PUT /website/blog/123 { "title" : "elasticsearchshi是是什么", "author" : "zhangsan", "titleScore" : 66.666 }
【注意】_source字段在我们检索时非常重要;
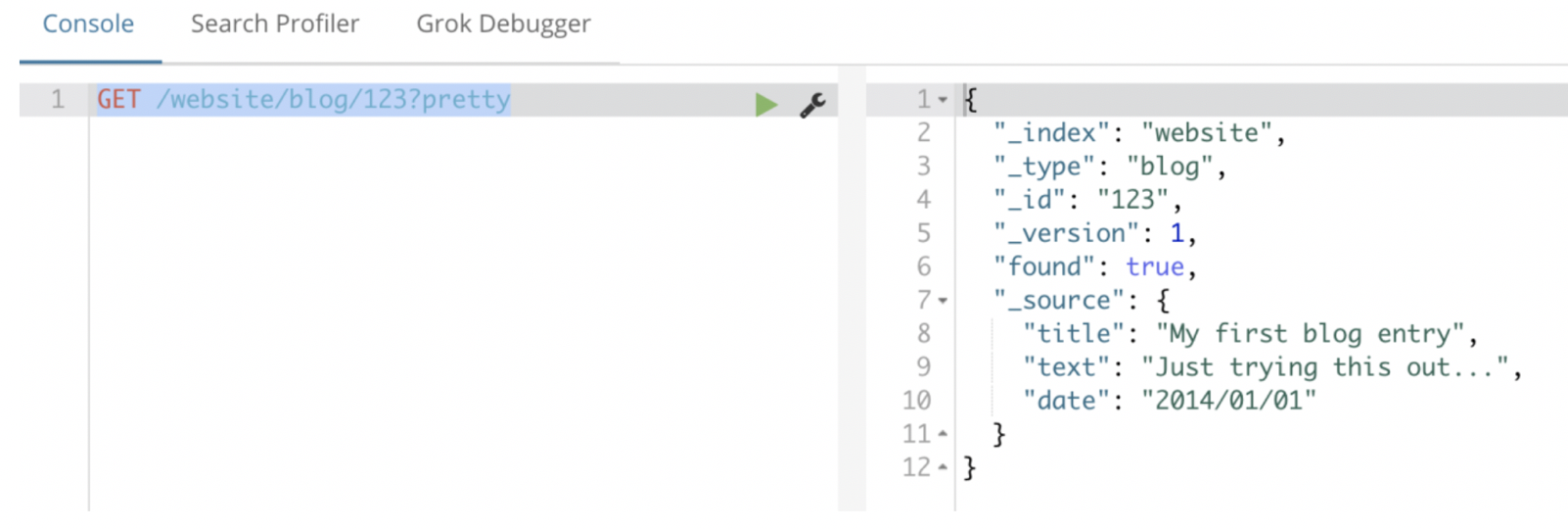
原始文档就是存储在_source中的;
其实我们在elasticsearch中搜索文档,查看文档的内容就是_source中的内容
我们可以在设置mapping的过程中将source字段开启或者关闭:
PUT weisite
{
"mappings":{
"article":{
"_source": {"enabled": true},
"properties":{
"id":{"type": "text", "store": true },
"title":{"type": "text","store": true},
"readCounts":{"type": "integer","store": true},
"times": {"type": "date", "index": "false"}
}
}
}
}
那么source字段有什么作用
| ID _source | 倒排索引 | ID 原始文档 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 {‘我爱中国’} | 我爱[1,2,3] 中国[1] | 1 我爱中国 |
| 2 {‘我爱游戏’} | 游戏[2] | 2 我爱游戏 |
| 3 {‘我爱游戏’} | 爱[1,2,3] | 3 我啥都爱 |
1、如果我们关闭source字段,也就是enable:false,那么在检索过程中会根据关键字比如”游戏”去倒排索引【记录了词项和文档之间的对应关系】中查询文档的ID,但是source字段的enable:false,那么原始文档中没有这些内容,就只能回显文档的ID,字段内容是找不到的
2、如果我们开启source字段,也就是enable:true,那么在检索过程过程中,客户端只需要解析存储的source JSON串,不要通过倒排索引表去检索,仅需要一次IO,就可以返回整个文档的结果
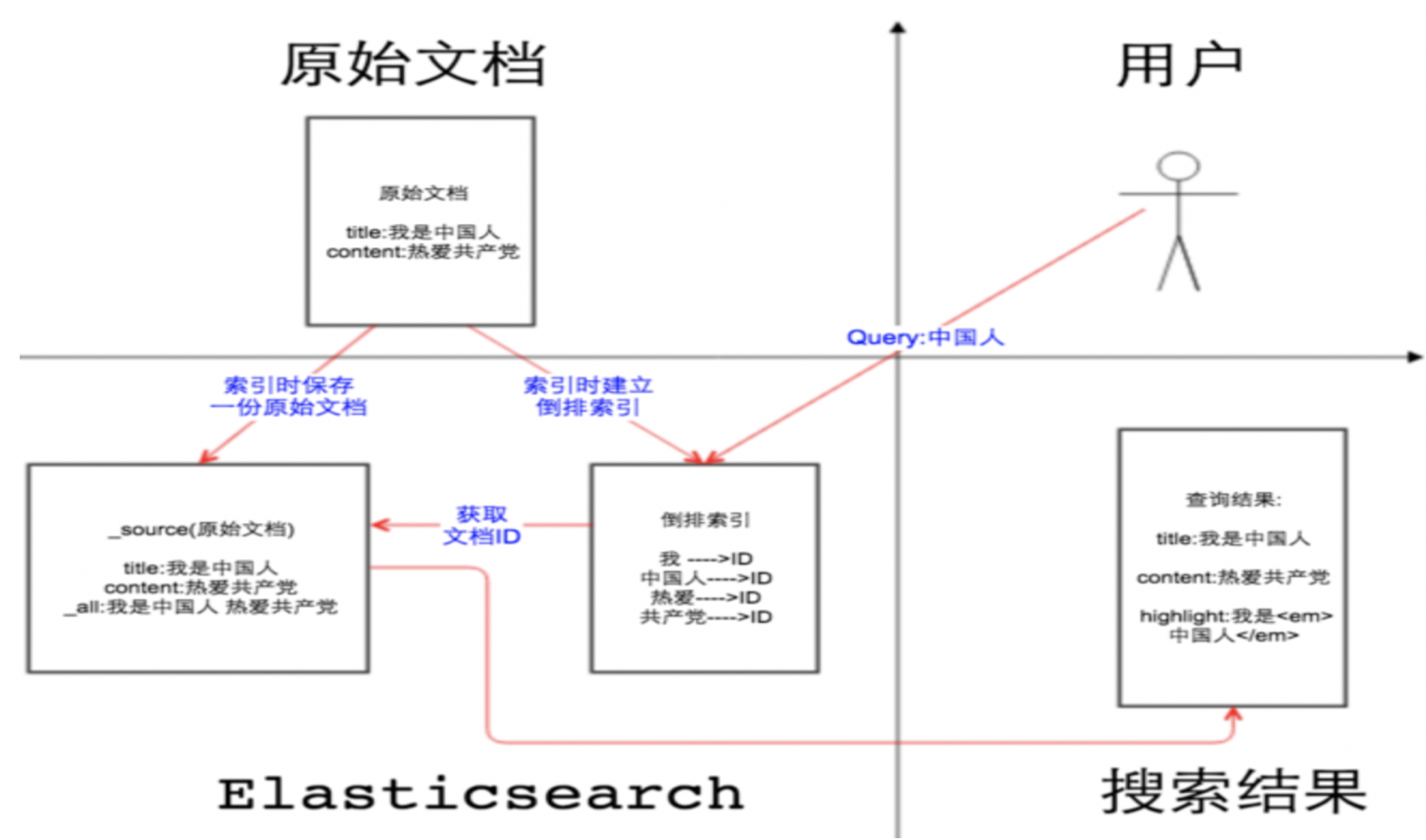
