
第0步. 什么是self-attention?
原文链接: Transformer 一篇就够了(一): Self-attenstion
接下来,我们将要解释和实现self-attention的全过程。
- 准备输入
- 初始化参数
- 获取key,query和value
- 给input1计算attention score
- 计算softmax
- 给value乘上score
- 给value加权求和获取output1
- 重复步骤4-7,获取output2,output3
import torch
第1步: 准备输入
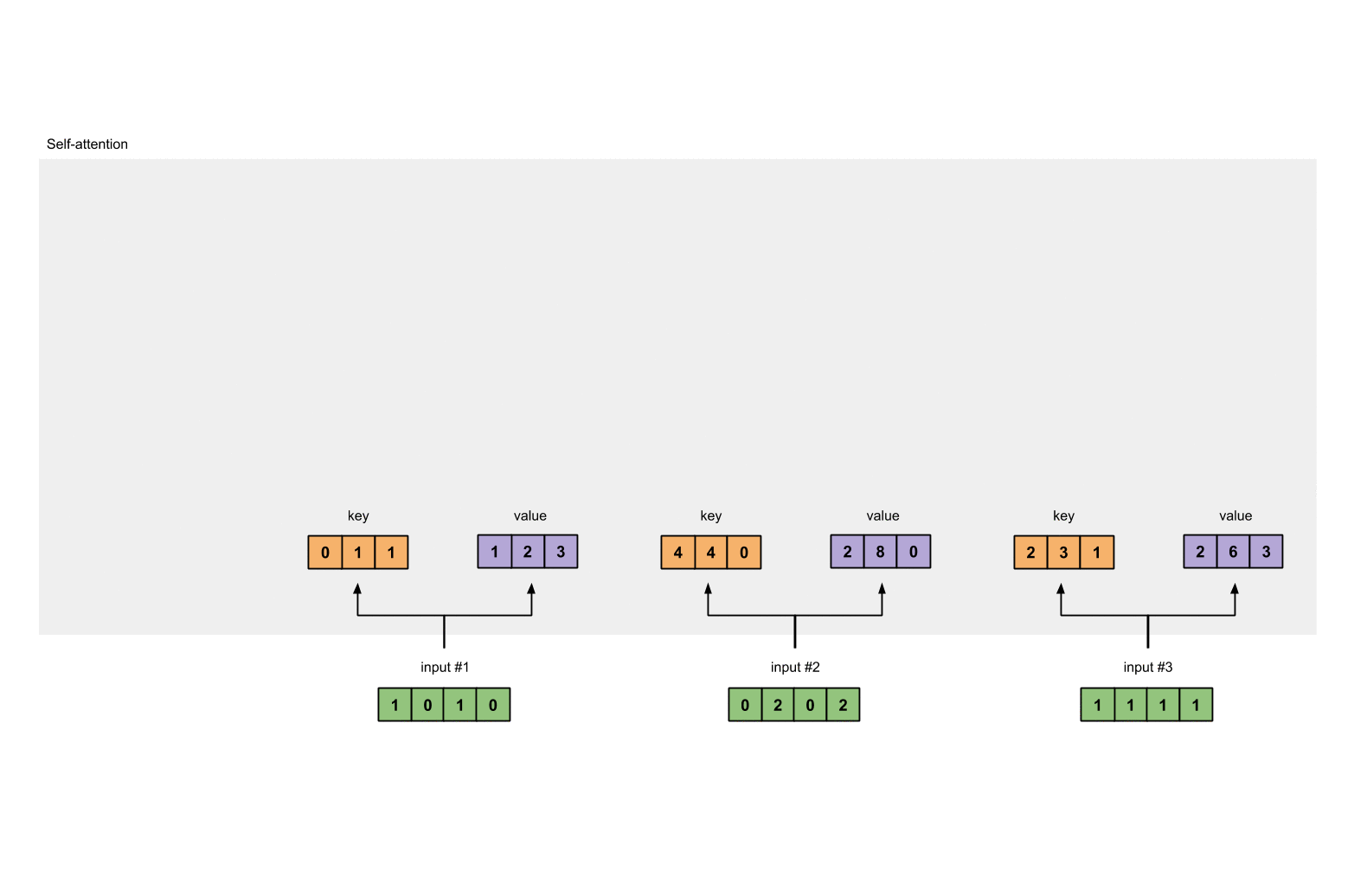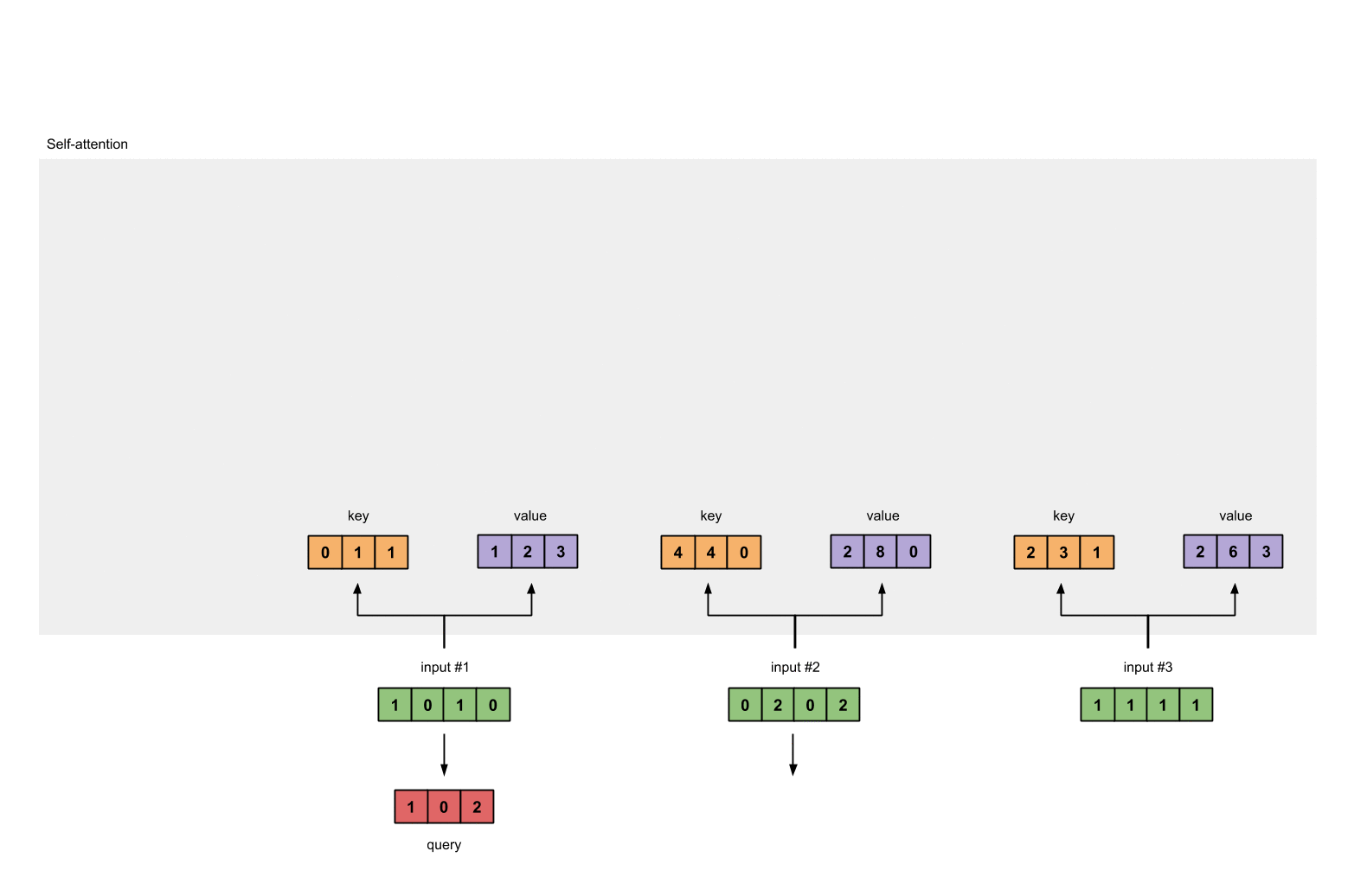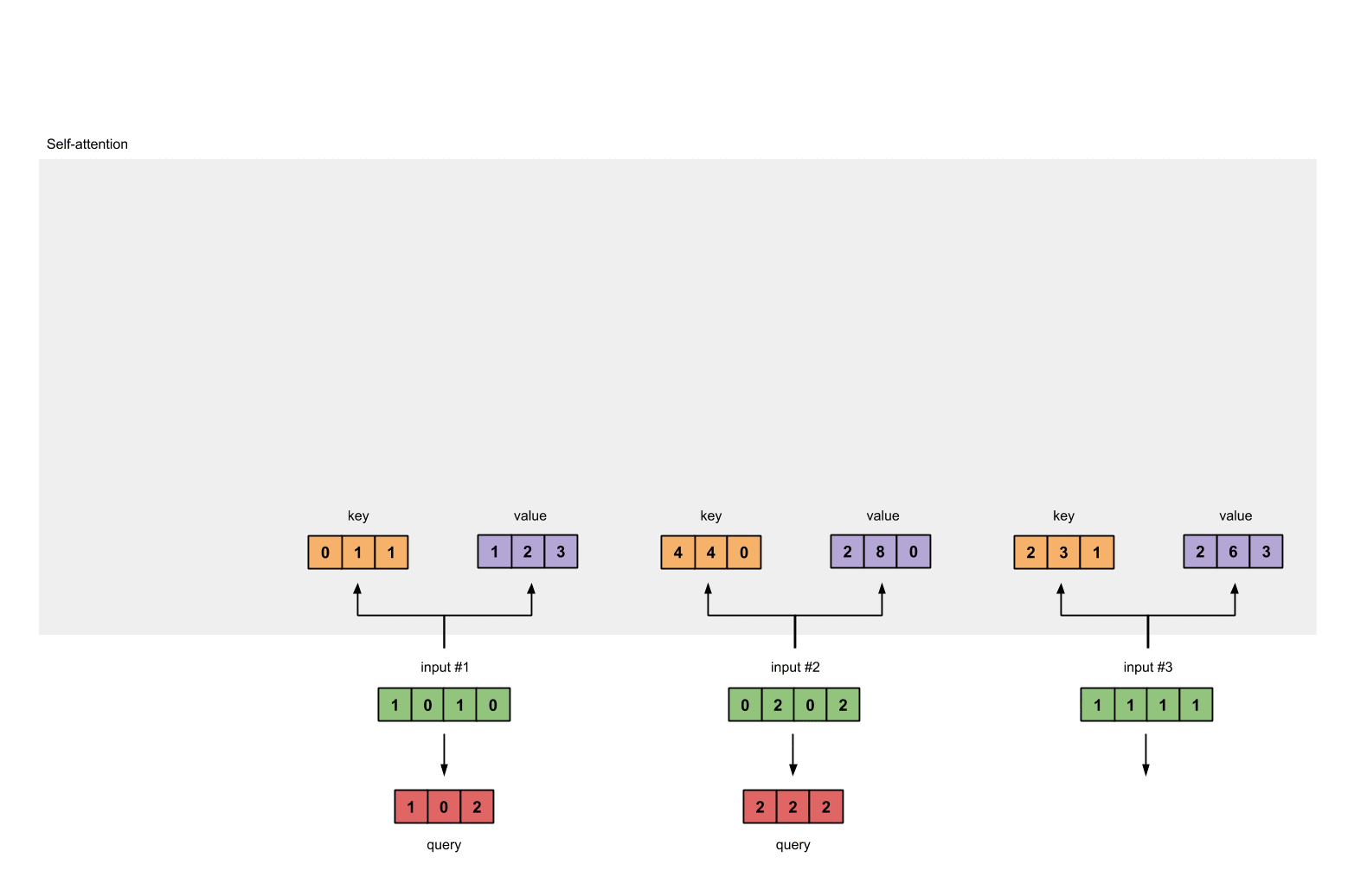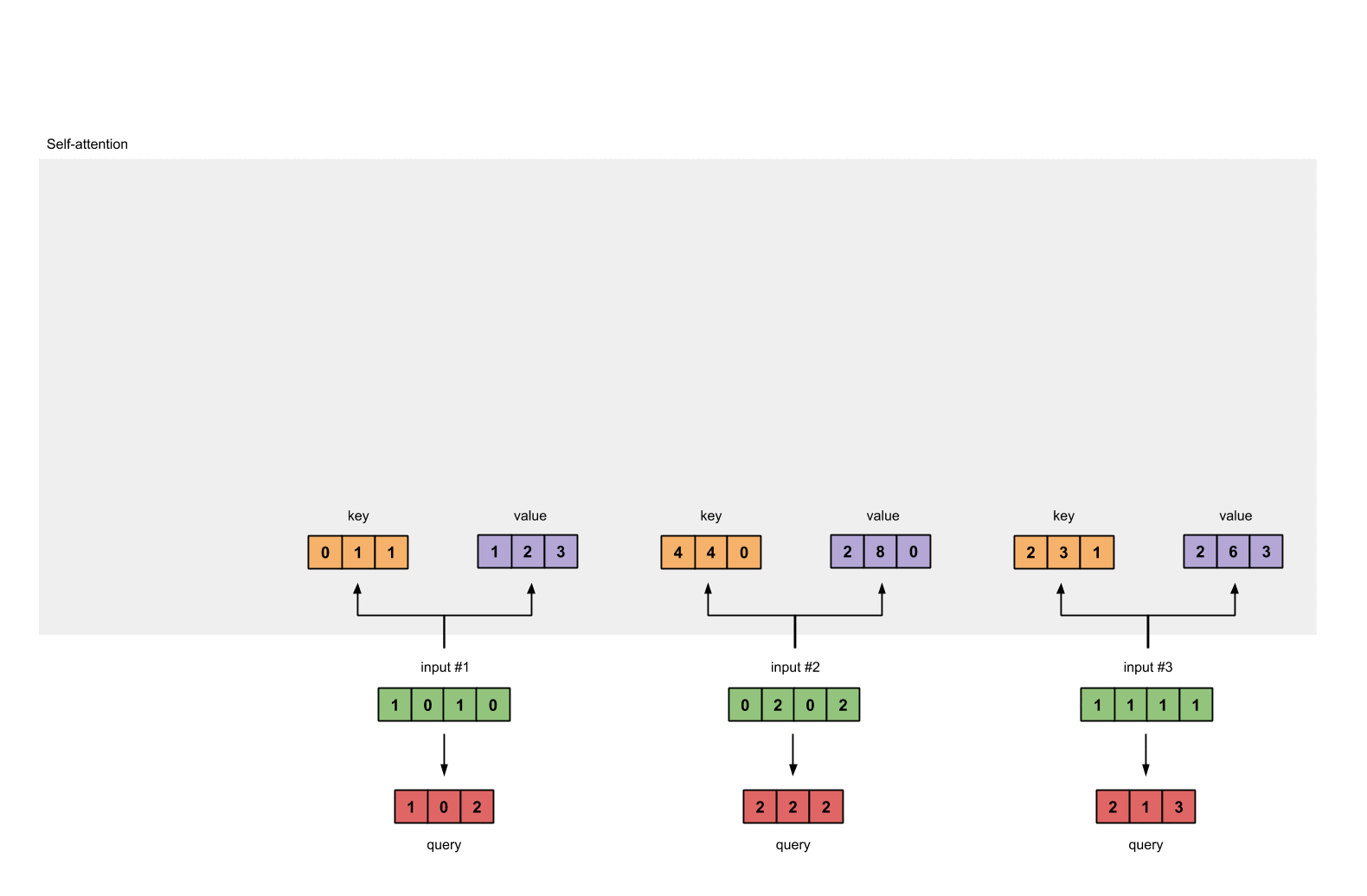
为了简单起见,我们使用3个输入,每个输入都是一个4维的向量。
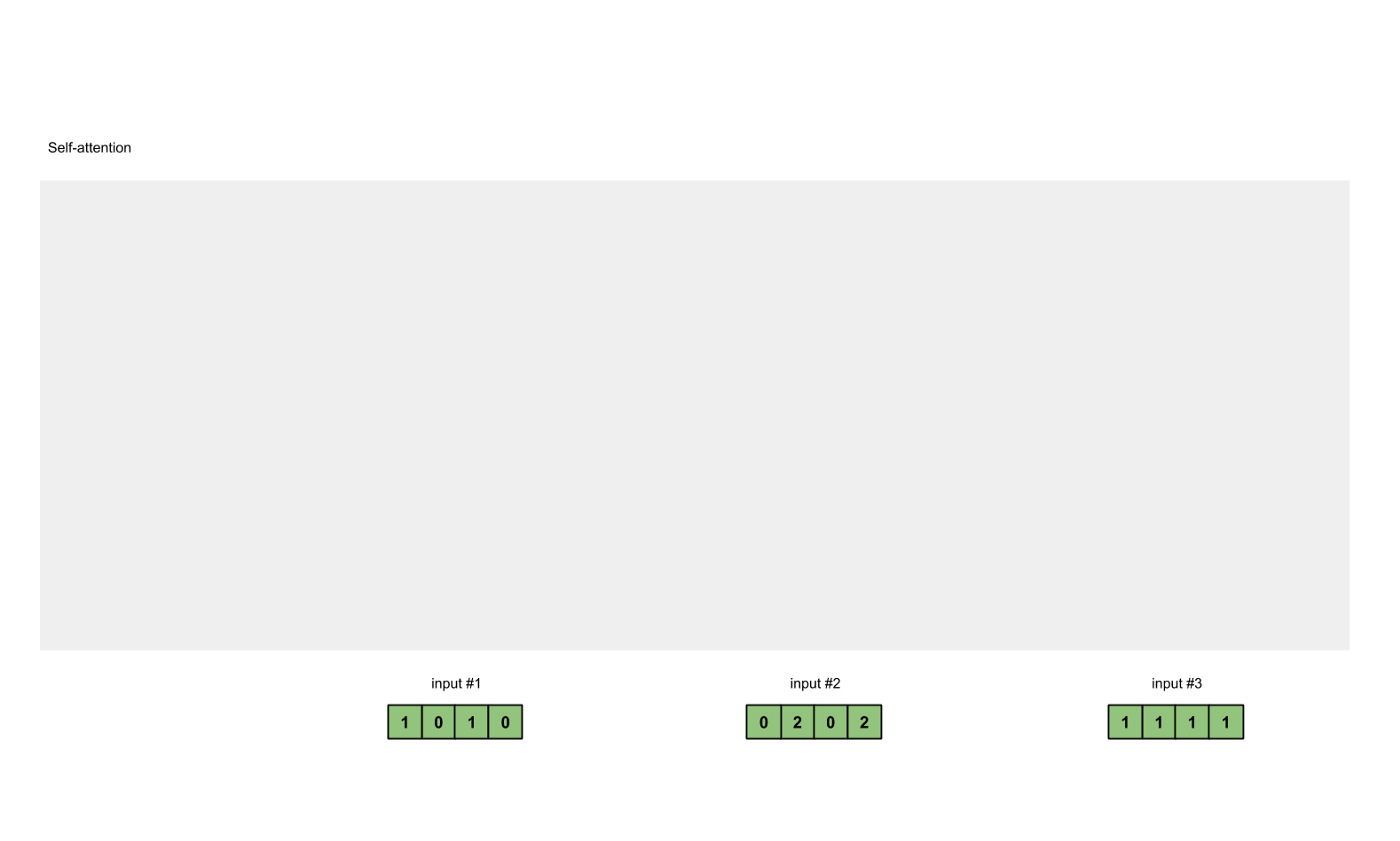
x = [
[1, 0, 1, 0], # Input 1
[0, 2, 0, 2], # Input 2
[1, 1, 1, 1] # Input 3
]
x = torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float32)
x
tensor([[1., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 2., 0., 2.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
第2步: 初始化参数
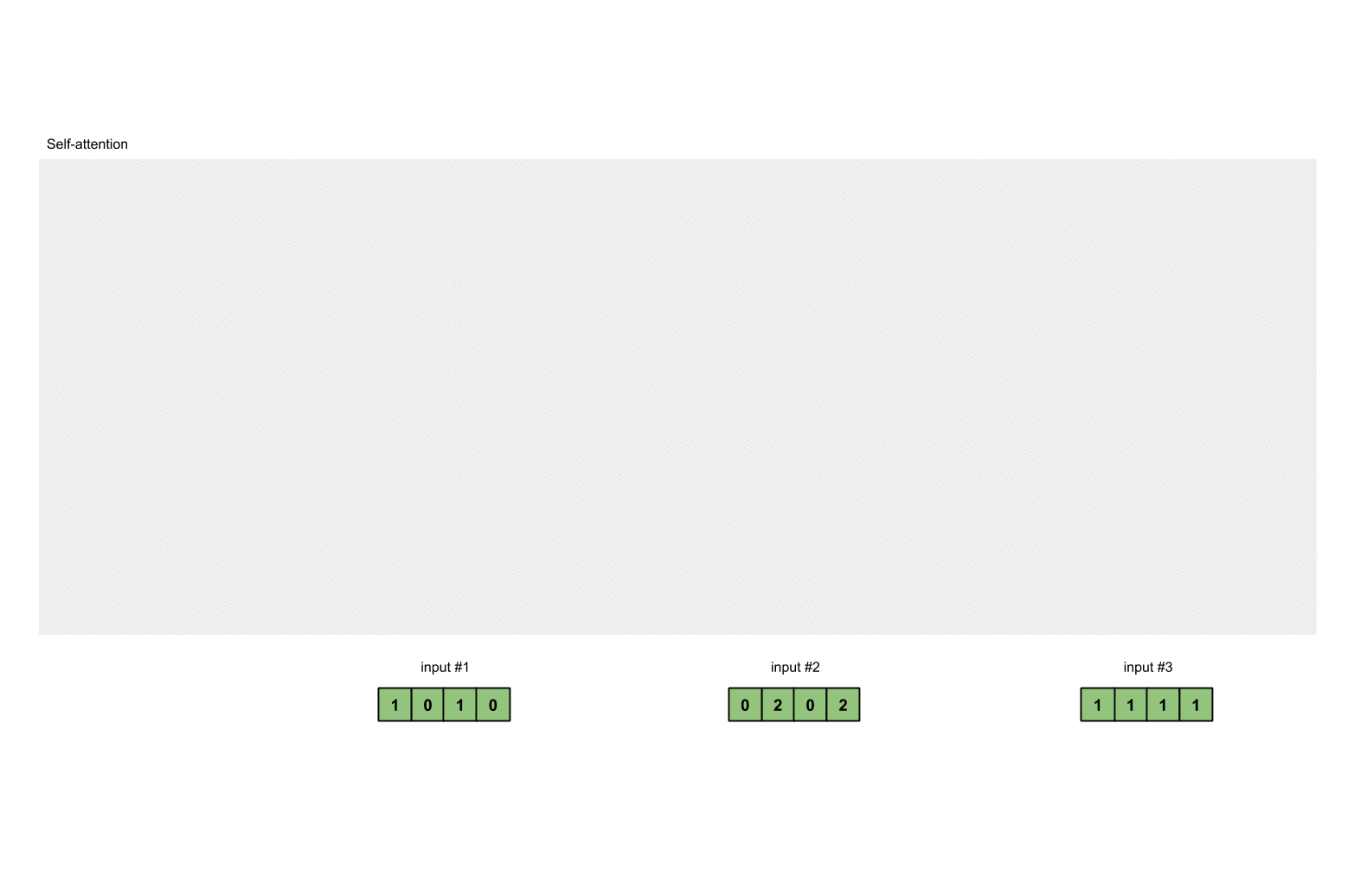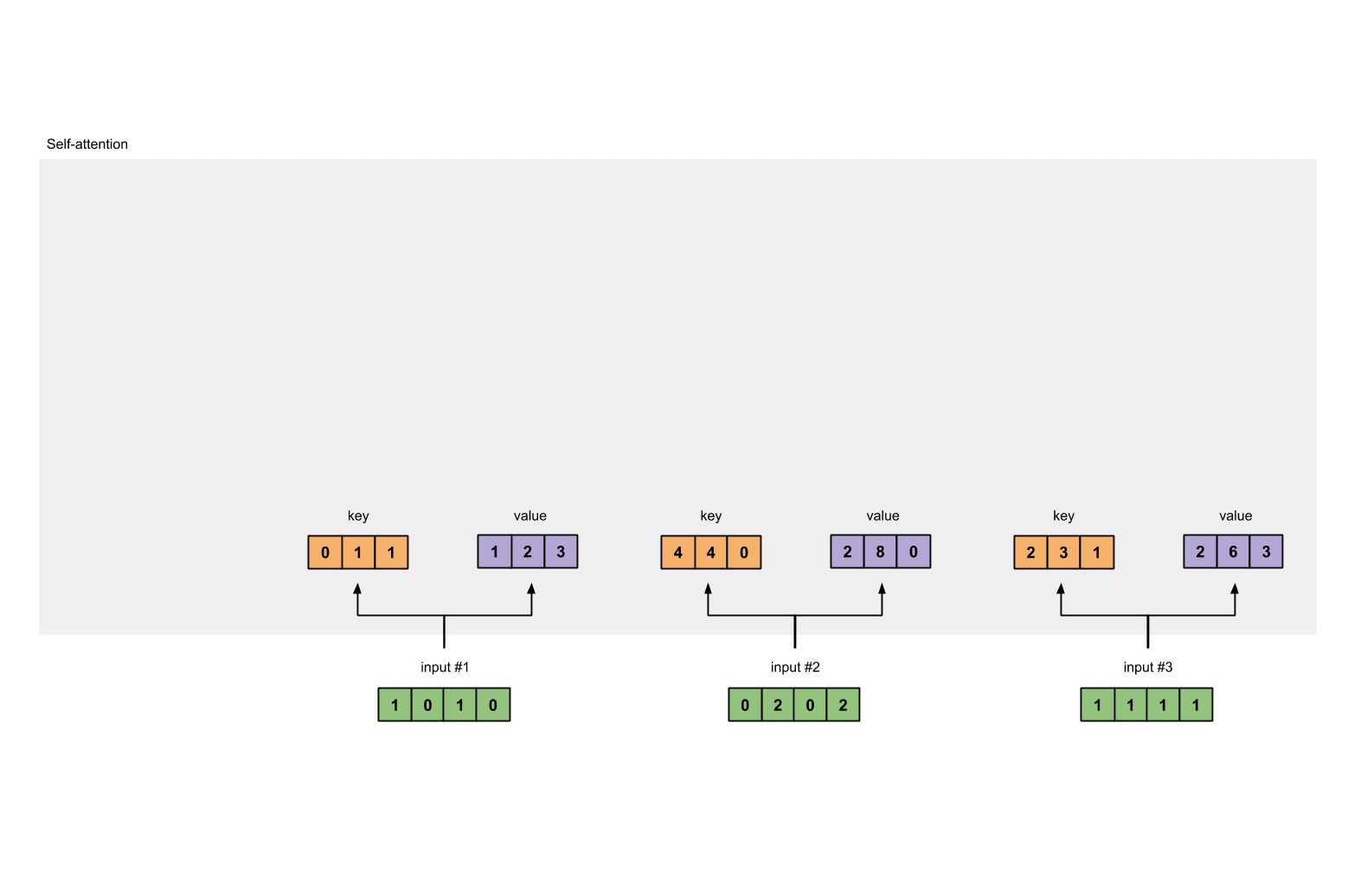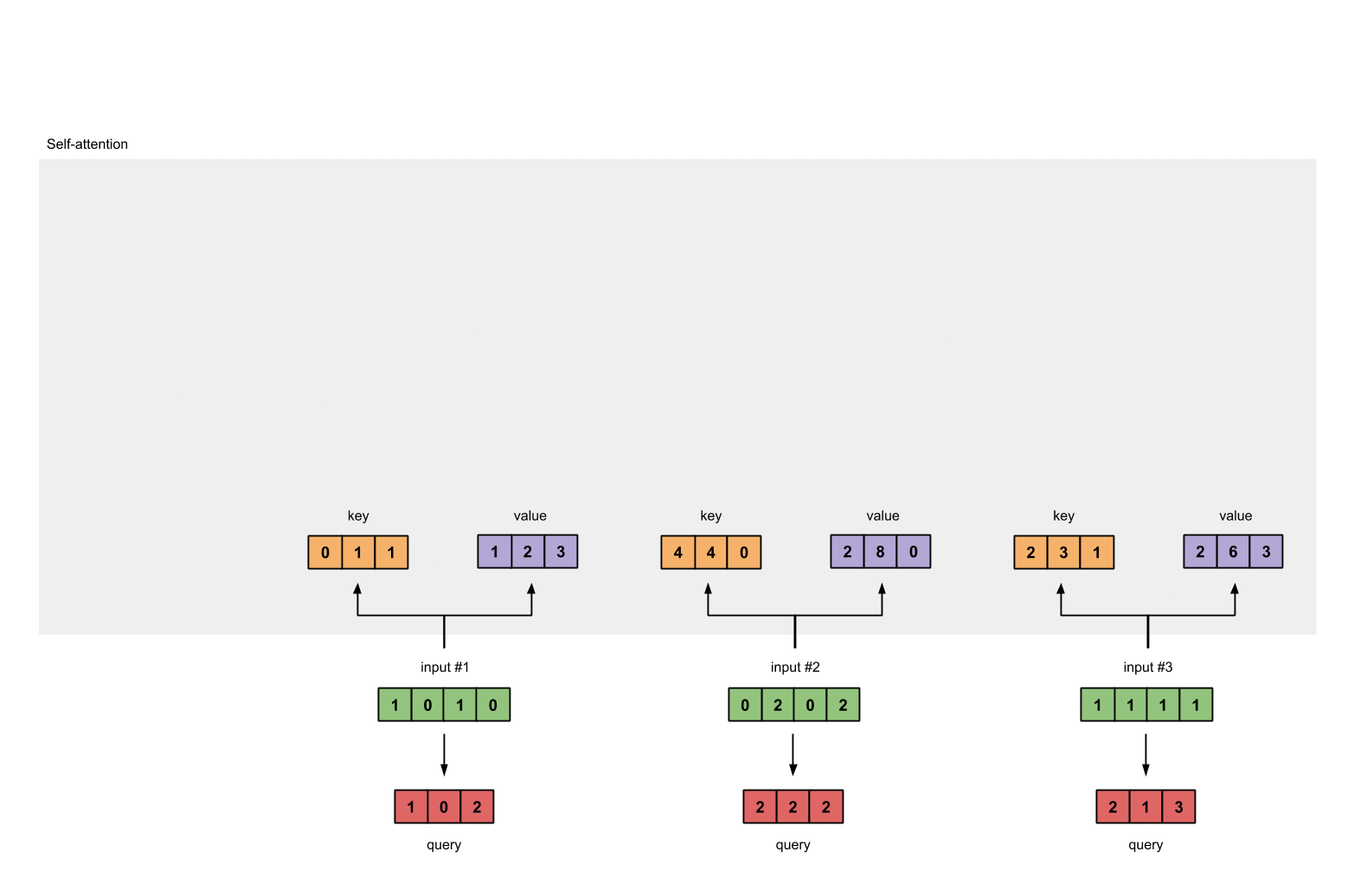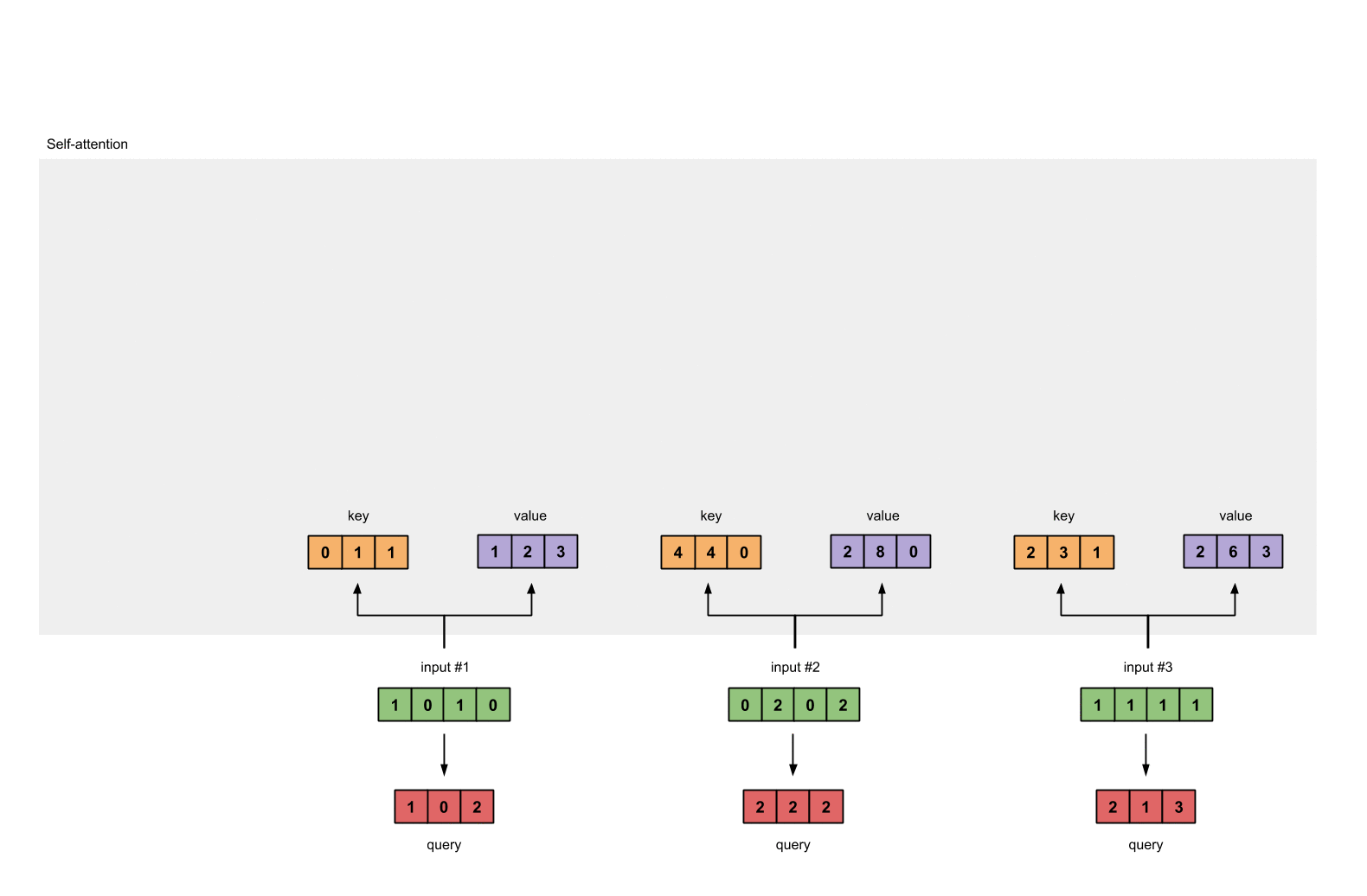
每一个输入都有三个表示,分别为key(橙黄色)query(红色)value(紫色)。比如说,每一个表示我们希望是一个3维的向量。由于输入是4维,所以我们的参数矩阵为 4\times3 维。
后面我们会看到,value的维度,同样也是我们输出的维度。
为了能够获取这些表示,每一个输入(绿色)要和key,query和value相乘,在我们例子中,我们使用如下的方式初始化这些参数。
w_key = [
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0]
]
w_query = [
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1]
]
w_value = [
[0, 2, 0],
[0, 3, 0],
[1, 0, 3],
[1, 1, 0]
]
w_key = torch.tensor(w_key, dtype=torch.float32)
w_query = torch.tensor(w_query, dtype=torch.float32)
