在cocos2dx中提供了一个数据存储类CCUserDefault,可以作为一个轻量级的数据库来使用。它支持五种数据bool、int、float、double、string的存储。
【3.x】
(1)去掉 “CC”
(2)获取单例:sharedUserDefault() 改为 getInstance()
(3)增加数据值:Data
//
void setDataForKey(const char* pKey, const Data& value);
Data getDataForKey(const char* pKey, const Data& defaultValue = Data::Null);
//【CCUserDefault】
CCUserDefault类和之前讲的CCDirector、SimpleAudioEngine一样,都是采用单例模式。
可以通过sharedUserDefault()函数来获取其唯一的实例对象。
CCUserDefault采用XML存储技术,就是一般的键值对,这个类似C++中的map的映射(键——值)。一个关键字对应一个值。其实现的接口也比较简单实用,通过传统的set()、get()方法访问和修改值。
它支持五种数据:bool、int、float、double、string。
1、原理
(1)类似map的映射(键——值)。一个关键字对应一个值,并利用set()/get()进行访问。
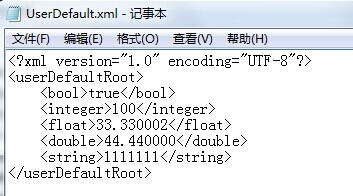
(2)数据直接存储在一个XML文件中,并且文件名为程序项目的名字,如“MyTest.xml”。
(3)首次使用时,XML不存在,CCUserDefault会自动创建相应的XML文件。
2、设置数据值set
通过(键——值)的方式进行设置。
//
void setBoolForKey( const char* pKey, bool value); //设置一个bool值
void setIntegerForKey(const char* pKey, int value); //设置一个int值
void setFloatForKey( const char* pKey, float value); //设置一个float值
void setDoubleForKey( const char* pKey, double value); //设置一个double值
void setStringForKey( const char* pKey, const std::string& value); //设置一个string值
//3、获取数据值get
通过关键字,来从XML文件中获取数据值。
若关键字不存在,会自动设置(键——值)映射,并设置对应的默认值defaultValue。
//
bool getBoolForKey( const char* pKey, bool defaultValue = false); //读取一个bool值
int getIntegerForKey(const char* pKey, int defaultValue = 0); //读取一个int值
float getFloatForKey( const char* pKey, float defaultValue = 0.0); //读取一个float值
double getDoubleForKey( const char* pKey, double defaultValue = 0.0); //读取一个double值
std::string getStringForKey( const char* pKey, const std::string& defaultValue = ""); //读取一个string值
//4、保存flush
当set完后,数据不会马上保存到XML文件中。
所以一定要记得用flush()来保存数据,否则会丢失!
//
CCUserDefault::sharedUserDefault()->flush();
//5、其他操作
获取单例对象、释放单例对象、获取XML文件路径、判断XML文件是否已经存在。
//
static CCUserDefault* sharedUserDefault(); //获取单例对象
static void purgeSharedUserDefault(); //释放单例对象
const static std::string& getXMLFilePath(); //获取XML路径
static bool isXMLFileExist(); //XML文件是否已创建
//6、使用技巧
(1)每次操作都要打长长的CCUserDefault::sharedUserDefault(),来获得单例对象。是不是很麻烦呢?可以通过宏定义来缩短长度。
//
#define UserDefault CCUserDefault::sharedUserDefault()
//(2)在使用的时候,要特别注意:区别 const char* 和 const std::string 是不一样的!
(3)当set完后,一定要记得用flush()来保存数据,否则会丢失!
【代码实战】
代码来源于TestCpp项目中。
1、需要引用以下的头文件和命名空间
因为要用到C++的string类型。
//
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//
2、宏定义获取单例对象的函数
//
#define UserDefault CCUserDefault::sharedUserDefault()
//3、编写数据存储相关操作,并在控制台输出数据值
//
//设置set
UserDefault->setBoolForKey( "bool", true);
UserDefault->setIntegerForKey("integer", 100);
UserDefault->setFloatForKey( "float", 33.33f);
UserDefault->setDoubleForKey( "double", 44.44);
UserDefault->setStringForKey( "string", "1111111");
//获取get,并输出到控制台
//通过关键字,获取数据
bool b = UserDefault->getBoolForKey("bool");
int i = UserDefault->getIntegerForKey("integer");
float f = UserDefault->getFloatForKey("float");
double d = UserDefault->getDoubleForKey("double");
string ret = UserDefault->getStringForKey("string");
//输出到控制台
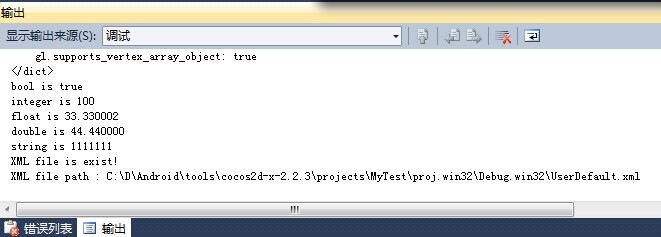
CCLOG( (b == true)? "bool is true" : "bool is false" );
CCLOG("integer is %d", i);
CCLOG("float is %f", f);
CCLOG("double is %f", d);
CCLOG("string is %s", ret.c_str());
//输出XML文件路径
if( UserDefault->isXMLFileExist() ) //是否存在
{
string path = UserDefault->getXMLFilePath();
CCLOG("XML file is exist!");
CCLOG( "XML file path : %s", path.c_str() );
}
else
{
CCLOG("XML file is not exist!");
}
//保存数据
UserDefault->flush();
//4、运行结果
5、分析与总结
(1)不知道大家是否发现输出的结果有问题?float我设置的是33.33,为何输出的是33.330002。不是应该输出33.330000才对吗?
这个就要讲讲C++浮点数的精度问题了,float是单精度浮点数,而double是双精度浮点数。float的有效精度在6~7位,超过7位就可能会失真,就像上面的那个例子一样。而double的有效精度在15~16位,超过16位才会失真。
(2)getXMLFilePath()获取的XML文件路径为绝对路径。另外XML文件保存的路径为项目的Debug.win32中,说明XML文件是保存在应用程序所在目录下的。