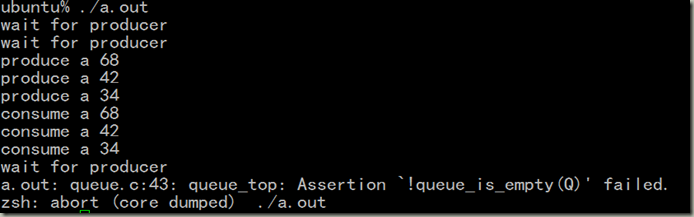
1. 程序一,错误之处,当一个消费者在等待,此时一个生产者生产一个产品后把该消费者的等待线程激活,但是此时她还没有抢到锁,这个时候又来了一个消费者,并且互斥锁正好被它抢走,那么经过if判断此时队列不空,新来的消费者消费完释放锁离开,这时前面的被激活的那个消费者抢到了锁,当它在进行消费的时候就发生了错误,因为这个时候队列时空的。程序如下:
#include "queue.h" #include <pthread.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #define BUF_SIZE 3 pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 互斥锁 保护队列 pthread_cond_t full; //同步量 有产品可取 pthread_cond_t empty; //同步量 有空位可放 Queue Q; void *producer(void* arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); if(Q.size_ == BUF_SIZE){ pthread_cond_wait(&empty, &mutex); } int data = rand()%100; printf("produce a %d ", data); queue_push(&Q, data); pthread_cond_signal(&full); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } } void *consumer(void* arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); if(queue_is_empty(&Q)){ printf("wait for producer "); pthread_cond_wait(&full, &mutex); } int data = queue_top(&Q); printf("consume a %d ", data); queue_pop(&Q); pthread_cond_signal(&empty); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } } int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { srand(100000); pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&full, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&empty, NULL);
queue_init(&Q); pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, producer, NULL); pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, consumer, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, consumer, NULL);
queue_destroy(&Q); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&full); pthread_cond_destroy(&empty); return 0; }
2.程序二,将上例中的if改为while循环,这样,当等待线程被唤醒时,若抢到锁,会再次检查一下当前队列是否为空,若为空,则又进入等待状态,否则方可取走产品,这样就有效消除了上述错误。代码省略。
3.程序三,将pthread_cond_signal改为 pthread_cond_broadcast ,signal是去通知一个等待该条件变量的线程,通常用来表示资源可用。而broadcast 则是通知等待的所有线程,通常用来表示状态的改变。代码如下:
#include "queue.h" #include <pthread.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #define BUF_SIZE 3 pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 互斥锁 保护队列 pthread_cond_t full; //同步量 有产品可取 pthread_cond_t empty; //同步量 有空位可放 Queue Q; void *producer(void* arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); while(Q.size_ == BUF_SIZE){ pthread_cond_wait(&empty, &mutex); } int data = rand()%100; printf("produce a %d ", data); queue_push(&Q, data); pthread_cond_broadcast(&full); // signal pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sleep(3); } } void *consumer(void* arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); while(queue_is_empty(&Q)){ printf("wait for producer "); pthread_cond_wait(&full, &mutex); } int data = queue_top(&Q); printf("consume a %d ", data); queue_pop(&Q); pthread_cond_broadcast(&empty); // signal pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } } int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { srand(100000); pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&full, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&empty, NULL); queue_init(&Q); pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, producer, NULL); pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, consumer, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, consumer, NULL); queue_destroy(&Q); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&full); pthread_cond_destroy(&empty); return 0; }
4.一些上课笔记
4.1 线程安全:多个线程同时运行一段代码,而能保证结果的正确性,这叫做线程安全。
4.2 实现线程安全的方法:
a) 互斥锁和信号量、条件变量
b) 原子操作
4.3 pthread_cond_wait(这个函数必须在加锁的条件下才能使用)操作的步骤:
a) 首先释放锁
b) 等待,直到接收到signal
c) 重新抢占锁
4.4 生产者消费者模型中正式生产或者消费的必要条件是
a) 抢到锁
b) 等待对应的条件变量:时机成熟。
4.5 为何以while代替if:
a) 三个消费者wait在full上。
b) 某生产者线程produce数据后调用了broadcast。
c) 如果采用if,第一个线程拿到锁,消费完数据,正常。其余两个线程发生错误。
d) 如果采用while,后面两个线程会再次检测队列状态。
e) 另外一个错误,生产者还是调用signal。
f) 此时一个等待线程被激活,然后尚未拿到锁,另一个线程抢到锁,直接绕过if语句(此时队列不为空),然后将数据消费,此时队列为空。之前的线程拿到锁,继续消费导致错误。