w_value = torch.tensor(w_value, dtype=torch.float32)
print("Weights for key: \n", w_key)
print("Weights for query: \n", w_query)
print("Weights for value: \n", w_value)
Weights for key:
tensor([[0., 0., 1.],
[1., 1., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[1., 1., 0.]])
Weights for query:
tensor([[1., 0., 1.],
[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 1.]])
Weights for value:
tensor([[0., 2., 0.],
[0., 3., 0.],
[1., 0., 3.],
[1., 1., 0.]])
Note: 通常在神经网络的初始化过程中,这些参数都是比较小的,一般会在Gaussian, Xavier and Kaiming distributions随机采样完成。
第3步:获取key,query和value

现在我们有了三个参数,现在就让我们来获取实际上的key,query和value。
keys的表示为:
[0, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 1, 0] [1, 1, 0] [0, 1, 1]
[0, 2, 0, 2] x [0, 1, 0] = [4, 4, 0]
[1, 1, 1, 1] [1, 1, 0] [2, 3, 1]
values的表示为:
[0, 2, 0]
[1, 0, 1, 0] [0, 3, 0] [1, 2, 3]
[0, 2, 0, 2] x [1, 0, 3] = [2, 8, 0]
[1, 1, 1, 1] [1, 1, 0] [2, 6, 3]

querys的表示为:
[1, 0, 1]
[1, 0, 1, 0] [1, 0, 0] [1, 0, 2]
[0, 2, 0, 2] x [0, 0, 1] = [2, 2, 2]
[1, 1, 1, 1] [0, 1, 1] [2, 1, 3]
Notes: 在我们实际的应用中,有可能会在点乘后,加上一个bias的向量。
keys = x @ w_key
querys = x @ w_query
values = x @ w_value
print("Keys: \n", keys)
# tensor([[0., 1., 1.],
# [4., 4., 0.],
# [2., 3., 1.]])
print("Querys: \n", querys)
# tensor([[1., 0., 2.],
# [2., 2., 2.],
# [2., 1., 3.]])
print("Values: \n", values)
# tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
# [2., 8., 0.],
# [2., 6., 3.]])
Keys:
tensor([[0., 1., 1.],
[4., 4., 0.],
[2., 3., 1.]])
Querys:
tensor([[1., 0., 2.],
[2., 2., 2.],
[2., 1., 3.]])
Values:
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[2., 8., 0.],
[2., 6., 3.]])
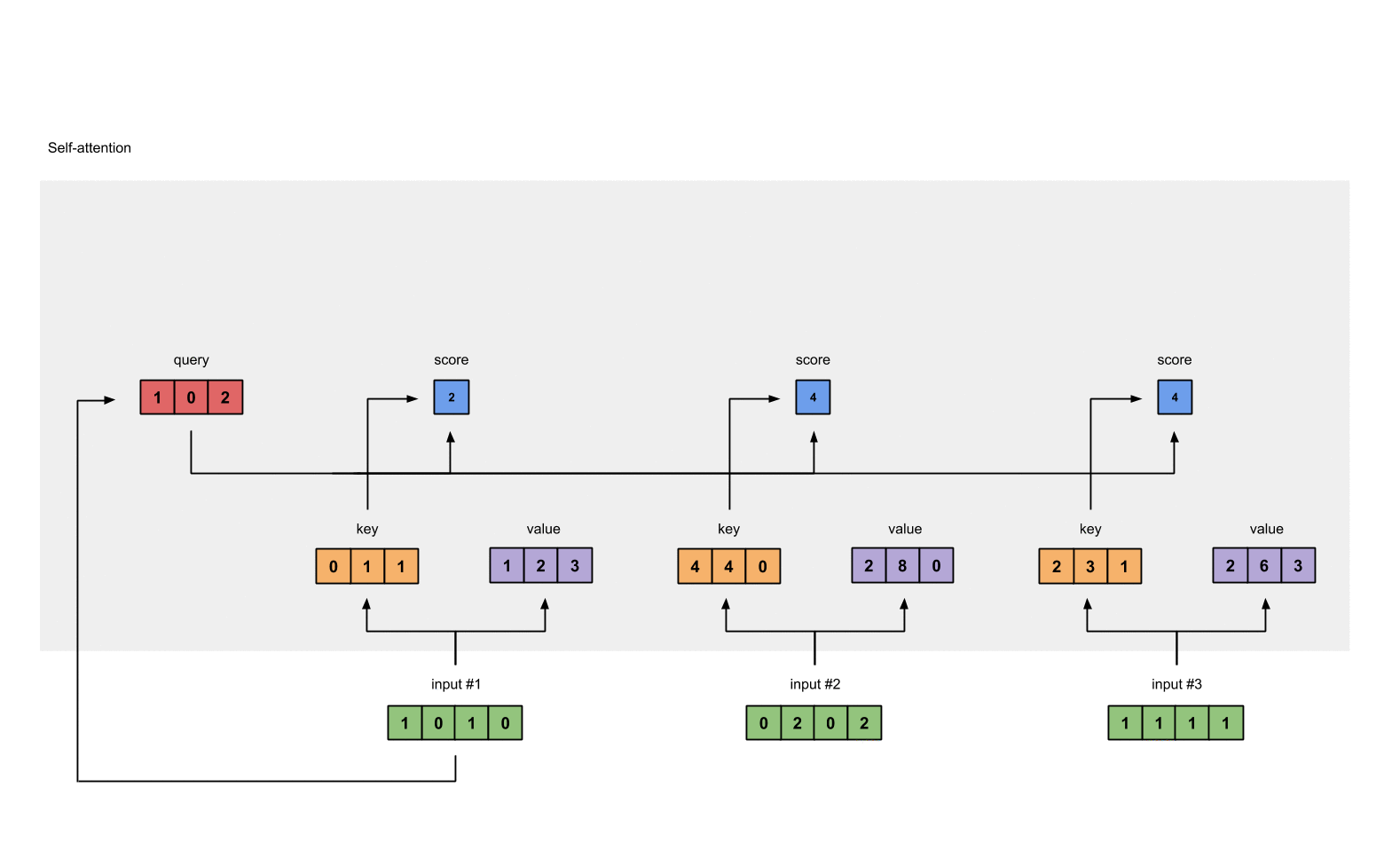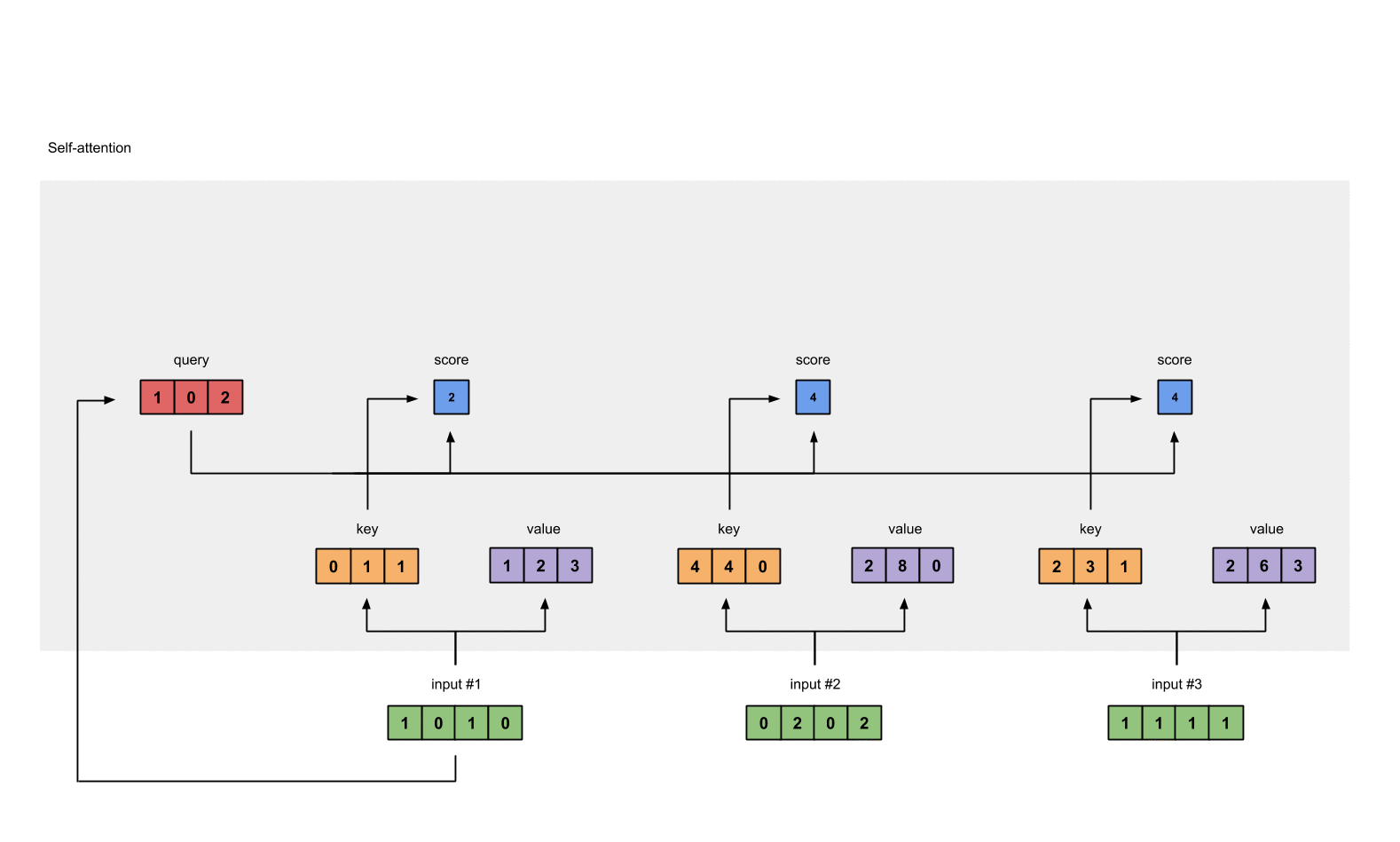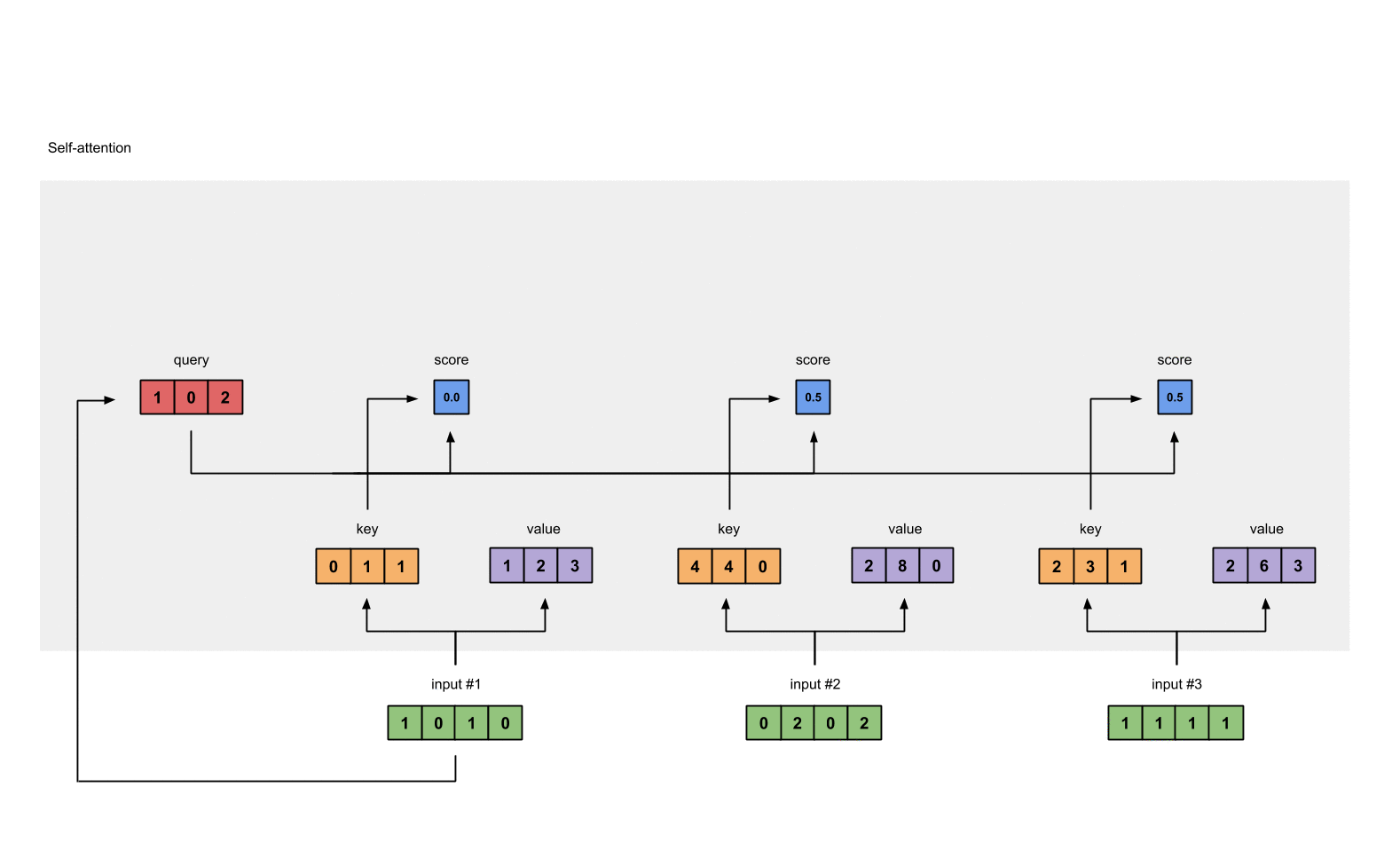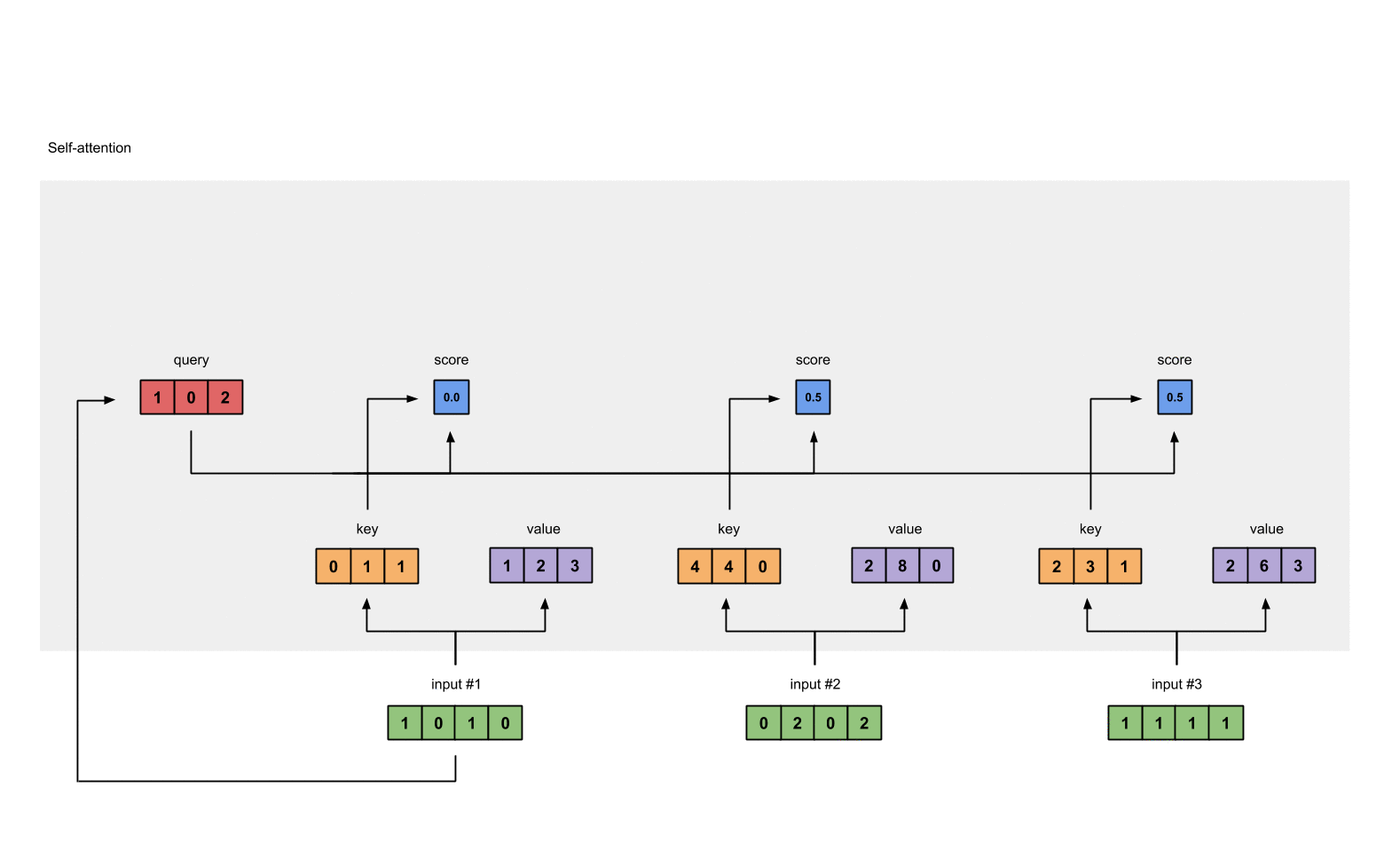
第4步: 计算 attention scores

为了获取input1的attention score,我们使用点乘来处理所有的key和query,包括它自己的key和value。这样我们就能够得到3个key的表示(因为我们有3个输入),我们就获得了3个attention score(蓝色)。
[0, 4, 2]
[1, 0, 2] x [1, 4, 3] = [2, 4, 4]
[1, 0, 1]
这里我们需要注意一下,这里我们只有input1的例子。后面,我们会对其他的输入的query做相同的操作。
attn_scores = querys @ keys.T
print(attn_scores)
# tensor([[ 2., 4., 4.], # attention scores from Query 1
# [ 4., 16., 12.], # attention scores from Query 2
# [ 4., 12., 10.]]) # attention scores from Query 3
tensor([[ 2., 4., 4.],
[ 4., 16., 12.],
[ 4., 12., 10.]])
