前言
最近在学习网络编程,用到几个应该比较常用的网络编程函数,所以写篇博客来记录一下,毕竟学得快忘得也快。国庆节在宿舍写着博客看着各个景点人山人海倒也快哉~
gethostbyname( )
这个函数可以返回给定域名的域名信息。
参数:域名
返回值:
- 一个 hostent 结构体的地址(也就是一个指向 hostent 结构体的指针)
- 0(如果域名不能解析成 IP 地址)
从netdb.h头文件我们可以找到 hostent 结构体的说明:
struct hostent {
char *h_name; /*official host name */
char **h_aliases; /*other aliases */
int h_addrtype; /*address type */
int h_length; /* address length */
char **h_addr_list; /* list of addresses */
};
#define h_addr h_addr_list[0]
上面结构体中的 **h_addr_list 是一个二进制整数的链表,输出的时候要用 inet_ntop( ) 函数转换成点分十进制。
inet_ntop( )
inet_ntop( ) 和 inet_ntop( ) 都是IP地址转换函数,可以在将IP地址在“二进制整数”和“点分十进制”之间转换。而且,这2个函数能够处理 ipv4 和 ipv6 。
const char *inet_ntop(int af, const void *src, char *dst, socklen_t cnt);
这个函数转换网络二进制结构到ASCII类型的地址,参数的作用和inet_pton相同,只是多了一个参数 socklen_t cnt ,他是所指向缓存区 dst 的大小,避免溢出,如果缓存区太小无法存储地址的值,则返回一个空指针,并将 errno 置为 ENOSPC 。
现在那就来实战一下吧:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct hostent *hptr;
char *name, **pptr, str[32];
int count = 0;
if (argc < 2) {
printf("The arguments is not enough!");
return -1;
}
name = argv[1];
hptr = gethostbyname(name);
if (hptr) {
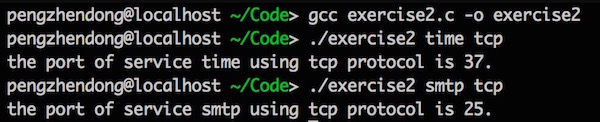
printf("the offical name is %s.\n", hptr->h_name);
for(pptr = hptr->h_aliases; *pptr != NULL; pptr++) {
printf("the alias name is %s\n", *pptr);
}
switch (hptr->h_addrtype) {
case AF_INET:
printf("the address type is AF_INET.\n");
break;
case AF_INET6:
printf("the address type is AF_INET6.\n");
break;
default:
break;
}
printf("the address length is %d Bytes.\n", hptr->h_length);
for (pptr = hptr->h_addr_list; *pptr != NULL; pptr++) { //**pptr后移四个字节,即地址后移四位
count ++;
printf("the %dth address is %s.\n", count, inet_ntop(hptr->h_addrtype, *pptr, str, sizeof(str))); //即将转换成的点分十进制存到字符串 str 中返回,溢出则返回空指针
}
} else {
printf("Error!\n");
}
return 0;
}
编译运行:
getservbyname
这个函数可以返回给定服务名和协议名的相关服务信息。
参数:服务名和协议名
返回值:
- 一个指向 servent 结构体的指针
- 空指针(发生错误)
从netdb.h头文件我们可以找到 hostent 结构体的说明:
struct servent {
char *s_name; /*official service name */
char **s_aliases; /*other aliases */
int s_port; /*port for this service */
char **s_proto; /* protocol to use */
};
返回的结构体中的端口号是按网络字节顺序保存的整数,输出的时候要用 ntohs() 函数转换按主机顺序保存的整数。
ntohs( )
网络字节顺序NBO(Network Byte Order):按从高到低的顺序存储,在网络上使用统一的网络字节顺序,可以避免兼容性问题。
主机字节顺序(HBO,Host Byte Order):不同的机器HBO不相同,与CPU设计有关,数据的顺序是由cpu决定的,而与操作系统无关。
网络字节顺序与本地字节顺序之间的转换函数:
htonl()--"Host to Network Long"
ntohl()--"Network to Host Long"
htons()--"Host to Network Short"
ntohs()--"Network to Host Short"
现在就来实战一下吧:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <netdb.h>
int main (int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct servent *sptr;
char *service, *protocol;
if (argc < 3) {
printf("The arguments is not enough!\n");
return -1;
}
service = argv[1];
protocol = argv[2];
sptr = getservbyname(service, protocol);
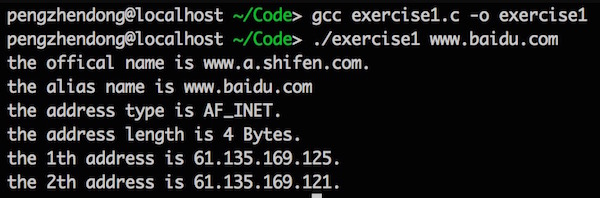
if (sptr) {
printf("the port of service %s using %s protocol is %d.\n", sptr->s_name, protocol, ntohs(sptr->s_port)); //将网络字节顺序的端口值转换成主机顺序
} else {
printf("Error!\n");
}
return 0;
}
编译运行: