【转】http://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/6123307.html
话不多说,直接上代码:
package com.cdms.aop.aspectImpl;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 创建 by 草帽boy on 2017/4/1.
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class ICacheAopAction {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.cdms.aop.ICache)")
private void controllerAspect(){}
@Before("controllerAspect()")
public void Before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String classname = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs());
System.out.println("@before Execute! --class name: " + classname + ", method name: " + methodName + " " + args );
}
@Around("controllerAspect()")
public Object Around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("@Around:执行目标方法之前...");
Object obj= proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("@Around:执行目标方法之后...");
System.out.println("@Around:被织入的目标对象为:" + proceedingJoinPoint.getTarget());
System.out.println( "@Around:原返回值:" + obj + ",这是返回结果的后缀");
return obj;
}
@AfterThrowing("controllerAspect()")
public void AfterThrowing(){
System.out.println("异常通知....");
}
@After("controllerAspect()")
public void After(JoinPoint point){
System.out.println("@After:模拟释放资源...");
System.out.println("@After:目标方法为:" +
point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() +
"." + point.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("@After:参数为:" + Arrays.toString(point.getArgs()));
System.out.println("@After:被织入的目标对象为:" + point.getTarget());
}
@AfterReturning("controllerAspect()")
public void AfterReturning(JoinPoint point){
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:模拟日志记录功能...");
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:目标方法为:" +
point.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() +
"." + point.getSignature().getName());
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:参数为:" +
Arrays.toString(point.getArgs()));
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:返回值为:" );
System.out.println("@AfterReturning:被织入的目标对象为:" + point.getTarget());
}
}
测试的结果是:
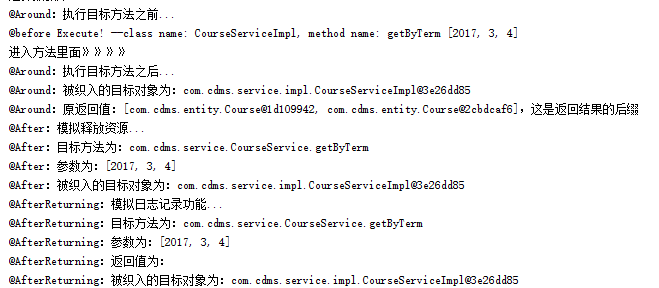
这样就很清楚的看出各种方法是在什么时候调用的啦