第5步: 计算softmax
给attention score应用softmax。
softmax([2, 4, 4]) = [0.0, 0.5, 0.5]
from torch.nn.functional import softmax
attn_scores_softmax = softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
print(attn_scores_softmax)
# tensor([[6.3379e-02, 4.6831e-01, 4.6831e-01],
# [6.0337e-06, 9.8201e-01, 1.7986e-02],
# [2.9539e-04, 8.8054e-01, 1.1917e-01]])
# For readability, approximate the above as follows
attn_scores_softmax = [
[0.0, 0.5, 0.5],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.9, 0.1]
]
attn_scores_softmax = torch.tensor(attn_scores_softmax)
print(attn_scores_softmax)
tensor([[6.3379e-02, 4.6831e-01, 4.6831e-01],
[6.0337e-06, 9.8201e-01, 1.7986e-02],
[2.9539e-04, 8.8054e-01, 1.1917e-01]])
tensor([[0.0000, 0.5000, 0.5000],
[0.0000, 1.0000, 0.0000],
[0.0000, 0.9000, 0.1000]])
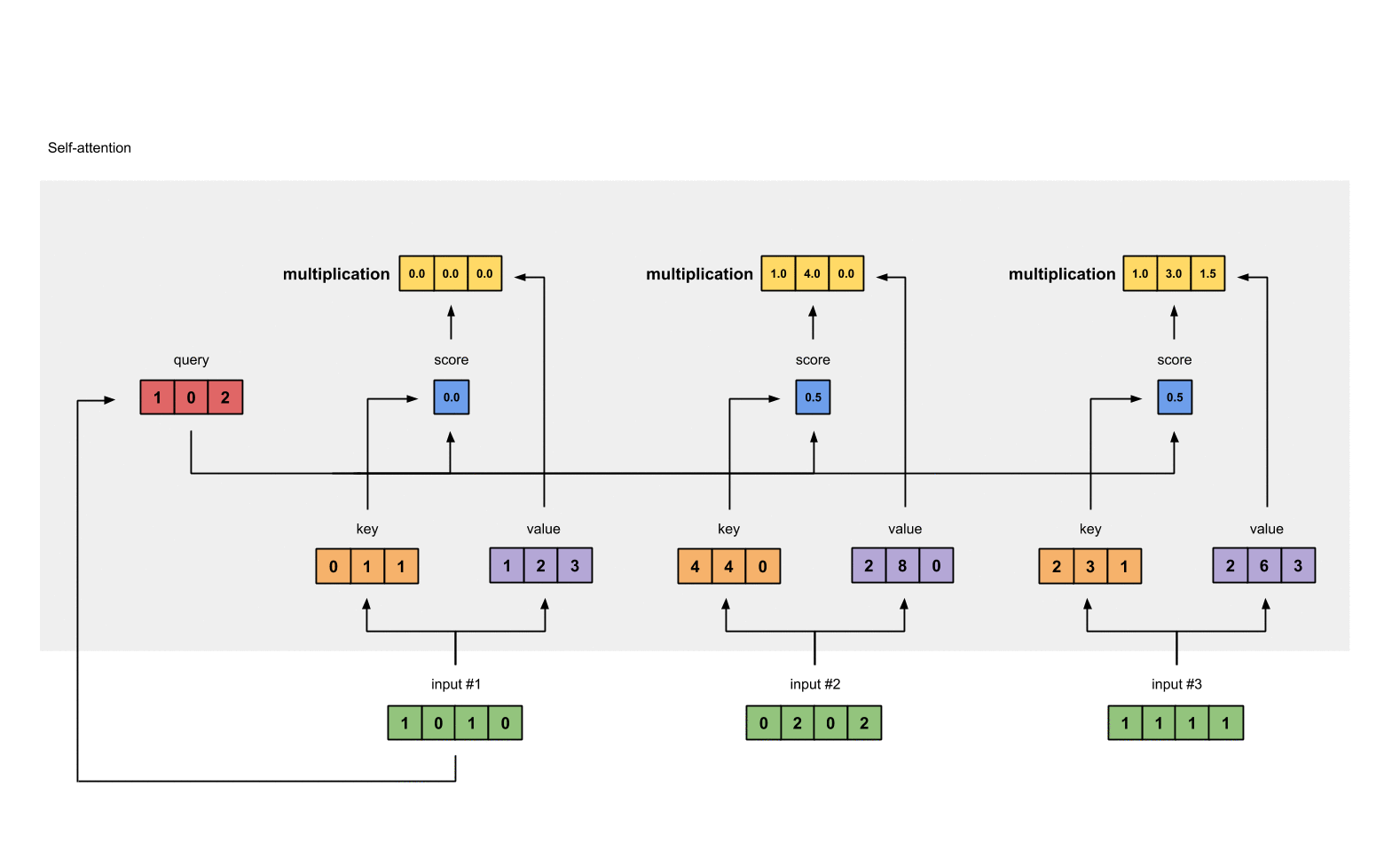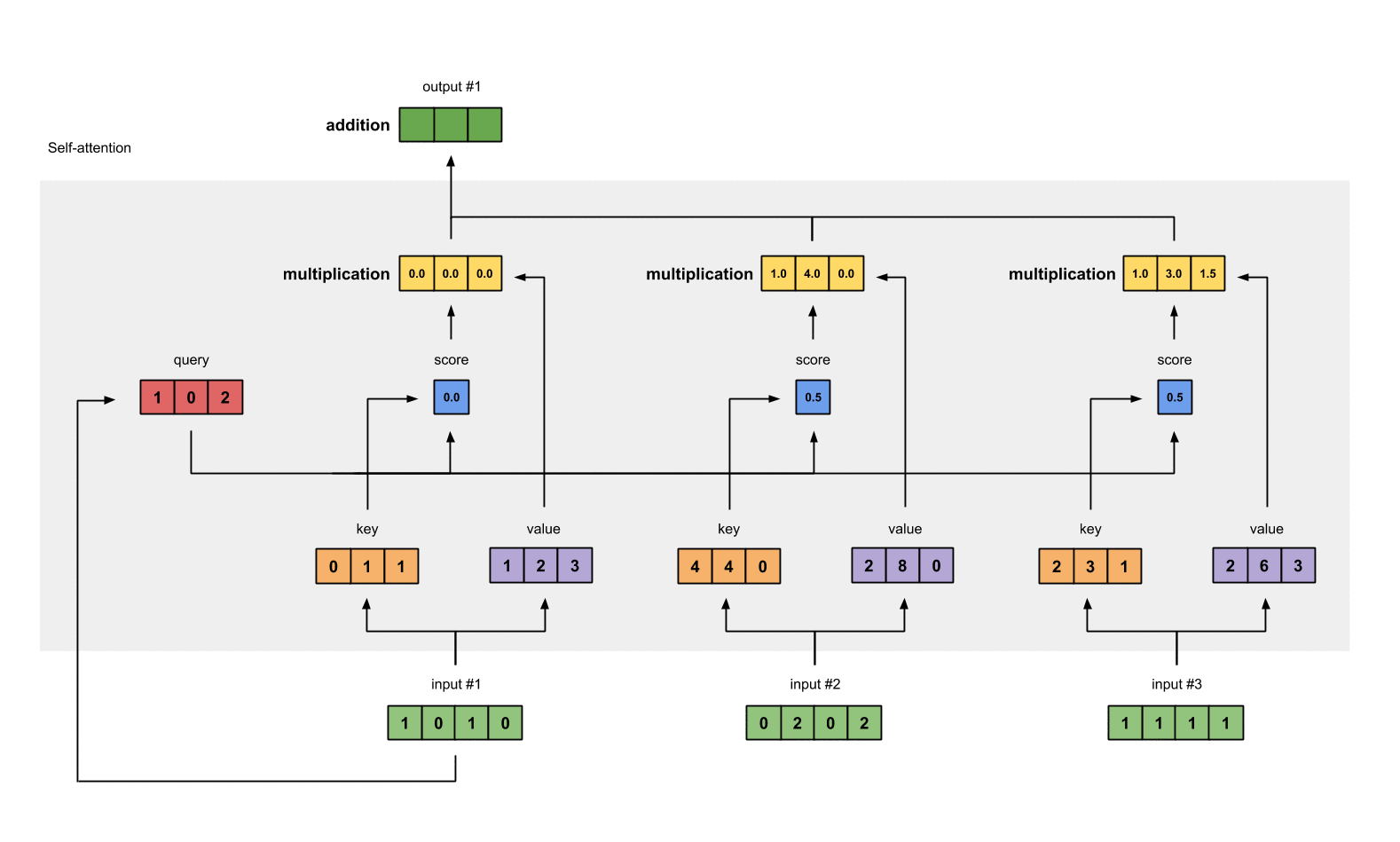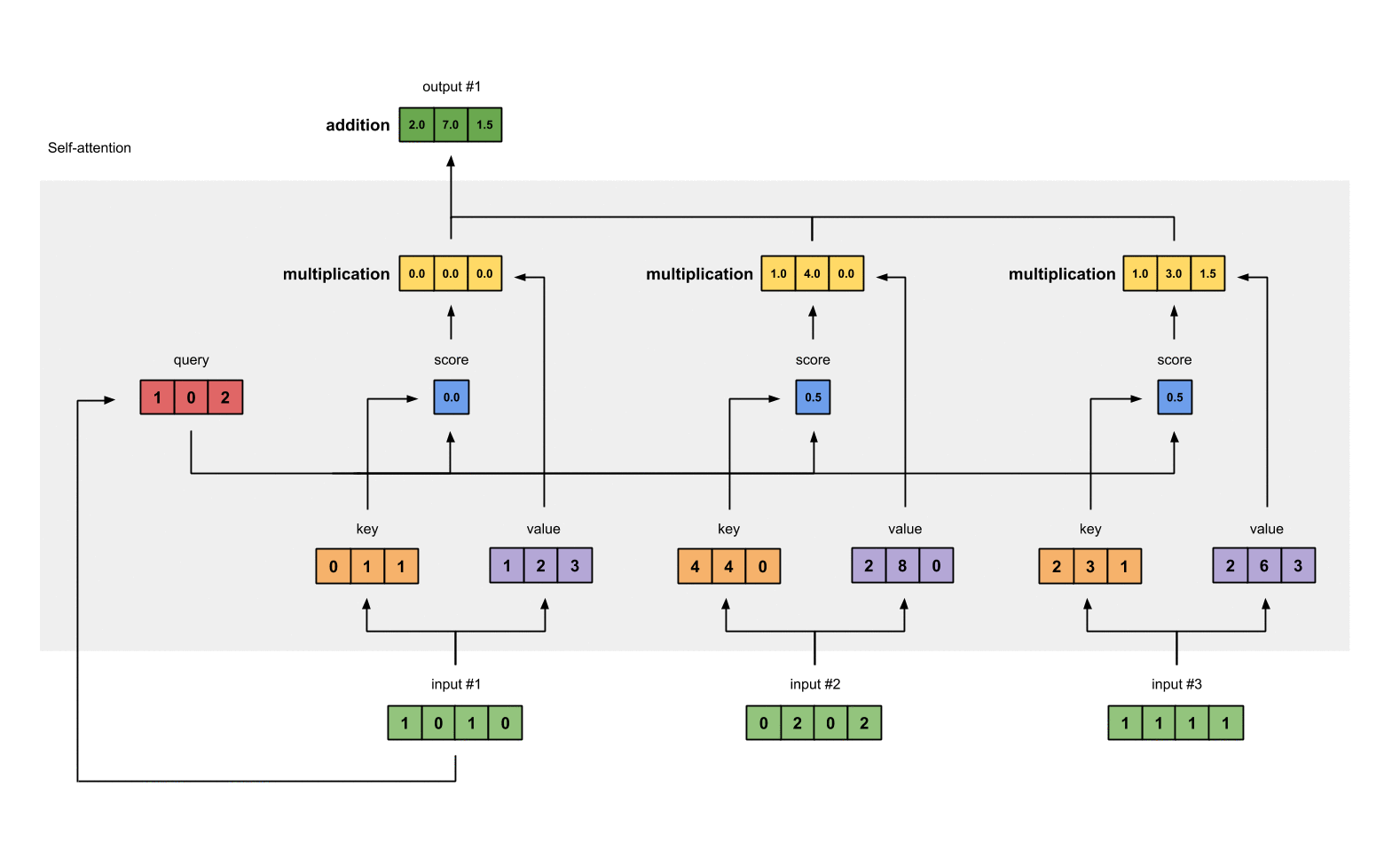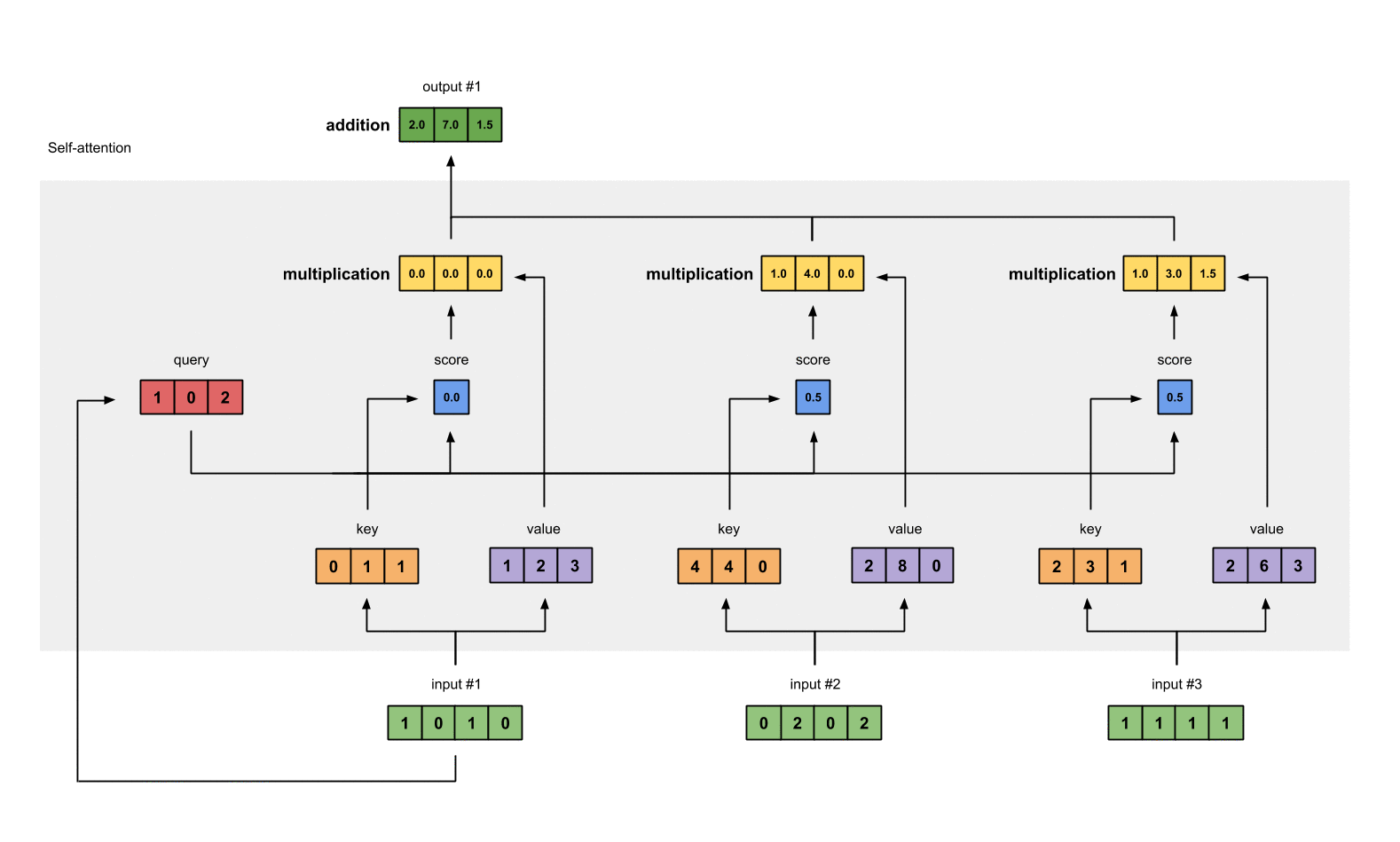
第6步: 给value乘上score

使用经过softmax后的attention score乘以它对应的value值(紫色),这样我们就得到了3个weighted values(黄色)。
1: 0.0 * [1, 2, 3] = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
2: 0.5 * [2, 8, 0] = [1.0, 4.0, 0.0]
3: 0.5 * [2, 6, 3] = [1.0, 3.0, 1.5]
weighted_values = values[:,None] * attn_scores_softmax.T[:,:,None]
print(weighted_values)
tensor([[[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]],
[[1.0000, 4.0000, 0.0000],
[2.0000, 8.0000, 0.0000],
[1.8000, 7.2000, 0.0000]],
[[1.0000, 3.0000, 1.5000],
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.2000, 0.6000, 0.3000]]])
第7步: 给value加权求和获取output
把所有的weighted values(黄色)进行element-wise的相加。
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
+ [1.0, 4.0, 0.0]
+ [1.0, 3.0, 1.5]
-----------------
= [2.0, 7.0, 1.5]
得到结果向量[2.0, 7.0, 1.5](深绿色)就是ouput1的和其他key交互的query representation。
第8步: 重复步骤4-7,获取output2,output3

现在,我们已经完成output1的全部计算,我们要对input2和input3也重复的完成步骤4~7的计算。
outputs = weighted_values.sum(dim=0)
print(outputs)
# tensor([[2.0000, 7.0000, 1.5000], # Output 1
# [2.0000, 8.0000, 0.0000], # Output 2
# [2.0000, 7.8000, 0.3000]]) # Output 3
tensor([[2.0000, 7.0000, 1.5000],
[2.0000, 8.0000, 0.0000],
[2.0000, 7.8000, 0.3000]])
福利: Tensorflow 2 实现
import tensorflow as tf
x = [
[1, 0, 1, 0], # Input 1
[0, 2, 0, 2], # Input 2
[1, 1, 1, 1] # Input 3
]
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32)
print(x)
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 0. 1. 0.]
[0. 2. 0. 2.]
[1. 1. 1. 1.]], shape=(3, 4), dtype=float32)
w_key = [
[0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 0]
]
