一般来说,利用复合键值对使用MR对键值对进行二次排序(MR默认只是对key排序,自定义的方式还对value排序就称为二次排序),需要做四件事:
1 定制复合键值对类型 2 定制分区类(对应job的setPartitionerClass方法) 3 定制排序比较器类(对应job的setSortComparatorClass方法) 4 定制分组比较类(对应job的setGroupingComparatorClass方法)
1)以下代码只是实现了第一点和第二点,也可以实现二次排序。
A.主类:keySort
1 package keySort; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 import java.io.File; 4 5 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 12 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 13 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat; 14 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 15 public class keySort { 16 public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, compositeKey, Text> { 17 private compositeKey comKey=new compositeKey(); 18 public void map(Text key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ 19 //System.out.println("key:"+key+"value:"+value); 20 //compositeKey.set(key.toString()+" "+value.toString()); 21 //System.out.println("compositekey:"+compositeKey+"value:"+value); 22 comKey.set(key, value); 23 context.write(comKey,value); 24 } 25 } 26 public static class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<compositeKey, Text>{ 27 //public Text realKey=new Text(); 28 @Override 29 public int getPartition(compositeKey key, Text value, int numredtasks) { 30 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 31 //String[] kk=key.toString().split(" "); 32 //realKey.set(kk[0]); 33 //System.out.println("partition key is:"+realKey.toString()); 34 return ((key.getNaturalKey()&Integer.MAX_VALUE)%numredtasks); 35 } 36 37 } 38 public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<compositeKey, Text, 39 Integer, Text>{ 40 @Override 41 public void reduce(compositeKey key,Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ 42 for (Text value : values) { 43 context.write(key.getNaturalKey(), value); 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 48 { 49 if(args.length!=2){ 50 System.err.println("Usage: MatrixMultiply <inputPathM> <inputPathN> <outputPath>"); 51 System.exit(2); 52 } 53 File outfile=new File(args[1]); 54 if(outfile.isDirectory()&&outfile.exists()){ 55 System.out.println("out exist?"+outfile.exists()); 56 File[] files=outfile.listFiles(); 57 for (File file : files) { 58 file.delete(); 59 } 60 outfile.delete(); 61 System.out.println("out exit?"+outfile.exists()); 62 } 63 else { 64 System.out.println("out do not exit"); 65 } 66 Configuration conf=new Configuration(); 67 Job job=new Job(conf,"SeconderySort"); 68 job.setNumReduceTasks(1);//设置为0的话,并不会执行分区过程,也就不能利用符合 69 job.setJarByClass(keySort.class); 70 job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class); 71 job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); 72 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(compositeKey.class); 73 job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); 74 job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class); 75 job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class); 76 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 77 job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); 78 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); 79 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); 80 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1); 81 } 82 }
B.自定义复合键值对类----compositeKey
1 package keySort; 2 import java.io.DataInput; 3 import java.io.DataOutput; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 8 import org.aspectj.weaver.patterns.ArgsAnnotationPointcut; 9 //接口Writable并没有使用泛型,但是接口Comparable<T>是泛型,其唯一的方法为: 10 //int compareTo(T o);所以compositeKey实现接口的时候使用了<compositeKey> 11 public class compositeKey implements WritableComparable<compositeKey>{ 12 private int naturalKey; 13 private int secondKey; 14 public void set(Text naturalkey,Text secondkey ) { 15 // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 16 this.naturalKey=Integer.parseInt(naturalkey.toString()); 17 this.secondKey=Integer.parseInt(secondkey.toString()); 18 } 19 public int getNaturalKey() { 20 return naturalKey; 21 } 22 @Override 23 //反序列化 24 public void readFields(DataInput arg0) throws IOException { 25 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 26 this.naturalKey=arg0.readInt(); 27 this.secondKey=arg0.readInt(); 28 29 } 30 @Override 31 //序列化 32 public void write(DataOutput arg0) throws IOException { 33 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 34 arg0.writeInt(naturalKey); 35 arg0.writeInt(secondKey); 36 } 37 @Override 38 public int compareTo(compositeKey o) { 39 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 40 int flag=this.naturalKey>o.naturalKey?1:(this.naturalKey==o.naturalKey?0:-1); 41 if(flag!=0) 42 return flag; 43 return this.secondKey>o.secondKey?1:(this.secondKey==o.secondKey?0:-1); 44 } 45 }
@Override就是覆盖的意思,表示在子类中重写父类中定义的方法,加上这个标示符可以使编译器在编译的时候帮我们检查是否与父类中的函数签名一致(函数名,参数个数,参数类型均相同)。
第11行可知,实现使用了泛型的接口的类,需要指定数据类型,并且在类中要实现接口中定义的所有方法(接口中的方法都是未实现的抽象方法),WritableComparable接口的定义如下:
public interface WritableComparable<T> extends Writable, Comparable<T> { }
所以,compositeKey实现此接口的时候形式如下,就是将T换为compositeKey:
public class compositeKey implements WritableComparable<compositeKey>{
C.所以,接口WritableComparable接口就只是继承了Writable接口和Comparable接口而已。
Writable用于对象的序列化和反序列化,所有需要序列化的类都需要继承这个接口,定义如下:
1 public interface Writable { 2 /** 3 * Serialize the fields of this object to <code>out</code>. 4 * 5 * @param out <code>DataOuput</code> to serialize this object into. 6 * @throws IOException 7 */ 8 void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException; 9 10 /** 11 * Deserialize the fields of this object from <code>in</code>. 12 * 13 * <p>For efficiency, implementations should attempt to re-use storage in the 14 * existing object where possible.</p> 15 * 16 * @param in <code>DataInput</code> to deseriablize this object from. 17 * @throws IOException 18 */ 19 void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException; 20 }
可见compositeKey需要实现write方法(序列化)和readFields(反序列化)方法,其具体实现是:
1 @Override 2 //反序列化 3 public void readFields(DataInput arg0) throws IOException { 4 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 5 this.naturalKey=arg0.readInt(); 6 this.secondKey=arg0.readInt(); 7 8 } 9 @Override 10 //序列化 11 public void write(DataOutput arg0) throws IOException { 12 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 13 arg0.writeInt(naturalKey); 14 arg0.writeInt(secondKey);
argo.readInt()表示序列化的是int型变量,字符串变量是.readUTF()。
而Comparable接口中只有一个方法:
int compareTo(T o);
所以,compositeKey还需要实现一个方法,就是compareTo方法:
1 @Override 2 public int compareTo(compositeKey o) { 3 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 4 int flag=this.naturalKey>o.naturalKey?1:(this.naturalKey==o.naturalKey?0:-1); 5 if(flag!=0) 6 return flag; 7 return this.secondKey>o.secondKey?1:(this.secondKey==o.secondKey?0:-1); 8 }
public class compositeKey implements WritableComparable<compositeKey>{
compositeKey实现接口的时候,使用的泛型就是对应着这里的compareTo方法。关于这个方法的返回值:首先调用形式是a.compareTo(o)
1,表示a大于o
0,表示两者相等
-1,表示a小于o
E:到这里,程序就可以顺利完成二次排序了,在map端排序的时候,会自动调用复合键值对定义的这个compareTo方法对复合键(compositeKey)排序。
结果如下:
排序前:
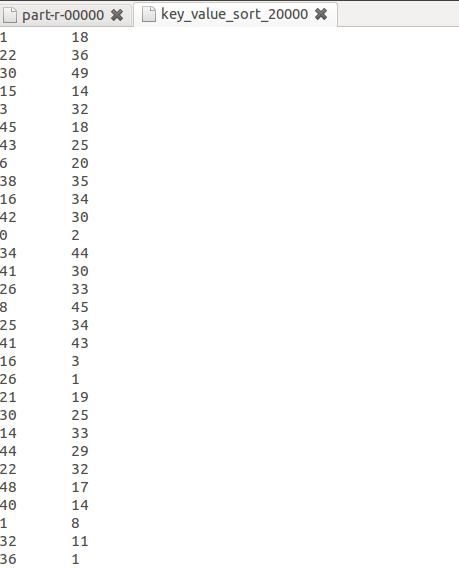
排序后:

2)以上是单机版,稍加修改为集群上跑得程序,并自动删除已存在的output目录:
keySort:
1 package keySort; 2 import java.io.IOException; 3 //import java.io.File; 4 5 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 12 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 13 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat; 14 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; 15 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 16 public class keySort { 17 public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<Text, Text, compositeKey, Text> { 18 private compositeKey comKey=new compositeKey(); 19 public void map(Text key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ 20 //System.out.println("key:"+key+"value:"+value); 21 //compositeKey.set(key.toString()+" "+value.toString()); 22 //System.out.println("compositekey:"+compositeKey+"value:"+value); 23 comKey.set(key, value); 24 context.write(comKey,value); 25 } 26 } 27 public static class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<compositeKey, Text>{ 28 //public Text realKey=new Text(); 29 @Override 30 public int getPartition(compositeKey key, Text value, int numredtasks) { 31 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 32 //String[] kk=key.toString().split(" "); 33 //realKey.set(kk[0]); 34 //System.out.println("partition key is:"+realKey.toString()); 35 return ((key.getNaturalKey()&Integer.MAX_VALUE)%numredtasks); 36 } 37 38 } 39 public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<compositeKey, Text, 40 Integer, Text>{ 41 private Text separator=new Text(); 42 @Override 43 protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException { 44 separator.set("-------------------------"); 45 context.write(null,separator); 46 47 }; 48 49 @Override 50 public void reduce(compositeKey key,Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{ 51 for (Text value : values) { 52 context.write(key.getNaturalKey(), value); 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception 57 { 58 if(args.length!=2){ 59 System.err.println("Usage: MatrixMultiply <inputPathM> <inputPathN> <outputPath>"); 60 System.exit(2); 61 } 62 /*本地运行时检测并删除输出文件夹 63 File outfile=new File(args[1]); 64 if(outfile.isDirectory()&&outfile.exists()){ 65 System.out.println("out exist?"+outfile.exists()); 66 File[] files=outfile.listFiles(); 67 for (File file : files) { 68 file.delete(); 69 } 70 outfile.delete(); 71 System.out.println("out exit?"+outfile.exists()); 72 } 73 else { 74 System.out.println("out do not exit"); 75 } 76 */ 77 Configuration conf=new Configuration(); 78 FileSystem hdfs=FileSystem.get(conf); 79 Path path=new Path(args[1]); 80 if(hdfs.exists(path)){ 81 hdfs.delete(path, true);//如果path是一个目录的话,true表示递归删除这个目录,如果path是文件的话,true 82 //或者false无所谓。另外FileSystem.delete(path)方法已废除。 83 System.out.println("output deleted!"); 84 } 85 else { 86 System.out.println("no output"); 87 } 88 Job job=new Job(conf,"SeconderySort"); 89 //job.setNumReduceTasks(1);//设置为0的话,并不会执行分区过程,也就不能利用符合 90 job.setJarByClass(keySort.class); 91 job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class); 92 job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); 93 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(compositeKey.class); 94 job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); 95 job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class); 96 job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class); 97 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 98 job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); 99 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); 100 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); 101 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true)?0:1); 102 } 103 }
compositeKey:
1 package keySort; 2 import java.io.DataInput; 3 import java.io.DataOutput; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 8 //接口Writable并没有使用泛型,但是接口Comparable<T>是泛型,其唯一的方法为: 9 //int compareTo(T o);所以compositeKey实现接口的时候使用了<compositeKey> 10 public class compositeKey implements WritableComparable<compositeKey>{ 11 private int naturalKey; 12 private int secondKey; 13 public void set(Text naturalkey,Text secondkey ) { 14 // TODO 自动生成的构造函数存根 15 this.naturalKey=Integer.parseInt(naturalkey.toString()); 16 this.secondKey=Integer.parseInt(secondkey.toString()); 17 } 18 public int getNaturalKey() { 19 return naturalKey; 20 } 21 @Override 22 //反序列化 23 public void readFields(DataInput arg0) throws IOException { 24 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 25 this.naturalKey=arg0.readInt(); 26 this.secondKey=arg0.readInt(); 27 28 } 29 @Override 30 //序列化 31 public void write(DataOutput arg0) throws IOException { 32 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 33 arg0.writeInt(naturalKey); 34 arg0.writeInt(secondKey); 35 } 36 @Override 37 public int compareTo(compositeKey o) { 38 // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 39 int flag=this.naturalKey>o.naturalKey?1:(this.naturalKey==o.naturalKey?0:-1); 40 if(flag!=0) 41 return flag; 42 return this.secondKey>o.secondKey?1:(this.secondKey==o.secondKey?0:-1); 43 } 44 }
原以为放在集群上跑,会造成每个reduce中顺序混乱,因为并没有定义分组比较类(setGroupingComparatorClass),目前认为没必要定义这个类,示例代码分析:
1 public class PersonNameComparator extends WritableComparator { 2 3 protected PersonNameComparator() { 4 super(Person.class, true); 5 } 6 7 @Override 8 public int compare(WritableComparable o1, WritableComparable o2) { 9 Person p1 = (Person) o1; 10 Person p2 = (Person) o2; 11 return p1.getLastName().compareTo(p2.getLastName()); 12 } 13 }
虽然是定义了分组排序的类,但是在排序函数compare内部还是调用了自定义的复合键类的方法compareTo方法。这个操作是在reduce端完成的。如下所述:
当reduce阶段将在本地磁盘上的map输出的记录进行流化处理(streaming)的时候,需要要进行分组。在分组中,记录将被按一定方式排成一个有逻辑顺序的流,并被传输给reduce。在分组阶段,所有的记录已经经过了次排序。
结果如下所示:
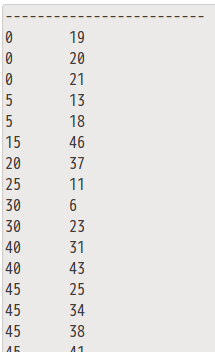
-------------------

-------------------------------------------------
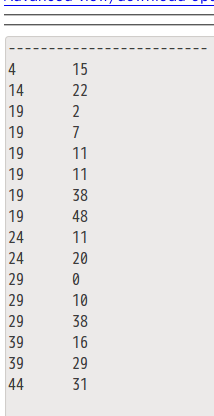
-------------------------------------
-
---------------------------------------------------

谢谢:
http://www.cnblogs.com/datacloud/p/3584640.html