一.什么是异常
本质就是程序上的错误,包含编译期间和运行期间的错误。在程序运行过程中,意外发生的情况,背离我们程序的意图的表现,都可以理解为异常。
二.异常分类
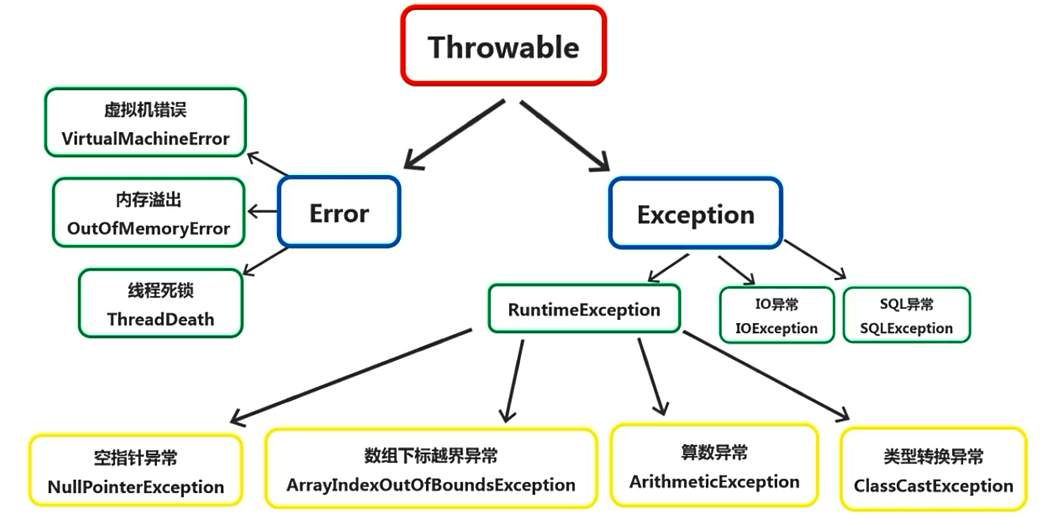
注:Throwable是Java异常的根类,Error和Exception是Throwable的子类;
Error是程序无法处理的错误,表示运行程序中较严重的问题,它们在应用程序控制和处理范围之外,而且绝大多数是程序运行时不允许出现的状况(是处理不到的),对于设计合理的应用程序,即使确实发生了错误,本质也不应该试图去处理它所引起的异常状况;
Exception是程序本身可以处理的异常。异常处理通常指针对这种类型异常处理,包括非检查异常(编译器不要求强制处理的异常)【包括RuntimeException及其相关子类】和检查异常(编译器要求处理的异常)【包括IO异常,SQL异常等】
Python异常结构(对比):
1 BaseException # 所有异常的基类 2 +-- SystemExit # 解释器请求退出 3 +-- KeyboardInterrupt # 用户中断执行(通常是输入^C) 4 +-- GeneratorExit # 生成器(generator)发生异常来通知退出 5 +-- Exception # 常规异常的基类 6 +-- StopIteration # 迭代器没有更多的值 7 +-- StopAsyncIteration # 必须通过异步迭代器对象的__anext__()方法引发以停止迭代 8 +-- ArithmeticError # 各种算术错误引发的内置异常的基类 9 | +-- FloatingPointError # 浮点计算错误 10 | +-- OverflowError # 数值运算结果太大无法表示 11 | +-- ZeroDivisionError # 除(或取模)零 (所有数据类型) 12 +-- AssertionError # 当assert语句失败时引发 13 +-- AttributeError # 属性引用或赋值失败 14 +-- BufferError # 无法执行与缓冲区相关的操作时引发 15 +-- EOFError # 当input()函数在没有读取任何数据的情况下达到文件结束条件(EOF)时引发 16 +-- ImportError # 导入模块/对象失败 17 | +-- ModuleNotFoundError # 无法找到模块或在在sys.modules中找到None 18 +-- LookupError # 映射或序列上使用的键或索引无效时引发的异常的基类 19 | +-- IndexError # 序列中没有此索引(index) 20 | +-- KeyError # 映射中没有这个键 21 +-- MemoryError # 内存溢出错误(对于Python 解释器不是致命的) 22 +-- NameError # 未声明/初始化对象 (没有属性) 23 | +-- UnboundLocalError # 访问未初始化的本地变量 24 +-- OSError # 操作系统错误,EnvironmentError,IOError,WindowsError,socket.error,select.error和mmap.error已合并到OSError中,构造函数可能返回子类 25 | +-- BlockingIOError # 操作将阻塞对象(e.g. socket)设置为非阻塞操作 26 | +-- ChildProcessError # 在子进程上的操作失败 27 | +-- ConnectionError # 与连接相关的异常的基类 28 | | +-- BrokenPipeError # 另一端关闭时尝试写入管道或试图在已关闭写入的套接字上写入 29 | | +-- ConnectionAbortedError # 连接尝试被对等方中止 30 | | +-- ConnectionRefusedError # 连接尝试被对等方拒绝 31 | | +-- ConnectionResetError # 