w_query = [
[1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 1]
]
w_value = [
[0, 2, 0],
[0, 3, 0],
[1, 0, 3],
[1, 1, 0]
]
w_key = tf.convert_to_tensor(w_key, dtype=tf.float32)
w_query = tf.convert_to_tensor(w_query, dtype=tf.float32)
w_value = tf.convert_to_tensor(w_value, dtype=tf.float32)
print("Weights for key: \n", w_key)
print("Weights for query: \n", w_query)
print("Weights for value: \n", w_value)
Weights for key:
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 0. 1.]
[1. 1. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[1. 1. 0.]], shape=(4, 3), dtype=float32)
Weights for query:
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[0. 1. 1.]], shape=(4, 3), dtype=float32)
Weights for value:
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 2. 0.]
[0. 3. 0.]
[1. 0. 3.]
[1. 1. 0.]], shape=(4, 3), dtype=float32)
keys = tf.matmul(x, w_key)
querys = tf.matmul(x, w_query)
values = tf.matmul(x, w_value)
print(keys)
print(querys)
print(values)
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 1. 1.]
[4. 4. 0.]
[2. 3. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 0. 2.]
[2. 2. 2.]
[2. 1. 3.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 2. 3.]
[2. 8. 0.]
[2. 6. 3.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
attn_scores = tf.matmul(querys, keys, transpose_b=True)
print(attn_scores)
tf.Tensor(
[[ 2. 4. 4.]
[ 4. 16. 12.]
[ 4. 12. 10.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
attn_scores_softmax = tf.nn.softmax(attn_scores, axis=-1)
print(attn_scores_softmax)
# For readability, approximate the above as follows
attn_scores_softmax = [
[0.0, 0.5, 0.5],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.9, 0.1]
]
attn_scores_softmax = tf.convert_to_tensor(attn_scores_softmax)
print(attn_scores_softmax)
tf.Tensor(
[[6.3378938e-02 4.6831051e-01 4.6831051e-01]
[6.0336647e-06 9.8200780e-01 1.7986100e-02]
[2.9538720e-04 8.8053685e-01 1.1916770e-01]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 0.5 0.5]
[0. 1. 0. ]
[0. 0.9 0.1]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
weighted_values = values[:,None] * tf.transpose(attn_scores_softmax)[:,:,None]
print(weighted_values)
tf.Tensor(
[[[0. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0. 0. ]
[0. 0. 0. ]]
[[1. 4. 0. ]
[2. 8. 0. ]
[1.8 7.2 0. ]]
[[1. 3. 1.5]
[0. 0. 0. ]
[0.2 0.6 0.3]]], shape=(3, 3, 3), dtype=float32)
outputs = tf.reduce_sum(weighted_values, axis=0) # 6
print(outputs)
tf.Tensor(
[[2. 7. 1.5 ]
[2. 8. 0. ]
[2. 7.7999997 0.3 ]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)