一、前言
近期学习http框架。
眼下写的这个框架临时仅仅适用于学习之用,实际用于项目之中还须要不断的优化。
要从server或者网络获取数据。显示到UI上面,网络请求的操作不能放在UI线程中进行,android为我们封装了AsyncTask类来进行异步的请求操作。所以这个Http框架基于AsyncTask。
二、框架主要类
定义Request类,定义url。server返回数据,post的请求params,下载进度等參数。
定义HttpUtil类来封装http请求代码。
在里面定义execute()方法,该方法推断是get还是post。然后再去call get(),post() 方法。post() 请求须要的參数在Request中设置.
在AsyncTask中。doingBackground()方法中 execute http。将返回的数据写到内存中变成String返回,假设数据较大,能够先存到文件里。把path返回。在不同的callback中处理。
三、框架搭建
1. 首先,我们建立 HttpClientUtil.java 类,用于处理HTTP的get和post,里面定义execute()方法。该方法推断是get还是post,然后再去call get(),post() 方法。post() 请求须要的參数在Request中设置.:
/**
* @author Mr.傅
*/
public class HttpClientUtil {
/**
* 运行HTTP方法,Request 设置请求类型
* @param request
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static HttpResponse excute(Request request) throws Exception{
switch (request.requestMethod) {
case GET:
return get(request);
case POST:
return post(request);
default:
//这里未定义 DELETE 和 PUT 操作
throw new IllegalStateException("you doesn't define this requestmethod");
}
}
private static HttpResponse get(Request request) throws Exception {
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet get = new HttpGet(request.url);
addHeader(get, request.headers);
//返回的结果放到上一层进行处理
HttpResponse response = client.execute(get);
return response;
}
private static HttpResponse post(Request request) throws Exception {
HttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpPost post = new HttpPost(request.url);
addHeader(post, request.headers);
//post的请求參数在 Request 中定义,假设为空,则未定义
if (request.entity == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("you forget to set post content to the httpost");
}else {
post.setEntity(request.entity);
}
HttpResponse response = client.execute(post);
return response;
}
/**
* 请求头
* @param request
* @param headers
*/
public static void addHeader(HttpUriRequest request, Map<String, String> headers){
if (headers != null && headers.size() > 0 ) {
for(Entry<String, String> entry : headers.entrySet()){
request.addHeader(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
}
/**
* @author Mr.傅
*/
public class Request {
public enum RequestMethod{
GET,POST,DELETE,PUT
}
RequestMethod requestMethod;
public String url;
/**
* Http请求參数的类型。包含表单。string, byte等
*/
public HttpEntity entity;
public Map<String, String> headers;
public static final String ENCODING = "UTF-8";
/**
* 设置回调接口,该接口中的onSuccess和onFilure方法须要在体如今UI线程其中
*/
public ICallback callback;
private RequestTask task;
public Request(String url, RequestMethod method) {
this.url = url;
this.requestMethod = method;
}
public void setEntity(ArrayList<NameValuePair> forms){
try {
entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(forms, ENCODING);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void setEntity(String postContent){
try {
entity = new StringEntity(postContent, ENCODING);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void setEntity(byte[] bytes){
entity = new ByteArrayEntity(bytes);
}
/**
* 设置回调方法,在ui线程中定义须要请求 返回的 方法
* @param callback
*/
public void setCallback(ICallback callback) {
this.callback = callback;
}
/**
* UI线程中,运行该方法,开启一个AsyncTask,注意AsyncTask每次使用必须又一次new
*/
public void execute() {
task = new RequestTask(this);
task.execute();
}
}
public interface ICallback {
void onFilure(Exception result);
void onSuccess(Object result);
/**
* 将从server得到的HttpResponse进行解析,解析完毕以后。返回给UI线程
*/
Object handle(HttpResponse response);
}4. RequestTask 继承自 AsyncTask ,在doInBackground 进行HTTP请求。同一时候对HTTP请求返回的数据结果进行解析,通过调用callback中的handle方法。解析HTTP请求返回的參数,返回后的结果(假设抛出异常,将异常也返回)。在onPostExecute中进行处理,调用不同的方法。返回到UI线程,代码例如以下:
