1.什么是二叉搜索树(BinarySearchTrees)
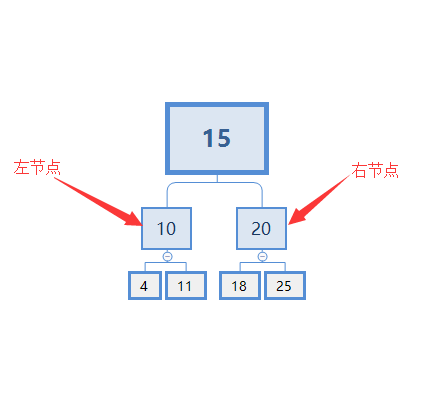
如下图所示:15为树的根节点,10为15的左节点,20为15的右节点,下面的节点如此类推。
每个父节点都有两个子节点(子节点可能为空),左子节点比父节点小,右子节点比父节点大。
2.二叉搜索树的各种功能
一、节点
每个节点应该含有两个子节点,一个可以进行比较的key(本文使用的是int)。节点可以根据需求来含有其它附属内容,本文为了方便测试,节点含有一个String和记录该节点下面共有多少个节点(包括自己)的Count。
节点实现:
UCLASS() class ALGORITHM_API ATreeNode : public AActor { GENERATED_BODY() public: // Sets default values for this actor's properties ATreeNode(); // Called every frame virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override; //设值 FORCEINLINE void SetValue(int Newkey, FString NewValue) { Key = Newkey; Value = NewValue; } FORCEINLINE ATreeNode* Get() { return this; } //获取或修改私有变量 FORCEINLINE int GetKey() { return Key; } FORCEINLINE void SetKey(int NewKey) { Key = NewKey; } FORCEINLINE int GetCount() { return Count; } FORCEINLINE void SetCount(int NewCount) { Count = NewCount; } FORCEINLINE FString GetValue() { return Value; } FORCEINLINE void SetValue(FString NewValue) { Value = NewValue; } FORCEINLINE ATreeNode* GetNode(bool Left) { if (Left) return LeftNode; return RightNode; } FORCEINLINE void SetNode(bool Left, ATreeNode* NewNode) { if (Left) LeftNode = NewNode; else { RightNode = NewNode; } } protected: // Called when the game starts or when spawned virtual void BeginPlay() override; private: int Key; FString Value; //左右节点 ATreeNode* LeftNode; ATreeNode* RightNode; //计算此节点下面共用多少个节点(包括自己) int Count; };
二、查找
如果想查找某个数字X,从根节点开始比较。如果X比根节点大,则去与根节点的右节点比较,如此类推,直到找到X(或子节点为空)为止。
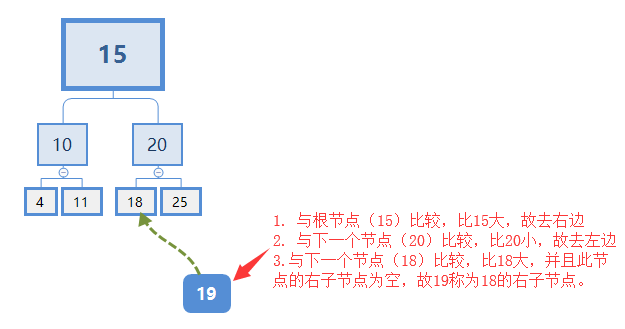
例如上图二叉搜索树中,如果想找25:
从根节点开始比较:25>15。去根节点右边,与下一个节点(20)比较,结果25>20。接着去右边,与下一个节点(25)比较,结果25=25,查找成功。
代码实现:
FString ABinarySearchTrees::GetValue(int InputKey) { ATreeNode* X = RootNode; while (X != nullptr) { //比较key的大小 int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果输入的key比X的小,去X的左边 if (Temp < 0) X = X->GetNode(true); //如果输入的key比X的大,去X的右边 else if (Temp > 0) X = X->GetNode(false); //如果相等,说明找到这个key了,输出Value else return X->GetValue(); } //如果X为空指针,说明找不到这个key return "NotFind"; }
三、插入新节点
如果新节点的key在树中已经存在,则把旧节点覆盖;如果没有,则插入。
与查找类似,设新节点的key为X,从根节点开始比较。如果X比根节点大,则去与根节点的右节点比较。如此类推,如果找到了某个节点的key与X相同,覆盖这个节点;如果没找到,则根据最后一次比较结果,插到最后一次比较的节点的左节点或右节点。
实现代码:
void ABinarySearchTrees::Put(int Newkey) { //每次插入前,都清空路线信息 RouteString = ""; //每次插入新节点都要更新根节点 RootNode = Put(RootNode, Newkey); RootNode->SetValue(": Root"); } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::Put(ATreeNode* X, int NewKey) { //如果X不存在,创造一个 if (!X) { ATreeNode* NewNode = GetWorld()->SpawnActor<ATreeNode>(ATreeNode::StaticClass()); NewNode->SetValue(NewKey, RouteString); //节点存起来,方便测试 NodeArray.Add(NewNode); //新节点自己算一个节点 NewNode->SetCount(1); return NewNode; } int Temp = CompareTo(NewKey, X->GetKey()); //如果要插入新节点,则新节点的所有父节点都要更新一次 if (Temp < 0) { RouteString.Append(": Left"); X->SetNode(true, Put(X->GetNode(true), NewKey)); } else if (Temp > 0) { RouteString.Append(": Right"); X->SetNode(false, Put(X->GetNode(false), NewKey)); } else { X->SetValue(RouteString); } //更新X节点的Count X->SetCount(1 + Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Size(X->GetNode(false))); return X; }
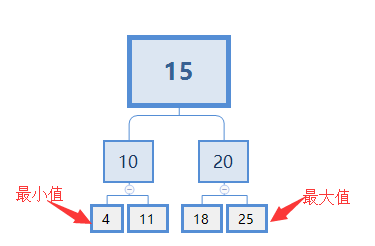
四、查找最小值、最大值
查找最小值:因为二叉搜索树中,左节点比父节点小,故最小值肯定在树的左下角。从根节点开始,判断它的左节点存不存在。如果存在,继续找这个左节点的左节点,如此类推,直到找到某个节点的左节点不存在时,此节点就是最小值。
查找最大值:因为二叉搜索树中,右节点比父节点大,故最大值肯定在树的右下角。从根节点开始,判断它的右节点存不存在。如果存在,继续找这个右节点的右节点,如此类推,直到找到某个节点的右节点不存在时,此节点就是最大值。
实现代码:
//寻找最小值 int ABinarySearchTrees::FindMin() { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindMin(RootNode); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } //寻找拥有最小值的节点 ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindMin(ATreeNode* X) { //当节点存在时 while (X) { //如果右节点存在,继续循环 if (X->GetNode(true)) { X = X->GetNode(true); } //如果右节点不存在,这个节点就是最小值 else { return X; } } return X; } int ABinarySearchTrees::FindMax() { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindMax(RootNode); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } //寻找拥有最大值的节点 ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindMax(ATreeNode* X) { //当节点存在时 while (X) { //如果右节点存在,继续循环 if (X->GetNode(false)) { X = X->GetNode(false); } //如果右节点不存在,这个节点就是最小值 else { return X; } } return X; }
五、给定一个key,寻找最接近它的节点
Floor:最接近此key,且小于等于它的节点。
Ceiling:最接近此key,且大于等于它的节点。
寻找Floor:从下面的例子中介绍思路
假设给定key为X,现有搜索树如下图
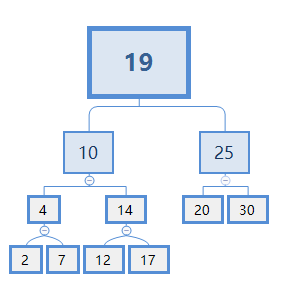
假设X=13:
1.从根节点开始比较,X比19小,去19节点的左边。
2.X>10,但由于最接近X的节点可能在10的右节点下面,故还需去10的右边继续找。
3.X<14, 去14的左边。
4.X>12,且12没子节点,故12就是X的Floor。
假设X=11:
1.从根节点开始比较,X比19小,去19节点的左边。
2.X>10,但由于最接近X的节点可能在10的右节点下面,故还需去10的右边继续找。
3.X<14, 去14的左边。
4.X<12,且12没左子节点,故10的右节点下面没有比X小的节点,10就是X的Floor。
思路:
1.X与根节点比较,如果X小,去根节点的左节点,继续比较,直到找到一个比X小的节点A为止。
2.去A节点的右节点找比X小的节点。如果找不到,A就是要找的节点;如果找到了,令此节点为B,判断B节点是否有右节点,如果有,重复步骤2;如果没有,B节点就是要找的节点。
寻找Ceiling的过程与Floor类似,在此不累赘。
实现代码:
//给定一个数字,寻找最接近它的key(比它小) int ABinarySearchTrees::FindFloor(int InputKey) { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindFloor(RootNode,InputKey); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindFloor(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey) { //如果X节点不存在,就别继续下去了 if (!X) return nullptr; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果存在节点的key与输入值相等,则这个节点就是最接近它了 if (Temp == 0) return X; //如果节点的key比较大,则去找它的左节点,直到找到小于等于输入值的节点为止 if (Temp < 0) return FindFloor(X->GetNode(true), InputKey); //如果节点的key比较小,则要找的节点可能在它的右节点的左端 ATreeNode* T = FindFloor(X->GetNode(false), InputKey); //如果找到了T,则说明找到了,返回T;如果找不到,说明X已经是最接近的了,返回X if (T) return T; else return X; } //给定一个数字,寻找最接近它的key(比它大) int ABinarySearchTrees::FindCeiling(int InputKey) { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindCeiling(RootNode, InputKey); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindCeiling(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey) { //如果X节点不存在,就别继续下去了 if (!X) return nullptr; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果存在节点的key与输入值相等,则这个节点就是最接近它了 if (Temp == 0) return X; //如果节点的key比较小,则去找它的右节点,直到找到大于等于输入值的节点为止 if (Temp > 0) return FindCeiling(X->GetNode(false), InputKey); //如果节点的key比较大,则要找的节点可能在它的左节点的左端 ATreeNode* T = FindCeiling(X->GetNode(true), InputKey); //如果找到了T,则说明找到了,返回T;如果找不到,说明X已经是最接近的了,返回X if (T) return T; else return X; }
六、给定一个keyX,求有多少个节点的key比X小(即求Rank(X))
这里就会用到节点里的Count了。这个Count记录了该节点下面共有多少个节点(包括自己)。
从例子介绍思路:
假设给定key为X,现有搜索树如下图
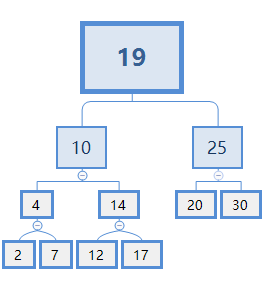
假设X=13,令根节点为A节点
1.从A节点开始比较,X比19小,去19节点的左边。
2.X>10,此时10和10左节点以下的所有节点都比X小,因为10的右节点下面可能还有节点比K小,所以还需要继续找,假设还有Y个节点在下面,则Rank(X)=1+4.Count+Y
3.X<14, 去14的左边。
4.X>12,且12没子节点,故Y=12.Count=1,Rank(X)=1+4.Count+Y=1+3+1=5。
思路:
令根节点为A节点
1. 从A节点开始比较:
如果X<A.key,则如果A的左节点存在,令A的左节点为A,重复步骤1;如果不存在,返回0;
如果X=A.key,则由于A的右节点下方都比A大,A的左节点下方都比A小,所以Rank(X)=A的左节点的Count;
如果X>A.key,则Rank(X)=1 + A的左节点的Count + A的右节点下方小于X的节点个数,进入步骤2。
2. 令A的右节点为A,重复步骤1。
3. 此循环结束后,便得到Rank(X)。
实现代码:
//求有多少个数字少于给定数字 int ABinarySearchTrees::Rank(int InputKey) { return Rank(InputKey, RootNode); } int ABinarySearchTrees::Rank(int InputKey, ATreeNode* X) { //如果节点不存在,返回0 if (!X) return 0; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果给定数字比X的key小,则去X的左边去找比给定数字小的数字 if (Temp < 0) return Rank(InputKey, X->GetNode(true)); //如果给定数字比X的key大,则X和X的左节点都比给定数字小,把它们算上后,去X的右节点找是否还有比给定数字小的数字 else if (Temp > 0) return 1 + Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Rank(InputKey, X->GetNode(false)); //因为右节点都比X大,而X的Key与给定数字相等,故比给定数字小的数字都在X的左节点里 else return Size(X->GetNode(true)); }
七、中序排列
通过对二叉搜索树进行中序排列,可以得到一个递增的有序数组。对某个节点进行中序排列就是先排此节点的左节点,再排这个节点,最后排此节点的右节点。
例如对下图的节点4进行中序排列:2,4,7。
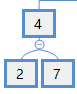
如果要对一个大节点排序,如下图:
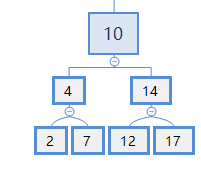
对节点10进行中序排列:需要先对节点4进行中序排列,然后排10,再对节点14进行中序排列
同样道理,对根节点排序(即整个二叉搜索树进行中序排列):
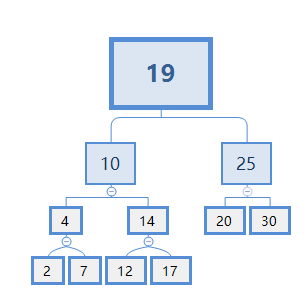
对节点19进行中序排列:需要先对节点10进行中序排列,然后排19,再对节点25进行中序排列
实现代码:
void ABinarySearchTrees::InorderTraversal() { OrderNodeArray.Empty(); Inorder(RootNode); } void ABinarySearchTrees::Inorder(ATreeNode* X) { if (!X) return; //先去加X的左节点 Inorder(X->GetNode(true)); //再加X OrderNodeArray.Add(X->GetKey()); //最后加X的右节点 Inorder(X->GetNode(false)); }
八、删除节点
要删除一个节点,可能会遇到3种情况:
A. 这个节点没子节点,此情况最为简单,直接删除这个节点即可。
B. 这个节点只有一个子节点,把这个子节点和这个节点的父节点相连,然后删除这个节点
C. 这个节点有两个子节点,此情况最为复杂,稍后讨论