连接由对等方重置 32 | +-- FileExistsError # 创建已存在的文件或目录 33 | +-- FileNotFoundError # 请求不存在的文件或目录 34 | +-- InterruptedError # 系统调用被输入信号中断 35 | +-- IsADirectoryError # 在目录上请求文件操作(例如 os.remove()) 36 | +-- NotADirectoryError # 在不是目录的事物上请求目录操作(例如 os.listdir()) 37 | +-- PermissionError # 尝试在没有足够访问权限的情况下运行操作 38 | +-- ProcessLookupError # 给定进程不存在 39 | +-- TimeoutError # 系统函数在系统级别超时 40 +-- ReferenceError # weakref.proxy()函数创建的弱引用试图访问已经垃圾回收了的对象 41 +-- RuntimeError # 在检测到不属于任何其他类别的错误时触发 42 | +-- NotImplementedError # 在用户定义的基类中,抽象方法要求派生类重写该方法或者正在开发的类指示仍然需要添加实际实现 43 | +-- RecursionError # 解释器检测到超出最大递归深度 44 +-- SyntaxError # Python 语法错误 45 | +-- IndentationError # 缩进错误 46 | +-- TabError # Tab和空格混用 47 +-- SystemError # 解释器发现内部错误 48 +-- TypeError # 操作或函数应用于不适当类型的对象 49 +-- ValueError # 操作或函数接收到具有正确类型但值不合适的参数 50 | +-- UnicodeError # 发生与Unicode相关的编码或解码错误 51 | +-- UnicodeDecodeError # Unicode解码错误 52 | +-- UnicodeEncodeError # Unicode编码错误 53 | +-- UnicodeTranslateError # Unicode转码错误 54 +-- Warning # 警告的基类 55 +-- DeprecationWarning # 有关已弃用功能的警告的基类 56 +-- PendingDeprecationWarning # 有关不推荐使用功能的警告的基类 57 +-- RuntimeWarning # 有关可疑的运行时行为的警告的基类 58 +-- SyntaxWarning # 关于可疑语法警告的基类 59 +-- UserWarning # 用户代码生成警告的基类 60 +-- FutureWarning # 有关已弃用功能的警告的基类 61 +-- ImportWarning # 关于模块导入时可能出错的警告的基类 62 +-- UnicodeWarning # 与Unicode相关的警告的基类 63 +-- BytesWarning # 与bytes和bytearray相关的警告的基类 64 +-- ResourceWarning # 与资源使用相关的警告的基类。被默认警告过滤器忽略
三.异常处理分类
Java应用处理程序中,异常处理机制为抛出异常(会创建异常对象【包含异常类型,异常出现的程序状态等】),捕获异常【寻找相关的处理器进行处理,找不到对应的程序就停止了】,和很多语言都相同(如C#,Python等),而有的语言是使用状态码,如C。
对于Java而言,对于运行时异常,错误或可排查异常,Java技术要求的异常处理方式有所不同,它规定:1.对于可查异常必须捕捉,或者声明抛出;2.允许忽略不可查的RuntimeException(含子类)和Error(含子类)。
通过5个关键字来实现:try,catch,finally,throw,throws
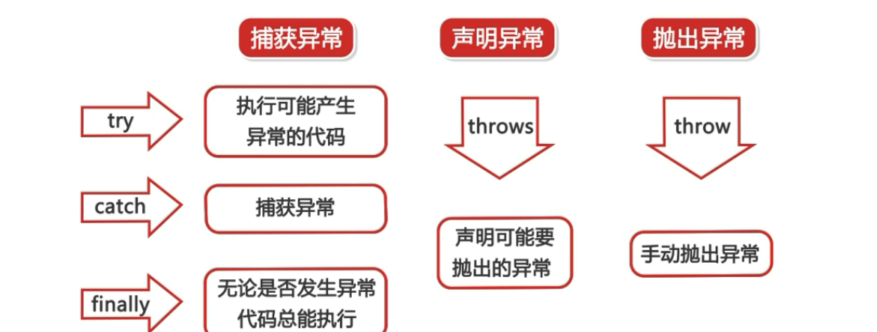
try块后面可接多个或零个catch块,如果没有catch块,则必须跟一个finally块。
例:

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class TryTest { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 System.out.println("===运算开始==="); 10 try { 11 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 12 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 13 int one = s.nextInt(); 14 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 15 int two = s.nextInt(); 16 System.out.println("两数之差是:" + one / two); 17 } 18 // 创建异常对象 19 catch (Exception e) { 20 System.out.println("程序出错了!!!"); 21 // 打印异常信息 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } finally { 24 System.out.println("===运算结束==="); 25 } 26 27 } 28 29 }

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.InputMismatchException; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 6 public class TryTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 System.out.println("===运算开始==="); 11 try { 12 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 13 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 14 int one = s.nextInt(); 15 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 16 int two = s.nextInt(); 17 System.out.println("两数之差是:" + one / two); 18 } 19 catch(ArithmeticException e){ 20 System.out.println("除数不能不0"); 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 23 } 24 catch (InputMismatchException e){ 25 System.out.println("请输入整数"); 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 28 } 29 catch (Exception e) { 30 System.out.println("其他错误"); 31 // 打印异常信息 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } finally { 34 System.out.println("===运算结束==="); 35 } 36 37 } 38 39 }
终止finally:
System.out()终止程序运行。


1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.InputMismatchException; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 6 public class TryTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 System.out.println("===运算开始==="); 11 try { 12 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 13 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 14 int one = s.nextInt(); 15 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 16 int two = s.nextInt(); 17 System.out.println("两数之差是:" + one / two); 18 } 19 catch(ArithmeticException e){ 20 //终止程序运行,如果运行到这儿不会往下运行 21 System.exit(1); 22 System.out.println("除数不能不0"); 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 25 } 26 catch (InputMismatchException e){ 27 System.out.println("请输入整数"); 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 30 } 31 catch (Exception e) { 32 System.out.println("其他错误"); 33 // 打印异常信息 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } finally { 36 System.out.println("===运算结束==="); 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 }
return关键字在异常处理中的使用:
由于finally的强制执行,所以不过try和catch中的return返回什么,只要finally中有返回值,最终返回的都是finally中的return值【不推荐使用】。

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.InputMismatchException; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 6 public class TryTest { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 int result=test(); 11 System.out.println("两数之差是:" + result); 12 13 14 } 15 public static int test(){ 16 System.out.println("===运算开始==="); 17 try { 18 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 19 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 20 int one = s.nextInt(); 21 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 22 int two = s.nextInt(); 23 return one/two; 24 } 25 catch(ArithmeticException e){ 26 //终止程序运行,如果运行到这儿不会往下运行 27 System.out.println("除数不能不0"); 28 return 0; 29 30 31 } 32 finally { 33 /* 34 * 无论输入什么,返回值都是finally中的返回值 35 */ 36 System.out.println("===运算结束==="); 37 return -1000; 38 } 39 } 40 41 }
四.throw和throws
通过throws声明要抛出何种类型的异常,通过throw将产生的异常抛出。
1.throws:
throws语句用在方法定义时s声明该方法要抛出的异常类型;
当方法抛出异常列表中的异常时,方法将不对这些类型及其子类类型的异常作处理,而抛向调用该方法的方法,由它去处理。

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.InputMismatchException; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 6 public class TryTestTwo { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 //如果直接接Exception,则必须处理Exception的异常,前面也可以分多个分别处理 10 try { 11 int result=test(); 12 System.out.println("one/two="+result); 13 } catch (InputMismatchException e) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 15 System.out.println("请输入整数"); 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } catch (ArithmeticException e) { 18 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 19 System.out.println("整数不能为0"); 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 23 } 24 /* 25 * 通过throws抛出异常时,针对可能出现的多种情况,解决方案: 26 * 1.throws后面接多个异常类型,中间用逗号分离; 27 * 2.直接接父类Exception 28 */ 29 30 //注:ArithmeticException, InputMismatchException是非检查异常,不强制处理,可以利用文档注释提示 31 /** 32 * 抛出异常 33 * @return 两个数字的商 34 * @throws ArithmeticException 35 * @throws InputMismatchException 36 */ 37 public static int test() throws ArithmeticException, InputMismatchException { 38 System.out.println("===运算开始==="); 39 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 40 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 41 int one = s.nextInt(); 42 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 43 int two = s.nextInt(); 44 System.out.println("===运算结束==="); 45 return one/two; 46 47 } 48 /* 49 public static int test() throws Exception{ 50 System.out.println("===运算开始==="); 51 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 52 System.out.print("请输入第一个数:"); 53 int one = s.nextInt(); 54 System.out.print("请输入第二个数:"); 55 int two = s.nextInt(); 56 System.out.println("===运算结束==="); 57 return one/two; 58 59 } 60 */ 61 62 63 }
2.throw:
throw抛出的只能是可抛出类Throwable或者其子类的实例对象。
当子类重写父类抛出异常的方法时,声明的异常必须是父类方法所声明异常的同类或子类。

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 4 public class SubTest extends FatherTest { 5 @Override 6 public void test() throws RuntimeException { 7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 8 //super.test(); 9 } 10 }
主动抛出异常作用:
规避可能出现的风险;完成一些程序的逻辑。
主动抛出异常方法:
1.自己抛出自己处理(通过try...catch包含throw语句--自己抛自己处理):

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class TryTestTree { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 test(); 8 } 9 10 public static void test() { 11 12 try { 13 System.out.print("输入年龄:"); 14 Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); 15 int age = s.nextInt(); 16 if (age <= 18 || age >= 80) { 17 //抛出特定的异常 18 throw new Exception("必须有朋友家人陪伴!"); 19 } else { 20 System.out.println("入住成功!"); 21 } 22 } catch (Exception e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 28 }
2.向上抛出异常(通过throws在方法声明处抛出异常类型--谁调用谁处理--调用者可以自己处理或者继续向上抛出异常):
注:此时可以抛出与throw对象相同的类型或者其父类

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class TryTestTree { 6 public static void main(String[] args){ 7 try { 8 //在这儿处理异常 9 test(); 10 } catch (Exception e) { 11 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 15 } 16 public static void test() throws Exception{ 17 Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in); 18 int age =s.nextInt(); 19 if (age<=18 || age>=80){ 20 throw new Exception("必须有朋友家人陪伴!"); 21 } 22 else{ 23 System.out.println("入住成功!"); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
3.自定义异常:
自己定义一个类去继承Throwable类或者它的子类去处理特定事务的异常。
4.异常链:
把异常发生得原因一个传一个串起来,即把低层的异常信息传给上层,这样逐层抛出。
由于新抛出得异常而导致异常丢失:

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 public class TryTestFive { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 try { 6 testThree(); 7 } catch (Exception e) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } 11 } 12 public static void testOne() throws HotelException { 13 throw new HotelException(); 14 } 15 16 public static void testTwo() throws Exception { 17 try { 18 testOne(); 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 throw new Exception("异常1"); 21 } 22 } 23 24 public static void testThree() throws Exception { 25 try { 26 testTwo(); 27 } catch (Exception e) { 28 throw new Exception("异常2"); 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 /* 33 * 输出:(由于新抛出异常而导致异常信息丢失) 34 * java.lang.Exception: 异常2 35 at com.swpu.test.TryTestFive.testThree(TryTestFive.java:28) 36 at com.swpu.test.TryTestFive.main(TryTestFive.java:6) 37 */
通过加参数或者通过initCause()方法解决异常丢失:

1 package com.swpu.test; 2 3 public class TryTestFive { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 try { 6 testThree(); 7 } catch (Exception e) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } 11 } 12 public static void testOne() throws HotelException { 13 throw new HotelException(); 14 } 15 16 public static void testTwo() throws Exception { 17 try { 18 testOne(); 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 //throw new Exception("异常1",e); 21 Exception e2=new Exception("异常2"); 22 e2.initCause(e); 23 throw e2; 24 } 25 } 26 27 public static void testThree() throws Exception { 28 try { 29 testTwo(); 30 } catch (Exception e) { 31 //1.throw new Exception("异常2",e); 32 //2. 33 Exception e1=new Exception("异常2"); 34 e1.initCause(e); 35 throw e1; 36 } 37 } 38 }
注(Python中的异常处理)
1.使用关键字try,exccept,else(无异常时执行完try会执行else),finally(最后都要执行);
2.Python中利用traceback模块打印详异常信息;

1 # _*_ encoding:utf-8 _*_ 2 __author__ = 'LYQ' 3 __date__ = '2019/4/24 16:44' 4 import traceback 5 try: 6 print("哈哈") 7 raise KeyError 8 except KeyError: 9 print("发生KeyError错误") 10 #输出异常详细信息 11 traceback.print_exc() 12 else: 13 print("如果没错我也要执行") 14 finally: 15 print("无论有无异常,我最后都要执行")
3.return关键字和Java中一样,只要finally中有return值,不管try和except和else中return什么,最后都会返回finally中的值【不推荐使用return】;
4.Python通过raise关键字抛出异常;
5.Python中通过继承Exception自定义异常,而不是继承BaseException,如果继承BaseException,则KeyboardInterrupt和SystemExit会捕获不到。
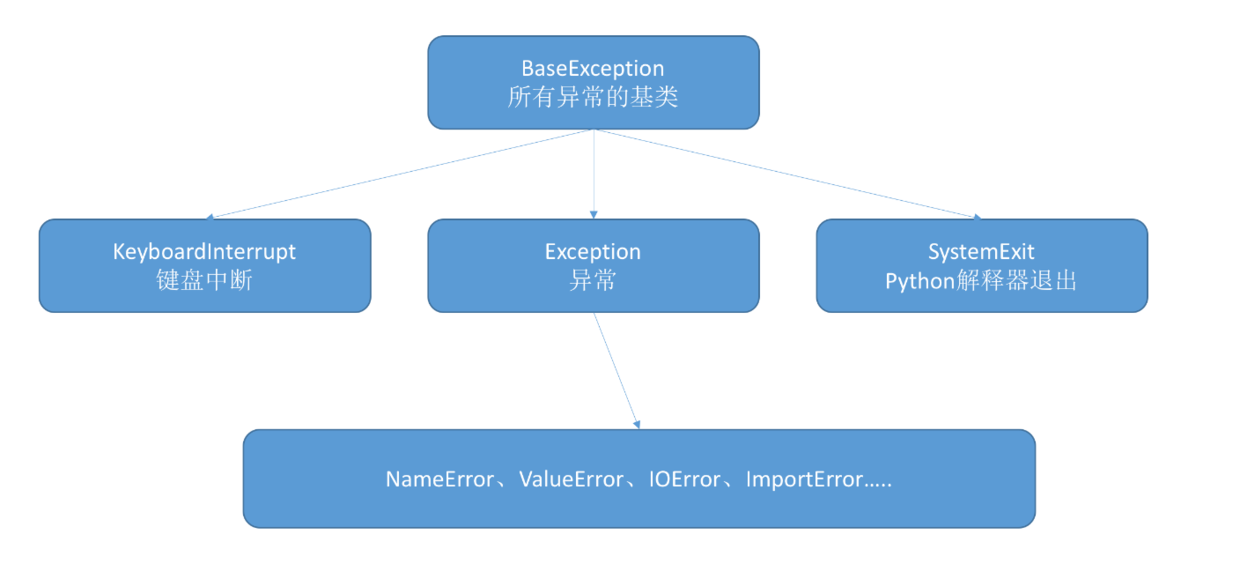
Python中异常继承树
