一 .wtforms 前戏知识点和源码解析
https://blog.csdn.net/u011884100/article/details/88095304
https://www.jianshu.com/p/abcd051d45fc
1. 生成器 和面向对象
生成器函数 form对象为什么可以被for循环? :变为可迭代对象。 class Foo(object): # def __iter__(self): # return iter([11,22,33]) def __iter__(self): yield 1 yield 2 yield 3 obj = Foo() for item in obj: print(item)
内成员
class Foo(object): x1 = 123 def func(self): pass print(dir(Foo)) """['__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__' , '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', 'func', 'x1'] """
__new__方法 - new方法的返回值决定对象到底是什么? class Bar(object): pass class Foo(object): def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): return "aaaa" obj = Foo() print(obj) # aaaa class Bar(object): pass class Foo(object): def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): return super(Foo,cls).__new__(cls,*args, **kwargs) obj = Foo() print(obj) # <__main__.Foo object at 0x000001CCE7048D68> class Bar(object): pass class Foo(object): def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): # return super(Foo,cls).__new__(cls,*args, **kwargs) return Bar() obj = Foo() print(obj) <__main__.Bar object at 0x0000022BBAFD8978> class Bar(object): def __init__(self,cls): self.cls = cls class Foo(object): def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): # return super(Foo,cls).__new__(cls,*args, **kwargs) return Bar(cls) obj = Foo() print(obj) # <__main__.Bar object at 0x000001C73DD78DA0>
类创建的两种方式 class Foo(object): a1 = 123 def func(self): return "AAA" obj=Foo() Foo = type("Foo",(object,),{'a1':123,'func':lambda self:666}) cc=Foo() # 自定义type # 注意:metaclass作用是指定当前类由谁来创建。 class MyType(type): pass class Foo(object,metaclass=MyType): a1 = 123 def func(self): return 666
metaclass
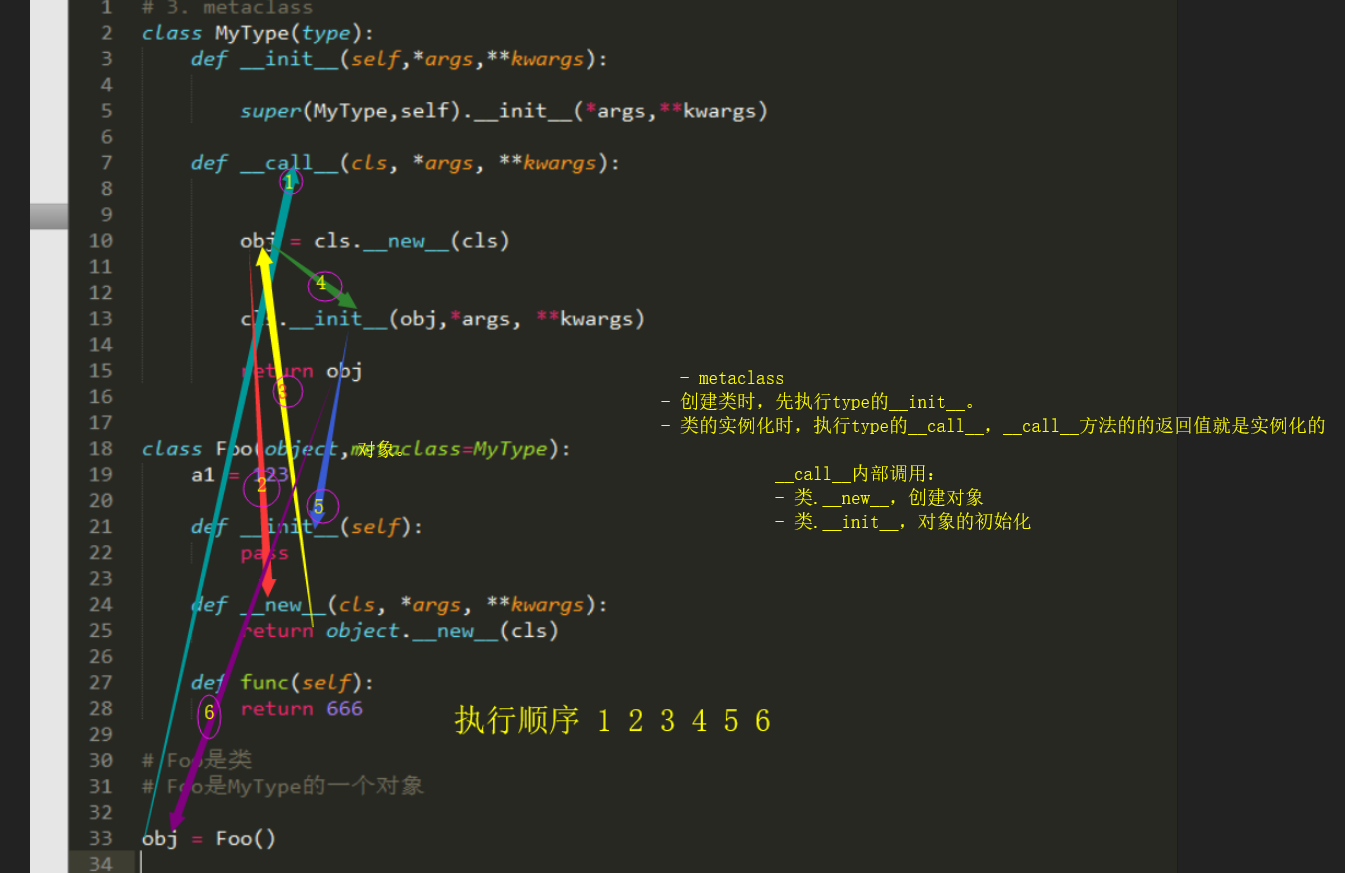
metaclass - 创建类时,先执行type的__init__。 - 类的实例化时,执行type的__call__,__call__方法的的返回值就是实例化的对象。 __call__内部调用: - 类.__new__,创建对象 - 类.__init__,对象的初始化
class MyType(type): def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): super(MyType,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs) def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs): obj = cls.__new__(cls) cls.__init__(obj,*args, **kwargs) return obj class Foo(object,metaclass=MyType): a1 = 123 def __init__(self): pass def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): return object.__new__(cls) def func(self): return 666 # Foo是类 # Foo是MyType的一个对象 obj = Foo() print(obj) # <__main__.Foo object at 0x000002668D98EEB8>
2. wtforms 源码解析
实例化流程分析 1. 执行type的 __call__ 方法,读取字段到静态字段 cls._unbound_fields 中; meta类读取到cls._wtforms_meta中 2. 执行构造方法 a. 循环cls._unbound_fields中的字段,并执行字段的bind方法,然后将返回值添加到 self._fields[name] 中。 即: _fields = { name: wtforms.fields.core.StringField(), } PS:由于字段中的__new__方法,实例化时:name = simple.StringField(label='用户名'),创建的是UnboundField(cls, *args, **kwargs),当执行完bind之后,才变成执行 wtforms.fields.core.StringField() b. 循环_fields,为对象设置属性 for name, field in iteritems(self._fields): # Set all the fields to attributes so that they obscure the class # attributes with the same names. setattr(self, name, field) c. 执行process,为字段设置默认值:self.process(formdata, obj, data=data, **kwargs) 优先级:obj,data,formdata; 再循环执行每个字段的process方法,为每个字段设置值: for name, field, in iteritems(self._fields): if obj is not None and hasattr(obj, name): field.process(formdata, getattr(obj, name)) elif name in kwargs: field.process(formdata, kwargs[name]) else: field.process(formdata) 执行每个字段的process方法,为字段的data和字段的raw_data赋值 def process(self, formdata, data=unset_value): self.process_errors = [] if data is unset_value: try: data = self.default() except TypeError: data = self.default self.object_data = data try: self.process_data(data) except ValueError as e: self.process_errors.append(e.args[0]) if formdata: try: if self.name in formdata: self.raw_data = formdata.getlist(self.name) else: self.raw_data = [] self.process_formdata(self.raw_data) except ValueError as e: self.process_errors.append(e.args[0]) try: for filter in self.filters: self.data = filter(self.data) except ValueError as e: self.process_errors.append(e.args[0]) d. 页面上执行print(form.name) 时,打印标签 因为执行了: 字段的 __str__ 方法 字符的 __call__ 方法 self.meta.render_field(self, kwargs) def render_field(self, field, render_kw): other_kw = getattr(field, 'render_kw', None) if other_kw is not None: render_kw = dict(other_kw, **render_kw) return field.widget(field, **render_kw) 执行字段的插件对象的 __call__ 方法,返回标签字符串
验证流程分析 a. 执行form的validate方法,获取钩子方法 def validate(self): extra = {} for name in self._fields: inline = getattr(self.__class__, 'validate_%s' % name, None) if inline is not None: extra[name] = [inline] return super(Form, self).validate(extra) b. 循环每一个字段,执行字段的 validate 方法进行校验(参数传递了钩子函数) def validate(self, extra_validators=None): self._errors = None success = True for name, field in iteritems(self._fields): if extra_validators is not None and name in extra_validators: extra = extra_validators[name] else: extra = tuple() if not field.validate(self, extra): success = False return success c. 每个字段进行验证时候 字段的pre_validate 【预留的扩展】 字段的_run_validation_chain,对正则和字段的钩子函数进行校验 字段的post_validate【预留的扩展】