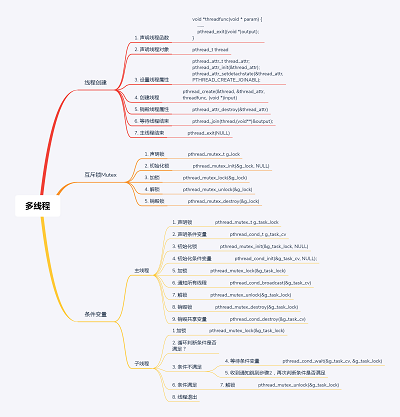
一、为什么要有线程 和 什么是线程?(why and waht)
1.概念:进程相当于一个项目,而线程就是为了完成项目需求,而建立的一个个开发任务。
2.为什么有进程还需线程
2.1资源问题 通信问题 执行问题
-
进程只能在一个时间干一件事,如果想同时干两件事或多件事,进程就无能为力了。
-
进程在执行的过程中如果阻塞,例如等待输入,整个进程就会挂起,即使进程中有些工作不依赖于输入的数据,也将无法执行。
二、如何创建线程?(how)
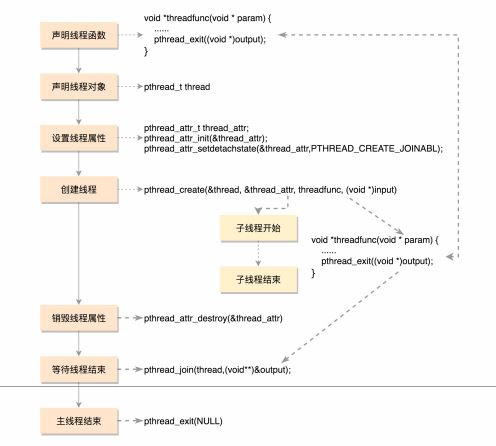
1 #include <pthread.h>
2 #include <stdio.h>
3 #include <stdlib.h>
4
5 #define NUM_OF_TASKS 5
6
7 void *downloadfile(void *filename)
8 {
9 printf("I am downloading the file %s!
", (char *)filename);
10 sleep(10);
11 long downloadtime = rand()%100;
12 printf("I finish downloading the file within %d minutes!
", downloadtime);
13 pthread_exit((void *)downloadtime);
14 }
15
16 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
17 {
18 char files[NUM_OF_TASKS][20]={"file1.avi","file2.rmvb","file3.mp4","file4.wmv","file5
19 pthread_t threads[NUM_OF_TASKS];
20 int rc;
21 int t;
22 int downloadtime;
23
24 pthread_attr_t thread_attr;
25 pthread_attr_init(&thread_attr);
26 pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&thread_attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE);
27
28 for(t=0;t<NUM_OF_TASKS;t++){
29 printf("creating thread %d, please help me to download %s
", t, files[t]);
30 rc = pthread_create(&threads[t], &thread_attr, downloadfile, (void *)files[t]);
31 if (rc){
32 printf("ERROR; return code from pthread_create() is %d
", rc);
33 exit(-1);
34 }
35 }
36
37 pthread_attr_destroy(&thread_attr);
38
39 for(t=0;t<NUM_OF_TASKS;t++){
40 pthread_join(threads[t],(void**)&downloadtime);
41 printf("Thread %d downloads the file %s in %d minutes.
",t,files[t],downloadtime)
42 }
43
44 pthread_exit(NULL);
三、线程特点(how)
线程数据
3.1
第一类是线程栈上的本地数据,比如函数执行过程中的局部变量。前面我们说过,函数的调
用会使用栈的模型,这在线程里面是一样的。只不过每个线程都有自己的栈空间。
3.2
第二类数据就是在整个进程里共享的全局数据。例如全局变量,虽然在不同进程中是隔离
的,但是在一个进程中是共享的。如果同一个全局变量,两个线程一起修改,那肯定会有问
题,有可能把数据改的面目全非。这就需要有一种机制来保护他们,锁机制。
3.3
这就是第三类数据,线程私有数据(Thread Specific Data),
int pthread_setspecific(pthread_key_t key, const void *value) 设置私有数据值
void *pthread_getspecific(pthread_key_t key) 获取私有数据值
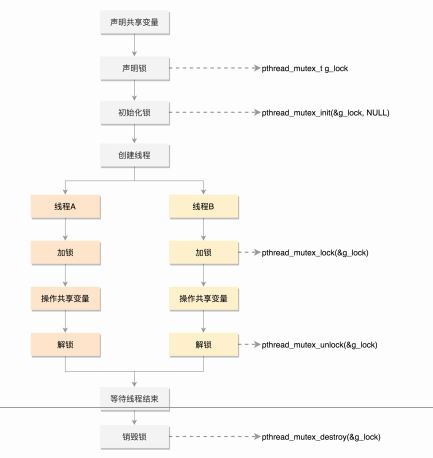
线程数据的保护
一种方式,Mutex,全称 Mutual Exclusion互斥锁
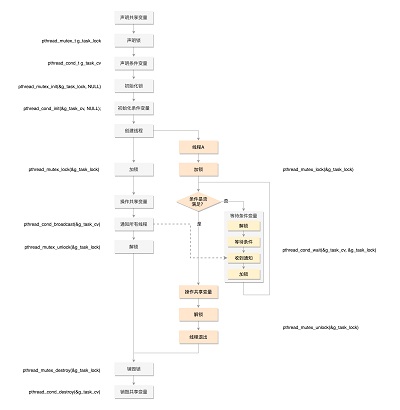
条件变量
总结