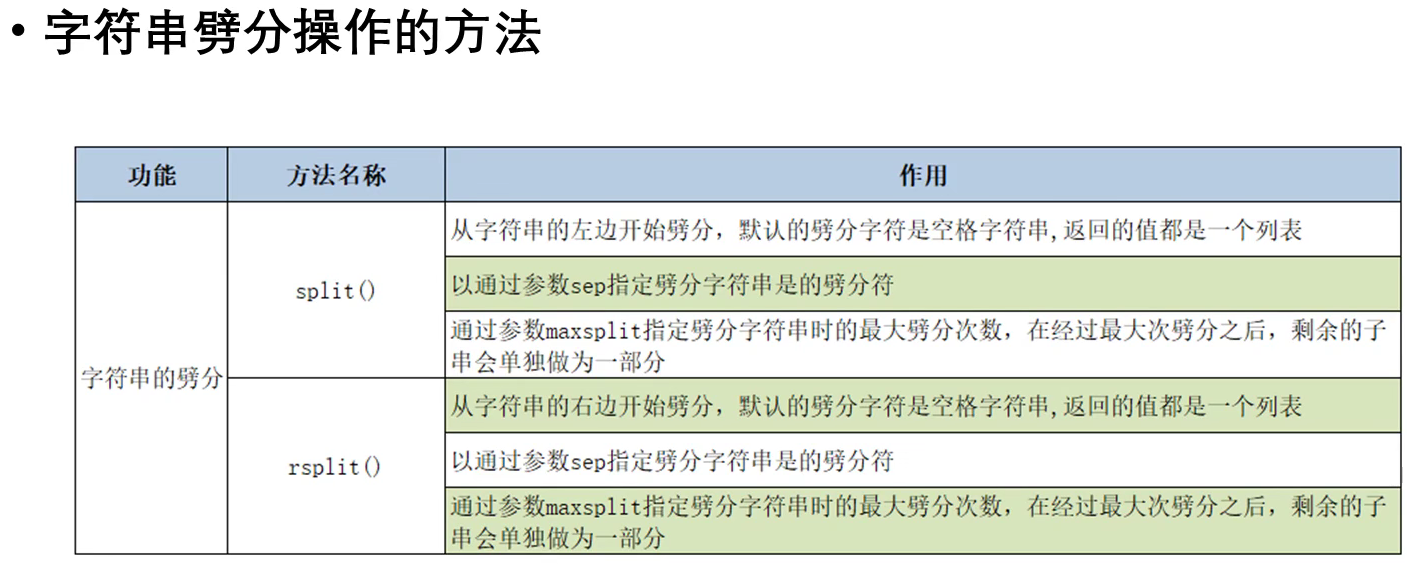
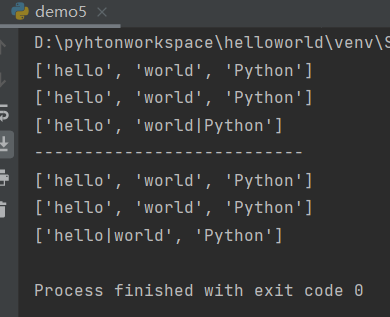
s = 'hello world Python' lst = s.split() print(lst) s1 = 'hello|world|Python' print(s1.split(sep='|')) print(s1.split(sep='|',maxsplit=1)) print('---------------------------') '''rsplit()从右侧开始分割''' print(s.rsplit()) print(s1.rsplit('|')) print(s1.rsplit(sep='|',maxsplit=1))
3.字符串的安判断
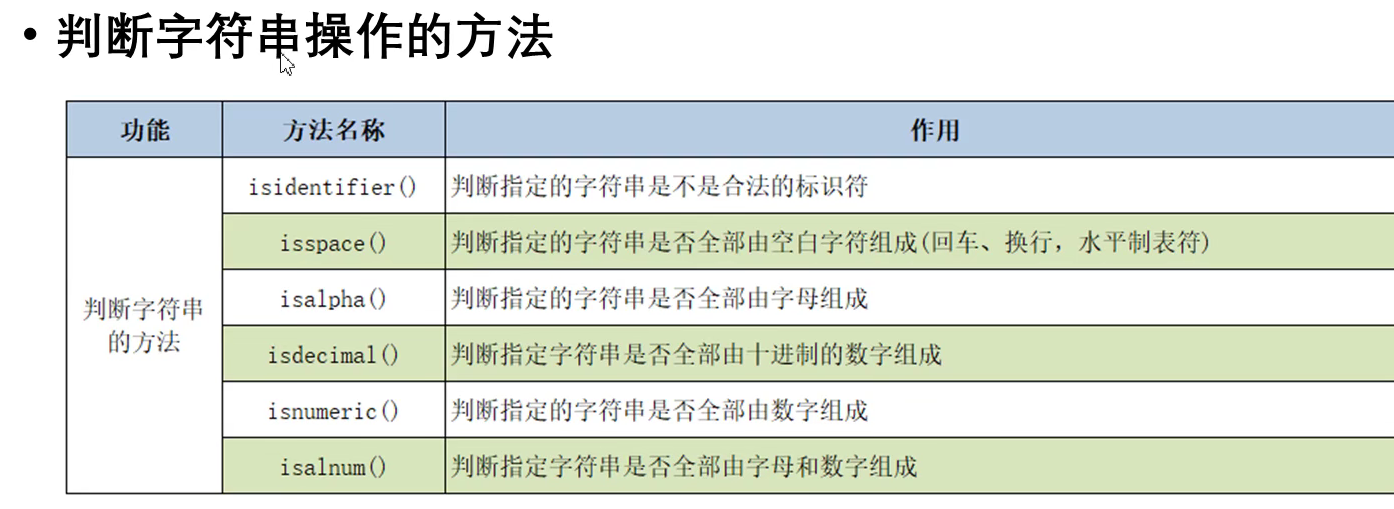
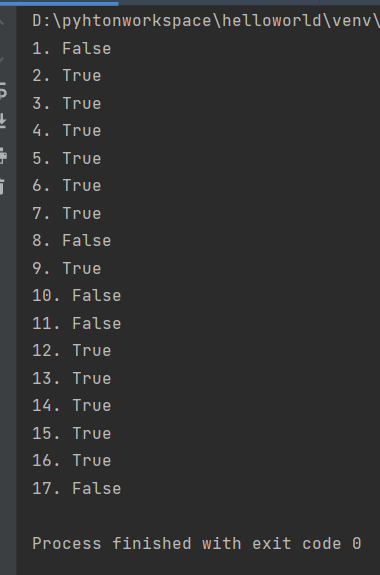
s = 'hello,python' print('1.', s.isidentifier()) #False print('2.', 'hello'.isidentifier()) #True print('3.', '张三'.isidentifier()) #True print('4.', '张三_123'.isidentifier()) #True print('5.', '\t'.isspace()) #True print('6.', 'abc'.isalpha()) #True print('7.', '张三'.isalpha()) #True print('8.', '张三1'.isalpha()) #False print('9.', '123'.isdecimal()) #True print('10.', '123四'.isdecimal()) #False print('11.', 'Ⅱ'.isdecimal()) #False