/**
* @author Mr.傅
* @version create time:2014年5月17日 下午2:19:39
*/
public class RequestTask extends AsyncTask<Object, Integer, Object> {
private Request request;
public RequestTask(Request request) {
super();
this.request = request;
}
@Override
protected Object doInBackground(Object... params) {
try {
HttpResponse response = HttpClientUtil.excute(request);
//response 解析代码放到相应的类中,相应handle中的bindData方法
return request.callback.handle(response);
} catch (Exception e) {
return e;
}
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Object result) {
super.onPostExecute(result);
if (result instanceof Exception) {//失败
request.callback.onFilure((Exception)result);
}else {//成功
request.callback.onSuccess(result);
}
}
}放入到详细的Callback中进行处理,然后返回到doInBackground中进行下一步处理。
/**
* @author Mr.傅
*/
public abstract class AbstractCallback implements ICallback{
/**
* 文件存放的路径
*/
public String path;
private static final int IO_BUFFER_SIZE = 4*1024;
@Override
public Object handle(HttpResponse response){
// file, json, xml, image, string
int statusCode = -1;
InputStream in = null;
try {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
switch (statusCode) {
case HttpStatus.SC_OK:
if (TextUtil.isValidate(path)) {
//将server返回的数据写入到文件其中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
if (entity.getContentEncoding() != null) {
String encoding = entity.getContentEncoding().getValue();
if (encoding != null && "gzip".equalsIgnoreCase(encoding)) {
in = new GZIPInputStream(entity.getContent());
} if (encoding != null && "deflate".equalsIgnoreCase(encoding)) {
in = new InflaterInputStream(entity.getContent());
}
} else {
in = entity.getContent();
}
byte[] b = new byte[IO_BUFFER_SIZE];
int read;
while ((read = in.read(b)) != -1) {
// TODO update progress
fos.write(b, 0, read);
}
fos.flush();
fos.close();
in.close();
//写入文件之后。再从文件其中将数据读取出来。直接返回对象
return bindData(path);
} else {
// 须要返回的是对象,而不是数据流,所以须要去解析server返回的数据
// 相应StringCallback 中的return content;
//2. 调用binData
return bindData(EntityUtils.toString(entity));
}
default:
break;
}
return null;
} catch (ParseException e) {
//这些异常处理都没有进行操作。后面的文章会再做处理
} catch (IOException e) {
}
return null;
}
/**
* 数据放入到不同的Callback中处理
*/
protected Object bindData(String content){
//StringCallback等方法中实现了该方法
return null;
}
/**
* 假设要存入到文件,则设置文件路径
*/
public AbstractCallback setPath(String path){
this.path = path;
return this;
}
}
public abstract class StringCallback extends AbstractCallback {
@Override
protected Object bindData(String content) {
//假设路径存在,则又一次讲数据从文件里读取出来
if (TextUtil.isValidate(path)) {
return IOUtiliteies.readFromFile(path);
}
return content;
}
}public class TextUtil {
public static boolean isValidate(String content){
return content != null && !"".equals(content.trim());
}
public static boolean isValidate(ArrayList<NameValuePair> content){
return content != null && content.size() > 0;
}
}private void requestString() {
//设置保存路径
String path = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + "mrfu_http.txt";
Request request = new Request("http://www.baidu.com", RequestMethod.GET);
request.setCallback(new StringCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Object result) {
mTestResultLabel.setText((String)result);
}
@Override
public void onFilure(Exception result) {
result.printStackTrace();
}
}.setPath(path));
request.execute();
}其中mTestResultLabel 是TextView
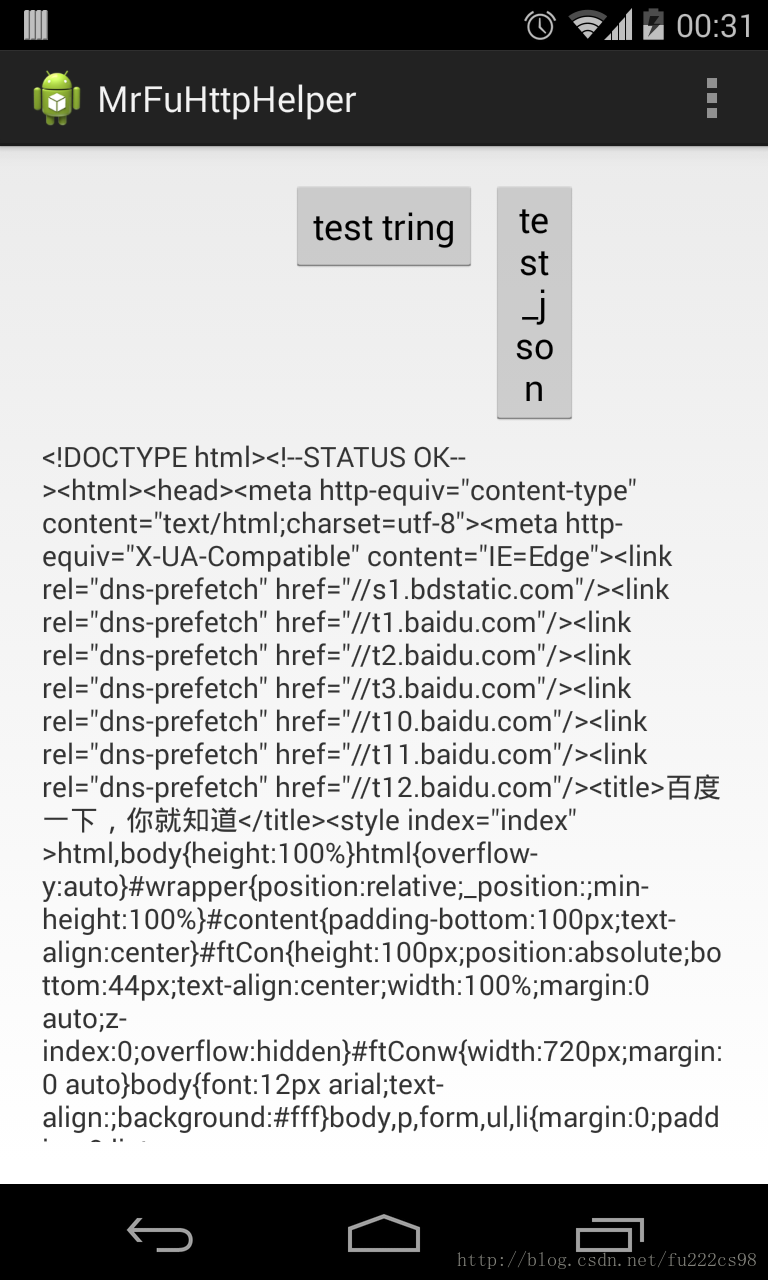
能够看到实现效果。这里我们在SD卡的根文件夹下将返回结果存入到了 "mrfu_http.txt" 文件里,同一时候显示到了 UI 上面:如图所看到的:
后面的文章中会将该框架逐步晚上,包含上面提到的。
特别感谢stay老师在这其中的帮助。
让我在框架学习这块实打实的迈出了第一步!