举个例子:
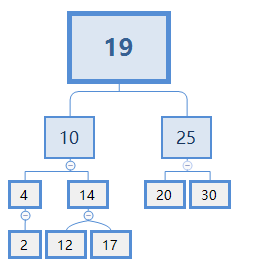
如果要删除节点2,则就是A情况,直接删除即可;
如果要删除节点4,则就是B情况,由于4节点是10节点的左节点,故把节点2放在节点10的左节点处,然后删除节点4。
如果要删除节点10,则就是C情况,首先,我们需要从节点10下面找一个节点X来代替它,如下图所示:
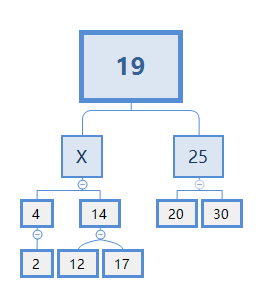
可以看出X肯定比4大,比14小。故X只能从14的下面去找。显然,在此例子中X=12。替代了后,我们当然需要把14的左节点删掉,替换效果:
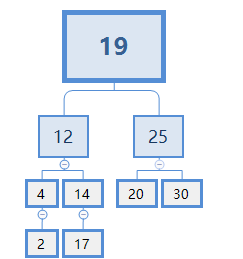
为了更直观的讨论,我们不妨将此树拓展一下:

删除节点10后:
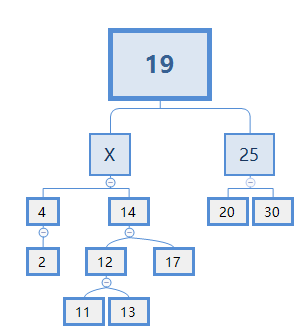
此时,X肯定比4大,比14小,X的候选者有11,12,13。
不能选12,因为12有两个节点,处理起来过于复杂,且会破坏二叉搜索树的结构
11可以选,处理起来最简单。
不能选13,因为如果X=13,就会破坏了二叉搜索树的结构,如下图:
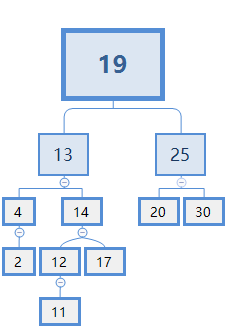
在二叉搜索树的结构中,父节点应该比它的右节点下面的所有节点都小。而此例子中,13>12>11。
选择11时,X=11,删除节点成功,如下图
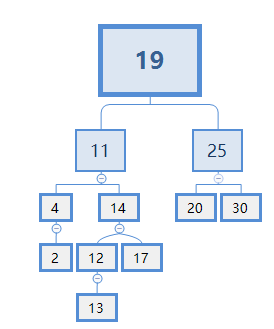
因此,回到情况C:这个节点有两个子节点,要删除它的操作是:
1. 从此节点的右节点下面找出最小的节点X。
2. 因为X节点是最小的,所以它的子节点数量肯定小于等于1个,把此子节点连到X的父节点上。
3. 然后用X节点替换要删除的节点。
4. 删除要删除的节点。
至于怎么删除最小节点,上面已经介绍了如何找到最小节点,要删除它只需在此基础上进行少量操作。
实现代码:
//删除最小的节点 void ABinarySearchTrees::DeleteMin() { RootNode = DeleteMin(RootNode); } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::DeleteMin(ATreeNode* X) { //如果X的左节点不存在,说明已经找到最小值了,删除它,返回它的右节点 if (!X->GetNode(true)) { ATreeNode* TempNode = X->GetNode(false); NodeArray.Remove(X); X->Destroy(); return TempNode; } //删除最小值后,把它的右节点和上一个节点连上 X->SetNode(true, DeleteMin(X->GetNode(true))); //更新节点数 X->SetCount(1 + Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Size(X->GetNode(false))); return X; } void ABinarySearchTrees::Delete(int InputKey) { RootNode = Delete(RootNode, InputKey); } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::Delete(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey) { if (!X) return nullptr; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //寻找要删除的节点,只要删了一个节点,它上面的所有节点都要更新一次,所以是SetNode if (Temp < 0) X->SetNode(true, Delete(X->GetNode(true), InputKey)); else if (Temp > 0) X->SetNode(false, Delete(X->GetNode(false), InputKey)); //找到要删除的节点了 else { //如果要删除的节点只有一个子节点或没有,那好办,只需把那个子节点替代它就好 if (!X->GetNode(false)) { ATreeNode* TempNode = X->GetNode(true); NodeArray.Remove(X); X->Destroy(); return TempNode; } if (!X->GetNode(true)) { ATreeNode* TempNode = X->GetNode(false); NodeArray.Remove(X); X->Destroy(); return TempNode; } //如果要删除的节点有两个个子节点,从它的右边找一个最小的节点来替代它 ATreeNode* T = X; X = FindMin(T->GetNode(false)); X->SetNode(false, DeleteMin(T->GetNode(false))); X->SetNode(true, T->GetNode(true)); NodeArray.Remove(T); T->Destroy(); } //更新节点数 X->SetCount(Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Size(X->GetNode(false)) + 1); return X; }
九、完整的全部代码