print('12.', '123'.isnumeric()) #True print('13.', '123四'.isnumeric()) #True print('14.', 'Ⅱ'.isnumeric()) #True print('15.', 'abc1'.isalnum()) #True print('16.', '张三123'.isalnum()) #True print('17.', 'abc!'.isalnum()) #False
4.字符串的替换与合并

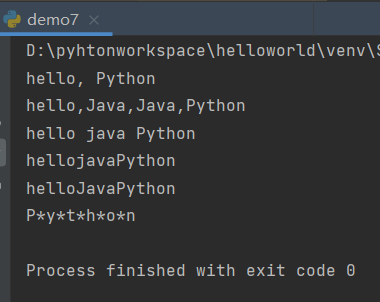
s = 'hello, Python' print(s.replace('Pyhthon','Java')) s1 = 'hello,Python,Python,Python' print(s1.replace('Python','Java',2)) lst = ['hello','java', 'Python'] print(' '.join(lst)) print(''.join(lst)) t = ('hello', 'Java', 'Python') print(''.join(t)) print('*'.join('Python'))
5.字符串的比较操作

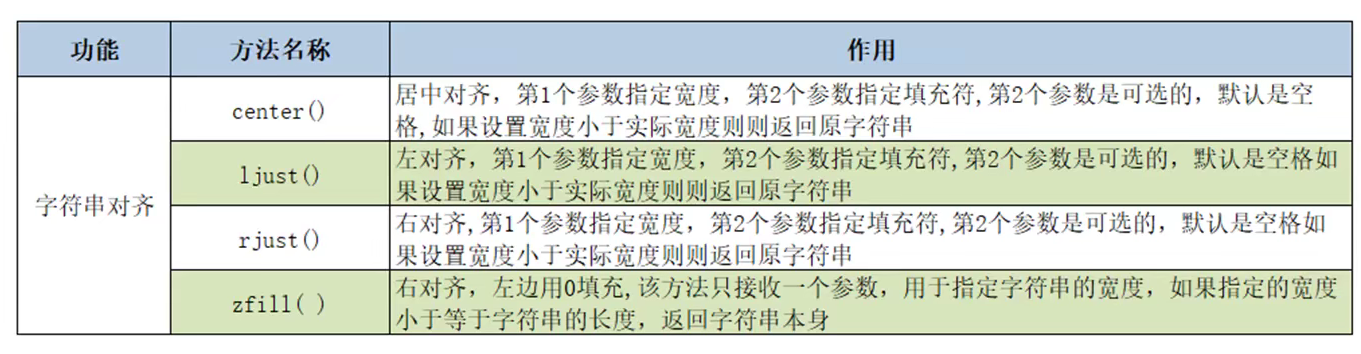
print('apple' > 'app') print('apple'> 'banana') print(ord('a'), ord('b')) print(ord('杨')) print(chr(97), chr(98)) print(chr(26472)) '''== 和 is的区别''' a = b = 'Python' c = 'Python' print(a == b) print(b == c) print(a is b) print(a is c) print(id(a), id(b), id(c))