零、洛谷链接
一、简要题意
给你一张图,要找出所有八连通的连通块,规定不管旋转、翻转后,只要相同的两个连通块算为同一种连通块。
对相同连通块染相同一个小写字母,按字典序输出染色后的图。
下面八个全为同一种连通块。
二、解法 + code
我们可以看出,本题最大的难点在于如何判断相似。
根据小学玄学知识&样例,我们有一些发现:
两个相似的图,从同一个点到别的点的直线距离(曼哈顿距离)相等。
来张图:
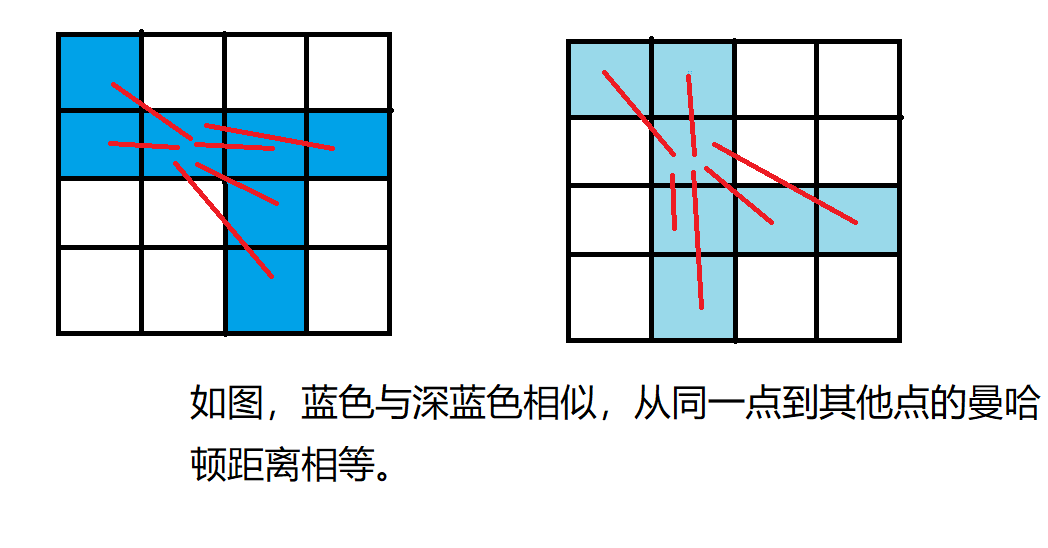
但是,我们在走连通块时,由于旋转和翻转的关系,并不能保障任意选择两点就是同一个点。
一看数据范围:(n≤100)
因此,可以将所有的点到其他点的曼哈顿距离都算出来,再加在一块求和,以这个数值作为比较相似的因素即可。
似乎是解决了?
快乐地把代码写出来♪:
// 仅放核心代码:
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
rep(i, 1, n)
{
rep(j, 1, m)
{
cin >> mapp[i][j];
}
}
rep(i, 1, n)
{
rep(j, 1, m)
{
if(mapp[i][j] == '1')
{
tempcnt = 0;
long long tempsum = 0;
bfs(i, j);
rep(k, 1, tempcnt)
{
rep(l, 1, tempcnt)
{
tempsum += sqrt(abs(temp[k].x - temp[l].x) * abs(temp[k].x - temp[l].x) + abs(temp[k].y - temp[l].y) * abs(temp[k].y - temp[l].y));
}
// cout << tempsum << endl;
}
// cout << "tempcnt:" << tempcnt << endl;
int f = 0;
rep(k, 1, cnt)
{
if(tempsum == hhash[k])
{
f = 1;
color(i, j, k);
break;
}
}
if(!f)
{
hhash[++cnt] = tempsum;
// cout << cnt << endl;
color(i, j, cnt);
}
}
}
}
rep(i, 1, n)
{
rep(j, 1, m)
{
printf("%c", mapp[i][j]);
}
printf("
");
}
return 0;
}
结果:
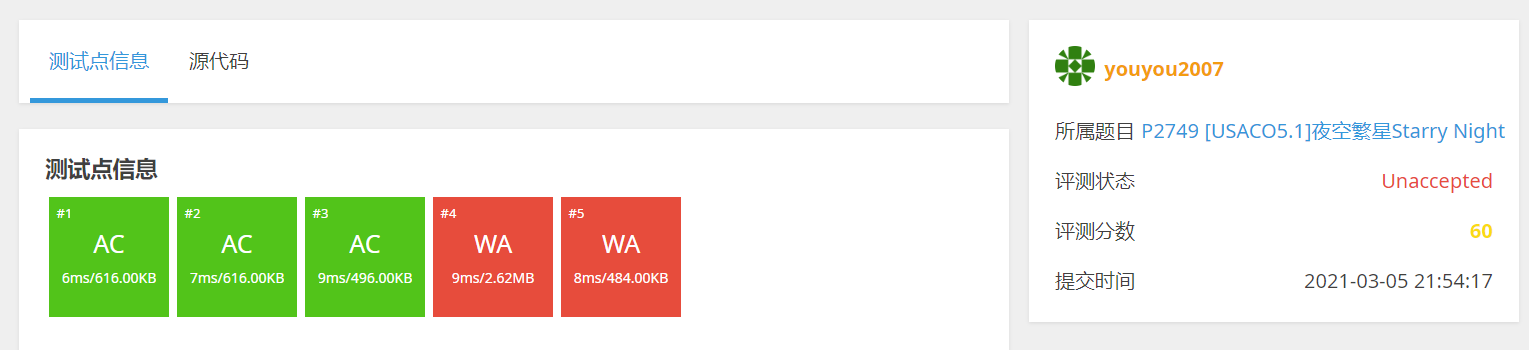
干得漂亮,有60分了
我们再来思考:因为曼哈顿距离带了根号,而这个代码里面全部取整了,所以两个仅有一点差别的图就会挂掉。、
所以带个double试试?
// by pjx Feb.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#define REP(i, x, y) for(register int i = x; i < y; i++)
#define rep(i, x, y) for(register int i = x; i <= y; i++)
#define PER(i, x, y) for(register int i = x; i > y; i--)
#define per(i, x, y) for(register int i = x; i >= y; i--)
using namespace std;
const int N = 605;
int n, m, tempcnt;
char mapp[N][N];
double hhash[N], tempsum;
int cnt;
int dx[] = {0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};//八个方向
int dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
queue <int> qx, qy;
struct node{//用来存连通块每个点的坐标
int x, y;
}temp[N * N];
void bfs(int x, int y)//搜索连通块
{
temp[++tempcnt].x = x;
temp[tempcnt].y = y;
qx.push(x);
qy.push(y);
mapp[x][y] = '2';//如果搜到了一个点,那把它标记为未染色过但搜索过
while(!qx.empty())
{
int tx = qx.front();
int ty = qy.front();
qx.pop();
qy.pop();
rep(i, 1, 8)
{
int xx = tx + dx[i];
int yy = ty + dy[i];
if(xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= m && mapp[xx][yy] == '1')
{
mapp[xx][yy] = '2';
qx.push(xx);
qy.push(yy);
temp[++tempcnt].x = xx;
temp[tempcnt].y = yy;
}
}
}
}
void color(int x, int y, int word)//给这个图重新染色
{
qx.push(x);
qy.push(y);
mapp[x][y] = char(word + 'a' - 1);
while(!qx.empty())
{
int tx = qx.front();
int ty = qy.front();
qx.pop();
qy.pop();
rep(i, 1, 8)
{
int xx = tx + dx[i];
int yy = ty + dy[i];
if(xx >= 1 && xx <= n && yy >= 1 && yy <= m && mapp[xx][yy] == '2')
{
mapp[xx][yy] = char(word + 'a' - 1);
qx.push(xx);
qy.push(yy);
}
}
}
}
bool check()//判断两个连通块是否为同一种
{
tempsum = 0.0000;
for(int k = 1; k <= tempcnt; k++)
{
for(int l = 1; l <= tempcnt; l++)
{
tempsum += sqrt(double(abs(temp[k].x - temp[l].x)) * double(abs(temp[k].x - temp[l].x)) + double(abs(temp[k].y - temp[l].y)) * double(abs(temp[k].y - temp[l].y)));
//因为带根号,为了更加精确,保留4位小数
}
}
for(int k = 1; k <= cnt; k++)
{
if(abs(tempsum - hhash[k]) <= 0.0001)//如果以前找到过与其总和一样的,就表明是第k种连通块
{
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
rep(i, 1, n)
{
rep(j, 1, m)
{
cin >> mapp[i][j];
}
}
rep(i, 1, n)
{
rep(j, 1, m)
{
if(mapp[i][j] == '1')
{
tempcnt = 0;
bfs(i, j);
if(check())
{
for(int k = 1; k <= cnt; k++)
{
if(abs(tempsum - hhash[k]) <= 0.0001)//如果以前找到过与其总和一样的,就表明是第k种连通块
{
color(i, j, k);//染第k种颜色
break;
}
}
}
else//否则,增加新的一种,染新的一种颜色
{
hhash[++cnt] = double(tempsum);
color(i, j, cnt);
}
}
}
}
rep(i, 1, n)
{
rep(j, 1, m)
{
printf("%c", mapp[i][j]);
}
printf("
");
}
return 0;
}
nice过了