节点.h: UCLASS() class ALGORITHM_API ATreeNode : public AActor { GENERATED_BODY() public: // Sets default values for this actor's properties ATreeNode(); // Called every frame virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override; //设值 FORCEINLINE void SetValue(int Newkey, FString NewValue) { Key = Newkey; Value = NewValue; } FORCEINLINE ATreeNode* Get() { return this; } //获取或修改私有变量 FORCEINLINE int GetKey() { return Key; } FORCEINLINE void SetKey(int NewKey) { Key = NewKey; } FORCEINLINE int GetCount() { return Count; } FORCEINLINE void SetCount(int NewCount) { Count = NewCount; } FORCEINLINE FString GetValue() { return Value; } FORCEINLINE void SetValue(FString NewValue) { Value = NewValue; } FORCEINLINE ATreeNode* GetNode(bool Left) { if (Left) return LeftNode; return RightNode; } FORCEINLINE void SetNode(bool Left, ATreeNode* NewNode) { if (Left) LeftNode = NewNode; else { RightNode = NewNode; } } protected: // Called when the game starts or when spawned virtual void BeginPlay() override; private: int Key; FString Value; //左右节点 ATreeNode* LeftNode; ATreeNode* RightNode; //计算此节点下面共用多少个节点(包括自己) int Count; };
二叉搜索树.h: class ATreeNode; UCLASS() class ALGORITHM_API ABinarySearchTrees : public AActor { GENERATED_BODY() public: // Sets default values for this actor's properties ABinarySearchTrees(); // Called every frame virtual void Tick(float DeltaTime) override; //查值 FString GetValue(int InputKey); //某个key是否存在? bool Search(int InputKey); //插入一个节点 void Put(int Newkey); ATreeNode* Put(ATreeNode* X, int NewKey); //提供一个方法让TreeNode之间进行比较 //如果a大于b,返回1;如果a小于b,返回-1;如果相等,返回0 int CompareTo(int a, int b); //寻找最小值 int FindMin(); //寻找拥有最小值的节点 ATreeNode* FindMin(ATreeNode* X); //寻找最大值 int FindMax(); //寻找拥有最大值的节点 ATreeNode* FindMax(ATreeNode* X); //给定一个数字,寻找最接近它的key(比它小) int FindFloor(int InputKey); ATreeNode* FindFloor(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey); //给定一个数字,寻找最接近它的key(比它大) int FindCeiling(int InputKey); ATreeNode* FindCeiling(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey); //求有多少个数字少于给定数字 int Size(ATreeNode* X); int Rank(int InputKey); int Rank(int InputKey, ATreeNode* X); //中序遍历 void InorderTraversal(); void Inorder(ATreeNode* X); //删除最小值 void DeleteMin(); ATreeNode* DeleteMin(ATreeNode* X); //删除某个节点 void Delete(int InputKey); ATreeNode* Delete(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey); protected: // Called when the game starts or when spawned virtual void BeginPlay() override; public: private: //根节点 ATreeNode* RootNode; //节点数组 TArray<ATreeNode*> NodeArray; //把节点接过的路线记录下来,方便测试 FString RouteString; //把节点按中序遍历放进数组 TArray<int> OrderNodeArray; }; 二叉搜索树.cpp: // Sets default values ABinarySearchTrees::ABinarySearchTrees() { // Set this actor to call Tick() every frame. You can turn this off to improve performance if you don't need it. PrimaryActorTick.bCanEverTick = true; } // Called when the game starts or when spawned