程序来自莫烦Python,略有删减和改动。
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torchvision
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
# Hyper Parameters
EPOCH = 1
BATCH_SIZE = 50
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False
# Mnist digits dataset
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'): # not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir. (./表示当前目录)
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
train_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(
root='./mnist/',
train=True, # this is training data
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to torch.FloatTensor of
# shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST,
)
print('train dataset shape: ', train_data.data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)
print('train dataset lable shape:', train_data.targets.size()) # (60000)
# plot one example
# plt.imshow(train_data.data[0].numpy(), cmap='gray')
# plt.title('%i' % train_data.targets[0])
# plt.show()
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (BATCH_SIZE, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
# pick 2000 samples to speed up testing
test_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./mnist/', train=False)
test_x = torch.unsqueeze(test_data.data, dim=1).type(torch.FloatTensor)[:2000]/255. # shape from (2000, 28, 28) to (2000, 1, 28, 28), value in range(0,1)
test_y = test_data.targets[:2000]
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2), # output shape (16, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2), # output shape (16, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 14, 14)
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2), # output shape (32, 7, 7)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # flatten the output of conv2 to (batch_size, 32 * 7 * 7)
output = self.out(x) # output shape (batch_size, 10)
return output
cnn = CNN()
print('CNN architecture:
', cnn)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# training and testing
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for iteration, (b_x, b_y) in enumerate(train_loader):
output = cnn(b_x) # cnn output, the size of b_x is ([batchsize, channel, height, width)
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # back propagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
if iteration % 100 == 0:
test_output = cnn(test_x)
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
accuracy = float((pred_y == test_y.data.numpy()).sum()) / float(test_y.size(0))
print('Epoch:{:<2d} | Iteration:{:<4d} | Train loss: {:6.3f} | Test accuracy: {:4.2f}'.format(epoch, iteration, loss.data.numpy(), accuracy))
# print 10 predictions from test data
test_output = cnn(test_x[:10])
pred_y = torch.max(test_output, 1)[1].data.numpy()
print(pred_y, 'prediction number')
print(test_y[:10].numpy(), 'real number')
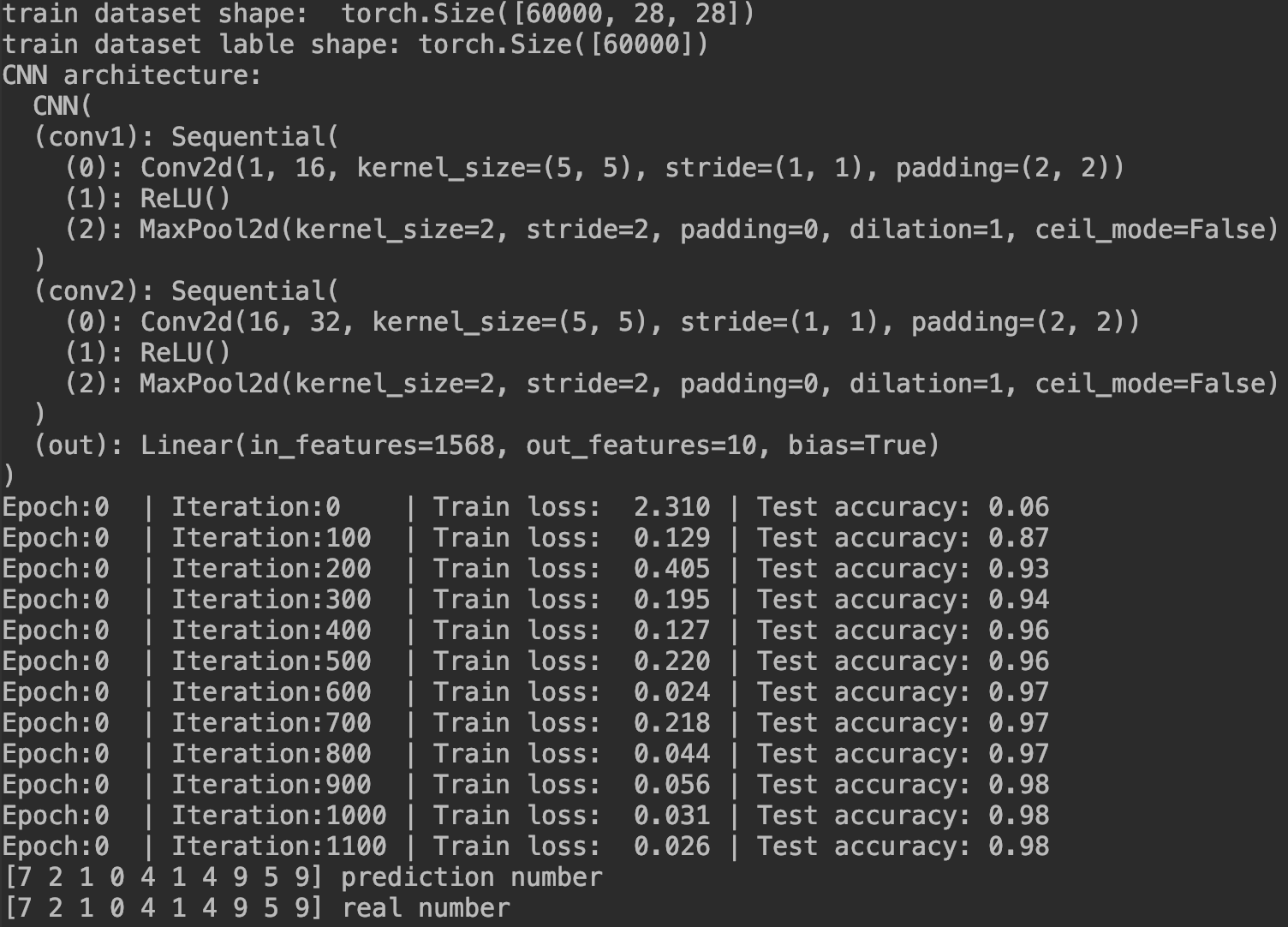
运行结果: