ref: http://www.studytonight.com/java/collection-framework.php
Collection Framework
collection frame work was not part of original Java release. Colelctions was added to J@SE 1.2 Prior to Java 2.
Java Provided adhoc classes such as Dictionary. Vector, Stackand Properties to store and manipulate groups ob objects.
Important Interfaces of Collection API
Interface:
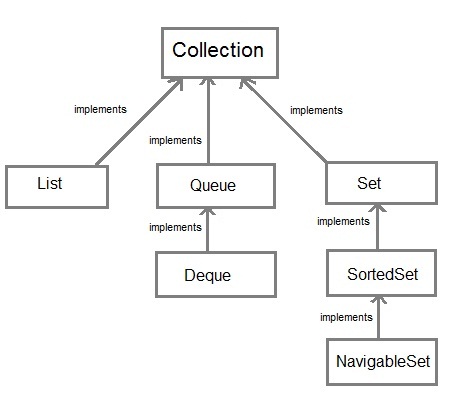
Collection: enables you to work with groups of object, it is at the top of the collection hierarchy
Deque: extends queue to handle double ended queue
List: extends collection to handle sequences list of object
Queue: extends collection to handle special kind of list in which element are removed only form the head
Set: extends collection to handle sets, which must contain unique element
Sorted Set: extends sets to handle sorted set
Why Collections were made Generic ?
generic added type safety to collection framework. Generics was introduced , now you can explicitly state the type of the collection
Collections and Autoboxing
primitive to warpper class
Most Commonly thrown Exceptions in Collection Framework
| Exception Name | Description |
|---|---|
| UnSupportedOperationException | occurs if a Collection cannot be modified |
| ClassCastException | occurs when one object is incompatible with another |
| NullPointerException | occurs when you try to store null object in Collection |
| IllegalArgumentException | thrown if an invalid argument is used |
| IllegalStateException | thrown if you try to add an element to an already full Collection |
Interfaces Detail
The Collection Interface
1. interface Collection<E>
2. common methods:
add( E obj )
addAll( Collection C)
remove( Object obj)
removeAll(Collection C)
contains(Object obj)
isEmpty()
size()
The List Interface
extends the Collection, defines storage as sequence of elements.
1. allow random access and insertion
2. allow duplicate elements
3. interface List <E>
4. additive methods :
get(int index)
set(int index, E obj)
indexOf(Object obj)
lastIndexOf(Object obj)
subList(int start, int last)
The Set Interface
no duplicates.
1. It does not define any method of its own, It has two sub interface, SortedSet, NavigableSet
2. SortedSet interface extends Set interface and arranges added elements in an ascending order
3. NavigableSet interface extends SortedSet interface,
and allow retrieval of elements based on the closest match to a given value or values
4. interface Set<E>
The Queue Interface
1. FIFO, extends Collection interface.
2. interface Queue <E>
3. There are couple of new methods added
poll() removes element at the head of the queue and returns null of queue is empty
remove() removes element at the head of the queue and throw NoSuchElementException is queue is empty
peek() returns the element at the head of the queue without removing it, return null if q is empty
element() same as peek(), but throw NoSuchElementException if queue is empty
offer(E obj) adds object to queue
The Dequeue Interface
1. Double ended queues can function as simple queue as well as standard Stacks
2. interface Dequeue<E>
*********************************分割线*************************************************
The Collection classes
Java provides a set of Collection classes that implements Collection interface. Some of these classes provide full implementations that can be used as it is and other abstract classes provides skeletal implementations that can be used as starting points for creating concrete collections
ArrayList class
1. extends AbstractList class and implements the List interface
2. ArrayList supports dynamic array that can grow as needed. ArrayList has three constructors
ArrayList()
ArrayList(Collection c)
ArrayList(int capacity)
3. ArrayList are created with an initial size, when this size is exceeded, it gets enlarged auomatically
4. It can contain Duplicates and maintains the insertion order
5. ArrayList is not synchronized
6. can be printed out directly using "System.out.println(al)"
Getting Array from an ArrayList
toArray() method is used to get an array from containing all the contents of the list.
There are reasons why you must obtain array from ArrayList whenever required
to obtain faster processing
to pass array to methods who do not accept COllection as arguments
to integrate and use collection with legacy code
LinkedList class
1. LinkedList class extends AbstractSequentialList and implements List, Dequeue and Queue interface
2. It can be used as List, Stack or Queue as it implements all the related interfaces
3. It can contain duplicates and is not synchronized.
HashSet class
1. HashSet extends AbstractSet class and implements the Set interface
2. It creates a collection that uses hash table for storage
3. HashSet does not maintain any order of elements
LinkedHashSet class
1. LinkedHashSet class extends HashSet class
2. LinkedHashSet maintains a linked list of entries in the set
3. LinkedHashSet stores elements in the order in which elements are inserted
TreeSet class
1. it extends AbstractSet class and implements the NavigableSet interface
2. It stores elements sorted ascending order
3. Uses a Tree structure to store elements
4. Access and retrieval times are quite fast
5. It has four Constructors
TreeSet()
TreeSet(Collection C)
TreeSet(Comparator comp)
TreeSet(sortedSet ss )
*********************cut***********************************************
Accessing a Collection
To access, modify or remove any element from any collection we need to first find the element
to find the element we need to cycle through the elements of the collection, there are 3 possible ways to cycle through the elements of any collection.
1. Iterator interface
2. ListIterator interface
3. for-each loop
Accessing elements using Iterator
Iterator interface is used to traverse a list in forward direction, enabling you to remove or modify the
elements of the collection. Each collection classes provide iterator() method to return an iterator
ArrayList<String> ar = new ArrayList<String>();
Iterator it = ar.iterator();
Accessing elements using ListIterator
ListIterator interface is used to traverse a list in both forward and backward direction
It is avaliable to only those collections that implement the List interface
Using for-each loop
******************************************************************************
Map Interface
A map strores data in key and value association. Both key and values are objects.
Although Maps are a part of Collection Framework, they can not actually be called as collections because of some
properties that they posses. However we can obtain a collection-view of maps
Interface Description
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Map maps unique key to value
Map.Entry describe an element in key and value pair in a map. This is an inner class of map
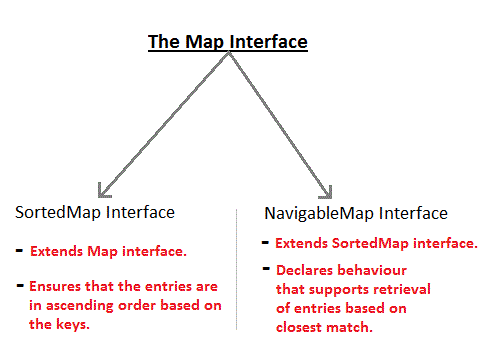
NavigableMap extends soortedMap to handle the retrieval of entries on closest match searches
SortedMap extends Map so hat key are maintained in an ascending order
Commonly used Methods defined by Map
- boolean containsKey(Object k): returns true if map contain k as key. Otherwise false.
- Object get(Object k) : returns values associated with the key k.
- Object put(Object k, Object v) : stores an entry in map.
- Object putAll(Map m) : put all entries from m in this map.
- Set keySet() : returns Set that contains the key in a map.
- Set entrySet() : returns Set that contains the entries in a map.
HashMap class
1. HashMap class extends AbstractMap and implements Map interface
2. It uses hashtable to store the map, This allow the execution time of get() and put() to be constant
3. HashMap has four constructor
HashMap()
HashMap(Map<? extends k, ? extends V> m)
HashMap(int capacity)
HashMap(int capacity, float fillratio)
TreeMap class
1. TreeMap class extends AbstractMap and implements Navigable interface
2. It creates Map, stored in a tree structure
3. A TreeMap provides an efficient means of storing key/value pair
4. It provides key/pair in sorted order
LinkedHashMap class
1. LinkedHashMap extends HashMap class.
2. It maintains a linkedList of entries in map in order in which thet are inserted.
3. LinkedHashMap defines the following constructors:
LinkedHashMap()
LinkedHashMap(Map<? extends k, ? extends V> m)
LinkedHashMap(int capacity)
LinkedHashMap(int capacity, float fillratio)
LinkedHashMap(int cappacity, float fillratio, boolean order)
4. It adds one new method removeEldestEntry(), this method is called by put() and putAll()
by default, this method does nothing, However we can override this method to remove oldest element in the map
syntax: protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry e)
EnumMap class
1. EnumMap extends AbstractMap and implements Map interface
2. It used for key as enum
************************cut*******************************************
Comparator Interface
In java , comparator interface is used to oder the object in your own way. It gives you ability to decide how
element are sorted within sorted collection and map
Comparator Interface defines compare() method, this method compare two object and return 0 upon equal and positive if obj1 > obj2, otherwise negative. This method can throw ClassCastException
example
class Student{
int roll;
String name;
Student(int r, String n){
roll = r; name = n;
}
public String toString(){return roll+" "+name};
}
class MyComparator implements Comparator{
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2){
if(s1.roll == s2.roll) rerurn 0;
else id(s1.roll > s2.roll) return 1;
else return -1;
}
}
public class Test{
pubic static void main(String[] args){
TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Mycomparator());
ts.add(new Student(45,"Rahul")); ts.add(new Student(11, "Adam"));
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
output: 11 Adam, 45 Rahul // it is sorted
************************cut*********************************************
Legacy Classes
Early version of java did not include the Collection framework. It only defined several classes and interface that provide method for storing objects. When Collection framework were added in J2SE 1.2, the original classes were reengineered to support the collection interface. These classes are also known as Legacy classes. All legacy claases and interface were redesign by JDK 5 to support Generics.
The following are the legacy classes defined by java.util package
1. Dictionary
2. HashTable
3. Properties
4. Stack
5. Vector
There is only one legacy interface Enumeration
# All legacy classes are synchronized