void ABinarySearchTrees::BeginPlay() { Super::BeginPlay(); FRandomStream Stream; Stream.GenerateNewSeed(); //生成节点 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { Put(Stream.RandRange(0, 100)); } Put(40); //测试二叉搜索树是否正确 for (int i = 0; i < NodeArray.Num(); i++) { UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, FString::FromInt(NodeArray[i]->GetKey())+ NodeArray[i]->GetValue()+" Count: "+ FString::FromInt(NodeArray[i]->GetCount())); } UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, FString::FromInt(Rank(49))); //测试搜索和查值功能 if (Search(40)) { UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, "Find 40: " + GetValue(40)); } //测试寻找最小值、最大值、Floor、Ceiling UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, "Min: " + FString::FromInt(FindMin()) + " Max: " + FString::FromInt(FindMax())); UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, "Floor of 50: " + FString::FromInt(FindFloor(50))); UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, "Ceiling of 50: " + FString::FromInt(FindCeiling(50))); //测试删除 Delete(40); //测试中序排序 InorderTraversal(); for (int i = 0; i < OrderNodeArray.Num(); i++) { UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, FString::FromInt(OrderNodeArray[i])); } for (int i = 0; i < NodeArray.Num(); i++) { if (!NodeArray[i]) return; UKismetSystemLibrary::PrintString(this, FString::FromInt(NodeArray[i]->GetKey()) + NodeArray[i]->GetValue() + " Count: " + FString::FromInt(NodeArray[i]->GetCount())); } } // Called every frame void ABinarySearchTrees::Tick(float DeltaTime) { Super::Tick(DeltaTime); } FString ABinarySearchTrees::GetValue(int InputKey) { ATreeNode* X = RootNode; while (X != nullptr) { //比较key的大小 int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果输入的key比X的小,去X的左边 if (Temp < 0) X = X->GetNode(true); //如果输入的key比X的大,去X的右边 else if (Temp > 0) X = X->GetNode(false); //如果相等,说明找到这个key了,输出Value else return X->GetValue(); } //如果X为空指针,说明找不到这个key return "NotFind"; } //某个key是否存在? bool ABinarySearchTrees::Search(int InputKey) { ATreeNode* X = RootNode; while (X != nullptr) { //比较key的大小 int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果输入的key比X的小,去X的左边 if (Temp < 0) X = X->GetNode(true); //如果输入的key比X的大,去X的右边 else if (Temp > 0) X = X->GetNode(false); //如果相等,说明找到这个key了 else return true; } //如果X为空指针,说明找不到这个key return false; } void ABinarySearchTrees::Put(int Newkey) { //每次插入前,都清空路线信息 RouteString = ""; //每次插入新节点都要更新根节点 RootNode = Put(RootNode, Newkey); RootNode->SetValue(": Root"); } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::Put(ATreeNode* X, int NewKey) { //如果X不存在,创造一个 if (!X) { ATreeNode* NewNode = GetWorld()->SpawnActor<ATreeNode>(ATreeNode::StaticClass()); NewNode->SetValue(NewKey, RouteString); //节点存起来,方便测试 