source字段默认是存储的, 什么情况下不用保留source字段?如果某个字段内容非常多,业务里面只需要能对该字段进行搜索,最后返回文档id,查看文档内容会再次到mysql或者hbase中取数据
把大字段的内容存在Elasticsearch中只会增大索引,这一点文档数量越大结果越明显,如果一条文档节省几KB,放大到亿万级的量结果也是非常可观的。
如果想要关闭_source字段,在mapping中的设置如下:
PUT weisite
{
"mappings":{
"article":{
"_source": {"enabled": false},
"properties":{
"id":{"type": "text", "store": true },
"title":{"type": "text","store": true},
"readCounts":{"type": "integer","store": true},
"times": {"type": "date", "index": "false"}
}
}
}
}
GET /weisite/article/1
GET /weisite/article/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "this"
}
}
}
如果只想存储几个字段的原始值,那么在_source属性下还有两个字段:include和exclude:
PUT weisite
{
"mappings":{
"article":{
"_source": {
"includes": [
"title"
],
"excludes": [
"content"
]
},
"properties":{
"id":{"type": "text", "store": true },
"title":{"type": "text","store": true},
"readCounts":{"type": "integer","store": true},
"times": {"type": "date", "index": true},
"content" : {"type" : "text" , "index": true}
}
}
}
}
还有一个store属性:
Store**属性为true的时候会将指定的字段写入索引**(然后查询的时候使用倒排索引去查询,相比_source多一次IO),默认是false的;
其次是,如果想让检索出的字段进行高亮显示,那么(store和source要至少保留一个)