下面是mongodb的一些基本概念:
- 文档是MongoDB中数据的基本单元,类似关系数据库中的行。
- 集合,是存储文档的容器,类似关系数据库中的表。
- MongoDB的单个实例容纳多个数据库,每个数据库都有自己的集合和权限。
- 每一个文档都有一个特殊的“_id”,它在文档所处的集合中是唯一的。
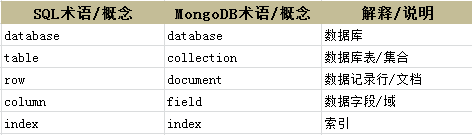
为了易于理解,咱们把MongoDB中的概念与关系数据库对比一下:
一、文档
文档是mongodb的核心概念。多个键值有序的放置在一起便是文档。简单的例子:
1 {"greeting":"Hello World","foo":15}
2 {"foo":15,"greeting":"Hello World"}
3 {"foo":15}
4 {"Foo":15}
5 {"Foo":"15"}
- 键名:不能含有空格及特殊字符'$'和'.',同时以下划线开头的键是保留的
- 键名区分大小写,如上述的3和4是不同的文档
- 文档中键名不能重复
- 文档区别类型,如上述的4和5,值的类型不一样所以属于不同的文档
- 键的值不仅是字符串还可以是其他类型
二、集合
集合就是一组文档,如果说文档如关系数据库中的行,那么集合就如同表。集合有如下特点:
1、无模式
集合是无模式的,这意味着集合里可以存储各种各样的文档。那么是不是mongodb中只需要一个集合就可以了呢?答案是否,下面是一些理由:
- 易于管理:如果各种各样的文档都放到一个集合中,那么对于开发者或管理员都是噩梦。
- 提高效率:在一个集合中查不同类型的文档,速度上肯定不如各个单独类型的集合快。
- 提高索引效率
2、命名
我们可以名字来标识集合,下面是一些约束:
- 不能为空字符串,如""
- 不能含有空格
- 不能以system.开头,这是系统保留前缀
- 不能含有特殊字符,如$
组织集合的一种常用惯例是按命名空间划分子集合,比如开发一个博客
三、数据库
数据库包括多个集合,一个实例中包括多个数据库,一般一个应用对应一个数据库。数据库的命名规则:
- 不能是空字符串
- 不能包括空格等特殊字符
- 应该全部小写
- 不能使用系统预留的,如admin,local,config
关于数据库的相关操作:
#查看当前数据库 > db test #切换当前数据库 > use local switched to db local > db local
获得帮助:
> help db.help() help on db methods db.mycoll.help() help on collection methods sh.help() sharding helpers rs.help() replica set helpers help admin administrative help help connect connecting to a db help help keys key shortcuts help misc misc things to know help mr mapreduce show dbs show database names show collections show collections in current database show users show users in current database show profile show most recent system.profile entries with time >= 1ms show logs show the accessible logger names show log [name] prints out the last segment of log in memory, 'global' is default use <db_name> set current database db.foo.find() list objects in collection foo db.foo.find( { a : 1 } ) list objects in foo where a == 1 it result of the last line evaluated; use to further iterate DBQuery.shellBatchSize = x set default number of items to display on shell exit quit the mongo shell >