NodeArray.Add(NewNode); //新节点自己算一个节点 NewNode->SetCount(1); return NewNode; } int Temp = CompareTo(NewKey, X->GetKey()); //如果要插入新节点,则新节点的所有父节点都要更新一次 if (Temp < 0) { RouteString.Append(": Left"); X->SetNode(true, Put(X->GetNode(true), NewKey)); } else if (Temp > 0) { RouteString.Append(": Right"); X->SetNode(false, Put(X->GetNode(false), NewKey)); } else { X->SetValue(RouteString); } //更新X节点的Count X->SetCount(1 + Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Size(X->GetNode(false))); return X; } //如果a大于b,返回1;如果a小于b,返回-1;如果相等,返回0 int ABinarySearchTrees::CompareTo(int a, int b) { if (a > b) { return 1; } else if (a < b) { return -1; } else { return 0; } } //寻找最小值 int ABinarySearchTrees::FindMin() { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindMin(RootNode); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } //寻找拥有最小值的节点 ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindMin(ATreeNode* X) { //当节点存在时 while (X) { //如果左节点存在,继续循环 if (X->GetNode(true)) { X = X->GetNode(true); } //如果右节点不存在,这个节点就是最小值 else { return X; } } return X; } int ABinarySearchTrees::FindMax() { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindMax(RootNode); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } //寻找拥有最大值的节点 ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindMax(ATreeNode* X) { //当节点存在时 while (X) { //如果右节点存在,继续循环 if (X->GetNode(false)) { X = X->GetNode(false); } //如果右节点不存在,这个节点就是最小值 else { return X; } } return X; } //给定一个数字,寻找最接近它的key(比它小) int ABinarySearchTrees::FindFloor(int InputKey) { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindFloor(RootNode,InputKey); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindFloor(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey) { //如果X节点不存在,就别继续下去了 if (!X) return nullptr; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果存在节点的key与输入值相等,则这个节点就是最接近它了 if (Temp == 0) return X; //如果节点的key比较大,则去找它的左节点,直到找到小于等于输入值的节点为止 if (Temp < 0) return FindFloor(X->GetNode(true), InputKey); //如果节点的key比较小,则要找的节点可能在它的右节点的左端 ATreeNode* T = FindFloor(X->GetNode(false), InputKey); //如果找到了T,则说明找到了,返回T;如果找不到,说明X已经是最接近的了,返回X if (T) return T; else return X; } //给定一个数字,寻找最接近它的key(比它大) int ABinarySearchTrees::FindCeiling(int InputKey) { //从根节点开始比较 ATreeNode* X = FindCeiling(RootNode, InputKey); if (X) return X->GetKey(); return 0; } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::FindCeiling(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey) { //如果X节点不存在,就别继续下去了 if (!X) return nullptr; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果存在节点的key与输入值相等,则这个节点就是最接近它了 if (Temp == 0) return X; //如果节点的key比较小,则去找它的右节点,直到找到大于等于输入值的节点为止 if (Temp > 0) return