在使用springmvc框架,会在web.xml文件配置一个DispatcherServlet,这正是web容器开始初始化,同时会在建立自己的上下文来持有SpringMVC的bean对象。
先从DispatcherServlet入手,从名字来看,它是一个Servlet。它的定义如下:
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
它是继承FrameworkServlet,来看一下整个的继承关系。
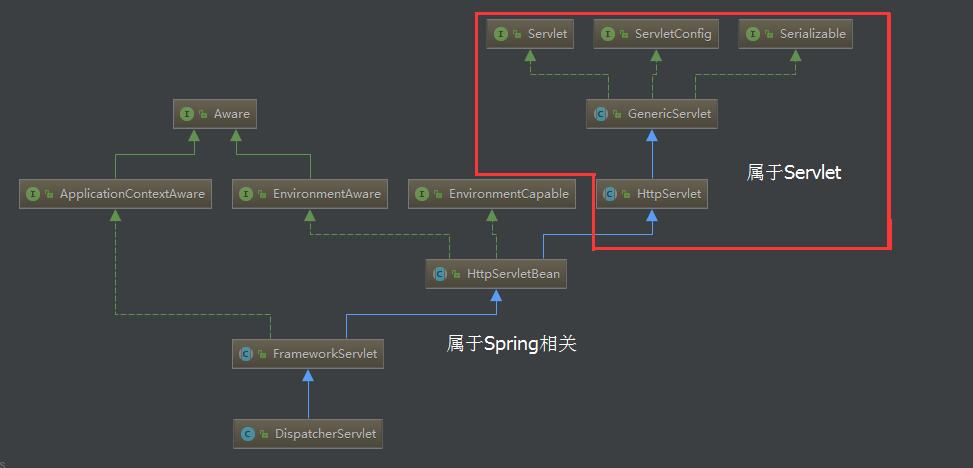
从继承关系来看,DispatcherServlet继承FrameworkServlet和HttpServletBean而继承HttpServlet,通过使用Servlet API 来对HTTP请求进行响应,成为SpringMVC的前端处理器。
先看一个时序图
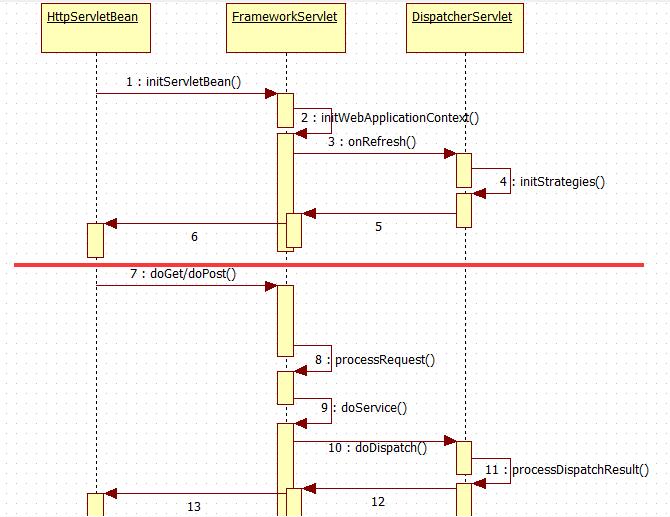
注:作为Servlet,DispatcherServlet的启动和Servlet的启动相关联的。在Servlet初始化过程中,Servlet的init方法会被调用,以进行初始化,然而DispatcherServlet的基类,所以从HttpServletBean中的初始化过程开始。
DispatcherServlet的工作分为2部分,一部分是初始化(也就是图的上半部分),有initServletBean()启动,通过initWebApplicationContext()方法最终调用DispatcherServlet中的initStrategies()方法。另一部分(也就是图的下半部分),是对HTTP请求进行响应,作为Servlet,Web容器会调用Servlet的doGet()和doPost()方法,在经过FrameworkServlet的processRequest()简单处理后,会调用DispatcherServlet的doService方法,在这个方法调用中封装了doDispatch(),继续调用processDispatchResult方法返回调用信息。
接下来看看初始化的源码的流程:
HttpServletBean.init方法
/**
* Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and
* invoke subclass initialization.
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
//获取Servlet初始化参数
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
try {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
//调用子类的方法
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
例如web.xml中配置参数:
<servlet>
<servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.lzyer.TestServlet</servlet-class>
<!--配置参数,可以通过ServletConfig获取参数-->
<init-param>
<param-name>servlet-name</param-name>
<param-value>TestServlet</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/TestServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
FrameworkServlet.initServletBean方法
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//创建Web应用上下文
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
FrameworkServlet.initWebApplicationContext()
/**
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
先看WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()),,主要是从ServletContext获取WebApplicationContext
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, String attrName) {
Assert.notNull(sc, "ServletContext must not be null");
//从ServletContext中获取
Object attr = sc.getAttribute(attrName);
if (attr == null) {
return null;
}
if (attr instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Exception) {
throw new IllegalStateException((Exception) attr);
}
if (!(attr instanceof WebApplicationContext)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Context attribute is not of type WebApplicationContext: " + attr);
}
return (WebApplicationContext) attr;
}
findWebApplicationContext和上面一样从ContextServlet中查找,如果不存在就调用下面的createWebApplicationContext方法。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
//获取contextClass
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//通过反射获取实例
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
//设置双亲上下文
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
//配置和刷新应用
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
看一下getContextClass()到底是哪个类? XmlWebApplicationContext.class
最后configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext调用refresh方法启动容器。
回到initWebApplicationContext方法中
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
这个会触发SpringMVC初始化策略
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
//映射关系
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
到此,SpringMVC的初始化的流程大概就是这样,下篇就是SpringMVC请求流程。