一、缓冲流
1、介绍
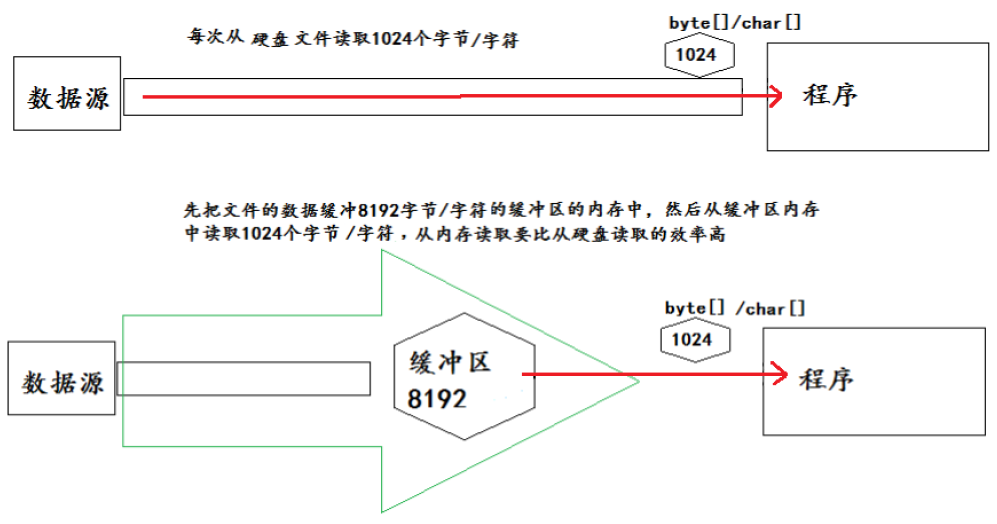
缓冲流:不能直接作用在文件上,需要包一层,它是一种处理流。用于提高文件的读写效率。它在流的基础上对流的功能进行了增强。提高读写速度的原因:内部提供了一个缓冲区。缺省使用 8192 个字节(8Kb)的缓冲区 。
源码示例:BufferedInputStream
1 public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream { 2 // 默认缓冲区的大小 3 private static int DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192; 4 }
要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流。而关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,可以省略。
2、BufferedInputStream,BufferedOutputStream(字节流的缓冲区)
代码示例:用字节流缓冲区处理非文本文件(图片,视频等)。缓冲流复制图片。
1 // 文件:F:\\hello.jpg 2 public class Main { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 try (// 造节点流 6 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((new File("F:\\hello.jpg"))); 7 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("F:\\hello_1.jpg")); 8 // 造缓冲流 9 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); 10 BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);) { 11 12 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; 13 int len; 14 while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) { 15 bos.write(buffer, 0, len); 16 } 17 18 // 刷新缓冲区.必须 19 // bos.flush(); 20 } catch (Exception e) { 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 25 // 用于copy 3.64G 的文件花费 18.925s
3、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter(字符流的缓冲区)
BufferedReader:从字符输入流中读取文本,缓冲各个字符,从而实现字符、数组和行的高效读取。可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者使用默认的大小。在大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
字符读取流缓冲区,该缓冲区提供了一个一次读一行的方法readLine(),方便于对文本数据的获取。当返回null时,表示读到文件末尾。
BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲各个字符,从而提供单个字符、数组和字符串的高效写入。可以指定缓冲区的大小,或者接受默认的大小。在大多数情况下,默认值就足够大了。
该缓冲区中提供了一个跨平台的换行符:newLine()。
代码示例:用字符流缓冲区处理文本文件。缓冲流复制文本文件。
1 // 文件:F:\\hello.txt 2 // 内容:任意 3 4 // 方式一:会自动换行 5 public class Main { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 try ( // 造节点流 9 FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("F:\\hello.txt")); 10 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("F:\\hello_1.txt")); 11 12 // 造缓冲流 13 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); 14 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);) { 15 16 // 使用char[]数组 17 char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; 18 int len; 19 while ((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1) { 20 bw.write(cbuf, 0, len); 21 } 22 23 // bw.flush(); 24 } catch (Exception e) { 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 29 30 // 方式二:不会自动换行 31 public class Main { 32 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 try ( // 造节点流 35 FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("F:\\hello.txt")); 36 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(new File("F:\\hello_1.txt")); 37 38 // 造缓冲流 39 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr); 40 BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);) { 41 42 // 使用readLine(),一次性读一行 43 String data; 44 while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) { 45 // data中不包含换行符,读一行写一行,不会自动换行.若想换行,可以: 46 // 方法一: 47 // bw.write(data + "\n"); 48 49 // 方法二: 50 bw.write(data); 51 bw.newLine(); 52 } 53 54 // bw.flush(); 55 } catch (Exception e) { 56 } 57 } 58 }
4、装饰设计模式
自定义的字符读取流缓冲区myReadLine(),将readLine()方法实现了一次。
代码示例:
1 class MyBufferedReader { 2 private final FileReader fileReader; 3 4 public MyBufferedReader(FileReader fileReader) { 5 this.fileReader = fileReader; 6 } 7 8 public String myReadLine() throws IOException { 9 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); 10 11 int len; 12 while ((len = fileReader.read()) != -1) { 13 if (len == '\r') { 14 continue; 15 } 16 if (len == '\n') { 17 return builder.toString(); 18 } 19 20 builder.append((char) len); 21 } 22 23 if (builder.length() != 0) { 24 return builder.toString(); 25 } 26 27 return null; 28 } 29 30 public void myClose() { 31 try { 32 fileReader.close(); 33 } catch (IOException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 39 // 注意关闭资源 40 // 文件:F:\\hello1.txt 41 // 内容: 42 我有a dream! 43 you need to have a dream!我有a dream! 44 you need to have a dream! 45 public class Main { 46 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 47 MyBufferedReader reader = new MyBufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("F:\\hello1.txt"))); 48 49 String temp; 50 while ((temp = reader.myReadLine()) != null) { 51 System.out.println(temp); 52 } 53 54 reader.myClose(); 55 } 56 } 57 58 // 结果.打印正常
二、转换流
1、介绍
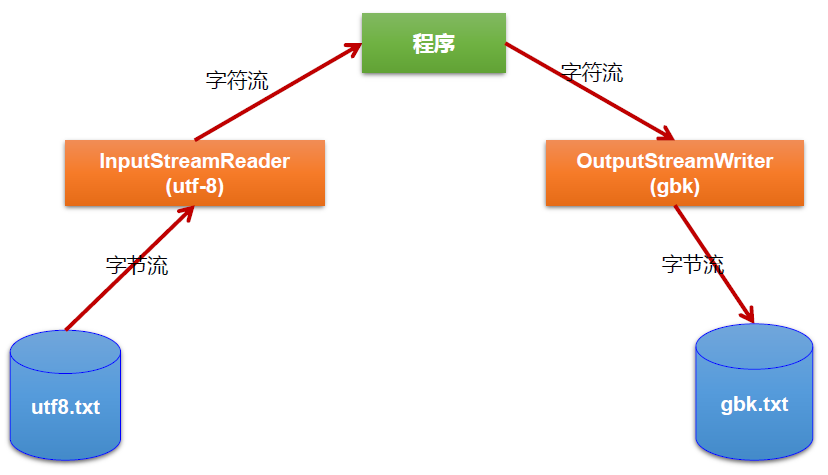
转换流提供了在字节流和字符流之间的转换。
InputStreamReader:将InputStream转换为Reader,实现将字节的输入流按指定字符集转换为字符的输入流。解码。
OutputStreamWriter:将Writer转换为OutputStream,实现将字符的输出流按指定字符集转换为字节的输出流。编码。
很多时候使用转换流来处理文件乱码问题。实现编和解码的功能。
2、InputStreamReader
每次调用InputStreamReader中的一个read()方法都会导致从底层输入流读取一个或多个字节。要启用从字节到字符的有效转换,可以提前从底层流读取更多的字节,使其超过满足当前读取操作所需的字节。
为了达到最高效率,可要考虑在InputStreamReader外套接一层BufferedReader。
键盘录入的标准写法:BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in))
代码示例:读文件。字节流->字符流
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("F:\\hello.txt")); 5 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8");) { 6 7 char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; 8 int len; 9 while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) { 10 String str = new String(cbuf, 0, len); 11 System.out.print(str); 12 } 13 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 } 16 } 17 }
代码示例:读键盘。缓冲流
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 try (// 从标准键盘输入. 5 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));) { 6 7 String line = null; 8 while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { 9 if ("over".equals(line)) { 10 return; 11 } 12 System.out.println(line); 13 } 14 } catch (Exception e) { 15 } 16 } 17 }
3、OutputStreamWriter
每次调用write()方法都会导致在给定字符(或字符集)上调用编码转换器。在写入底层输出流之前,得到的这些字节将在缓冲区中累积。可以指定此缓冲区的大小,不过,默认的缓冲区对数用途来说已足够大。注意,传递给write()方法的字符没有缓冲。
为了获得最高效率,可考虑在OutputStreamWriter外套接一层BufferedWriter。以避免频繁调用转换器。例:
Writer out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out))
代码示例:写文件。字符流->字节流
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("F:\\hello.txt")); 5 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("F:\\hello_1.txt")); 6 7 InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "UTF-8"); 8 OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "gbk");) { 9 10 char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; 11 int len; 12 while ((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1) { 13 osw.write(cbuf, 0, len); 14 } 15 16 isr.close(); 17 osw.close(); 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 } 20 } 21 }
代码示例:读\写键盘。缓冲流
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 5 BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));) { 6 7 String line = null; 8 while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) { 9 if ("over".equalsIgnoreCase(line)) { 10 break; 11 } 12 writer.write(line.toUpperCase()); 13 writer.newLine(); // 换行 14 writer.flush(); 15 } 16 17 reader.close(); 18 writer.close(); 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 } 21 } 22 }
4、字符集
ASCII:美国标准信息交换码。用一个字节的7位可以表示。
ISO8859-1:拉丁码表。欧洲码表。用一个字节的8位表示。
GB2312:中国的中文编码表。最多两个字节编码所有字符
GBK:中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。最多两个字节编码
Unicode:国际标准码,融合了目前人类使用的所有字符。为每个字符分配唯一的字符码。所有的文字都用两个字节来表示。
UTF-8:变长的编码方式,可用1-4个字节来表示一个字符。