FindCeiling(X->GetNode(false), InputKey); //如果节点的key比较大,则要找的节点可能在它的左节点的左端 ATreeNode* T = FindCeiling(X->GetNode(true), InputKey); //如果找到了T,则说明找到了,返回T;如果找不到,说明X已经是最接近的了,返回X if (T) return T; else return X; } int ABinarySearchTrees::Size(ATreeNode* X) { //如果节点不存在,返回0 if (!X) return 0; //如果节点存在,返回Count return X->GetCount(); } //求有多少个数字少于给定数字 int ABinarySearchTrees::Rank(int InputKey) { return Rank(InputKey, RootNode); } int ABinarySearchTrees::Rank(int InputKey, ATreeNode* X) { //如果节点不存在,返回0 if (!X) return 0; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //如果给定数字比X的key小,则去X的左边去找比给定数字小的数字 if (Temp < 0) return Rank(InputKey, X->GetNode(true)); //如果给定数字比X的key大,则X和X的左节点都比给定数字小,把它们算上后,去X的右节点找是否还有比给定数字小的数字 else if (Temp > 0) return 1 + Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Rank(InputKey, X->GetNode(false)); //因为右节点都比X大,而X的Key与给定数字相等,故比给定数字小的数字都在X的左节点里 else return Size(X->GetNode(true)); } void ABinarySearchTrees::InorderTraversal() { OrderNodeArray.Empty(); Inorder(RootNode); } void ABinarySearchTrees::Inorder(ATreeNode* X) { if (!X) return; //先去加X的左节点 Inorder(X->GetNode(true)); //再加X OrderNodeArray.Add(X->GetKey()); //最后加X的右节点 Inorder(X->GetNode(false)); } //删除最小的节点 void ABinarySearchTrees::DeleteMin() { RootNode = DeleteMin(RootNode); } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::DeleteMin(ATreeNode* X) { //如果X的左节点不存在,说明已经找到最小值了,删除它,返回它的右节点 if (!X->GetNode(true)) { ATreeNode* TempNode = X->GetNode(false); NodeArray.Remove(X); X->Destroy(); return TempNode; } //删除最小值后,把它的右节点和上一个节点连上 X->SetNode(true, DeleteMin(X->GetNode(true))); //更新节点数 X->SetCount(1 + Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Size(X->GetNode(false))); return X; } void ABinarySearchTrees::Delete(int InputKey) { RootNode = Delete(RootNode, InputKey); } ATreeNode* ABinarySearchTrees::Delete(ATreeNode* X, int InputKey) { if (!X) return nullptr; int Temp = CompareTo(InputKey, X->GetKey()); //寻找要删除的节点,只要删了一个节点,它上面的所有节点都要更新一次,所以是SetNode if (Temp < 0) X->SetNode(true, Delete(X->GetNode(true), InputKey)); else if (Temp > 0) X->SetNode(false, Delete(X->GetNode(false), InputKey)); //找到要删除的节点了 else { //如果要删除的节点只有一个子节点或没有,那好办,只需把那个子节点替代它就好 if (!X->GetNode(false)) { ATreeNode* TempNode = X->GetNode(true); NodeArray.Remove(X); X->Destroy(); return TempNode; } if (!X->GetNode(true)) { ATreeNode* TempNode = X->GetNode(false); NodeArray.Remove(X); X->Destroy(); return TempNode; } //如果要删除的节点有两个个子节点,从它的右边找一个最小的节点来替代它 ATreeNode* T = X; X = FindMin(T->GetNode(false)); X->SetNode(false, DeleteMin(T->GetNode(false))); X->SetNode(true, T->GetNode(true)); NodeArray.Remove(T); T->Destroy(); } //更新节点数 X->SetCount(Size(X->GetNode(true)) + Size(X->GetNode(false)) + 1); return X; }