1.Collection 概述
Collection接口是集合中的顶层接口,那么它中定义的所有功能子类都可以使用
Collection 层次结构中的根接口。Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。
一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。
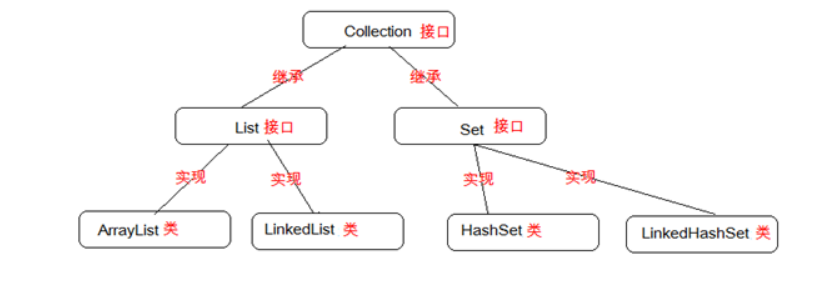
他的常用接口与实现类的继承关系如下图:
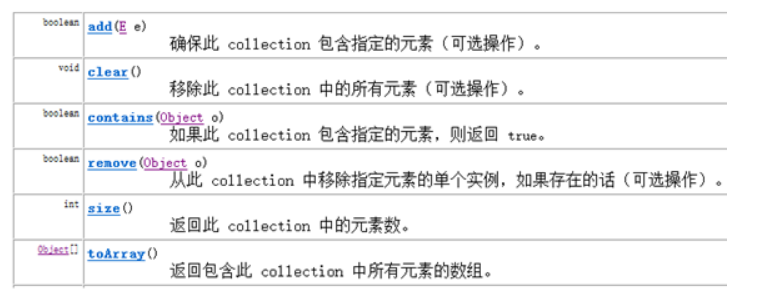
Collection接口的基本方法
Collection 的创建(以ArrayList为例)
public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<String>(); coll.add("a"); coll.add("b"); coll.add("c"); System.out.println(coll);// [a,b,c] coll.remove("b"); System.out.println(coll);// [a,b] System.out.println(coll.contains("c"));// true System.out.println(coll.contains("ab"));// false System.out.println(coll.size());// 2 String [] arr =coll.toArray(new String[0] ); for(String s :arr){ System.out.println(s); } //数组类型强转问题 a c }
这里涉及到一个数组类型强转的问题:
toArray()方法是返回一个Object类型的数组 如果要转为String 类型
String[] arr =(String[])coll.toArray() 这种方法是错误的
解决办法 :String [] arr = (String[])coll.toArray(new String[0]);
关于 toArray(T[] a)方法的描述:
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a)
- 返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型与指定数组的运行时类型相同。如果指定的数组能容纳该 collection,则返回包含此 collection 元素的数组。否则,将分配一个具有指定数组的运行时类型和此 collection 大小的新数组。
如果指定的数组能容纳 collection,并有剩余空间(即数组的元素比 collection 的元素多),那么会将数组中紧接 collection 尾部的元素设置为 null。(只有 在调用者知道此 collection 没有包含任何 null 元素时才能用此方法确定 collection 的长度。)