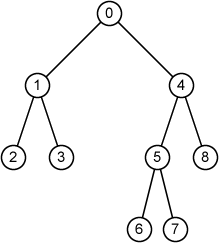
A rooted binary tree is a tree with a root node in which every node has at most two children.
Your task is to write a program which reads a rooted binary tree T and prints the following information for each node u of T:
- node ID of u
- parent of u
- sibling of u
- the number of children of u
- depth of u
- height of u
- node type (root, internal node or leaf)
If two nodes have the same parent, they are siblings. Here, if u and v have the same parent, we say u is a sibling of v (vice versa).
The height of a node in a tree is the number of edges on the longest simple downward path from the node to a leaf.
Here, the given binary tree consists of n nodes and evey node has a unique ID from 0 to n-1.
Input
The first line of the input includes an integer n, the number of nodes of the tree.
In the next n lines, the information of each node is given in the following format:
id left right
id is the node ID, left is ID of the left child and right is ID of the right child. If the node does not have the left (right) child, the left(right) is indicated by -1.
Output
Print the information of each node in the following format:
node id: parent = p , sibling = s , degree = deg, depth = dep, height = h, type
p is ID of its parent. If the node does not have a parent, print -1.
s is ID of its sibling. If the node does not have a sibling, print -1.
deg, dep and h are the number of children, depth and height of the node respectively.
type is a type of nodes represented by a string (root, internal node or leaf. If the root can be considered as a leaf or an internal node, print root.
Please follow the format presented in a sample output below.
Constraints
- 1 ≤ n ≤ 25
Sample Input 1
9 0 1 4 1 2 3 2 -1 -1 3 -1 -1 4 5 8 5 6 7 6 -1 -1 7 -1 -1 8 -1 -1
Sample Output 1
node 0: parent = -1, sibling = -1, degree = 2, depth = 0, height = 3, root node 1: parent = 0, sibling = 4, degree = 2, depth = 1, height = 1, internal node node 2: parent = 1, sibling = 3, degree = 0, depth = 2, height = 0, leaf node 3: parent = 1, sibling = 2, degree = 0, depth = 2, height = 0, leaf node 4: parent = 0, sibling = 1, degree = 2, depth = 1, height = 2, internal node node 5: parent = 4, sibling = 8, degree = 2, depth = 2, height = 1, internal node node 6: parent = 5, sibling = 7, degree = 0, depth = 3, height = 0, leaf node 7: parent = 5, sibling = 6, degree = 0, depth = 3, height = 0, leaf node 8: parent = 4, sibling = 5, degree = 0, depth = 2, height = 0, leaf
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=100; const int NIL=-1; struct Node { int par,left,right; }; Node T[maxn]; int D[maxn],H[maxn]; void setDepth(int u,int d)//求结点的深度 { if(u==NIL) return ; D[u]=d; setDepth(T[u].left,d+1); setDepth(T[u].right,d+1); } int setHeight(int u)//结点的高 { int h1=0,h2=0; if(T[u].left!=NIL) h1=setHeight(T[u].left)+1; if(T[u].right!=NIL) h2=setHeight(T[u].right)+1; return H[u]=h1>h2?h1:h2; } int getSibling(int u)//返回兄弟结点 { if(T[u].par==NIL) return NIL; if(T[T[u].par].left!=u&&T[T[u].par].left!=NIL) return T[T[u].par].left; if(T[T[u].par].right!=u&&T[T[u].par].right!=NIL) return T[T[u].par].right; return NIL; } void print(int u) { cout<<"node "<<u<<": "; cout<<"parent = "<<T[u].par<<", "; cout<< "sibling = " <<getSibling(u)<<", "; int deg=0; if(T[u].left!=NIL) deg++; if(T[u].right!=NIL) deg++; cout<<"degree = "<<deg<<", "; cout<<"depth = "<<D[u]<<", "; cout<<"height = "<<H[u]<<", "; if(T[u].par==NIL) cout<<"root"<<endl; else if(T[u].left==NIL&&T[u].right==NIL) cout<<"leaf"<<endl; else cout<<"internal node"<<endl; } int main() { int n; cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) T[i].par=NIL; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { int v,l,r; cin>>v>>l>>r; T[v].left=l; T[v].right=r; if(l!=NIL) T[l].par=v; if(r!=NIL) T[r].par=v; } int root=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) if(T[i].par==NIL) root=i; setDepth(root,0); setHeight(root); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) print(i); return 0; }