可重复利用的线程(关于队列计数器,可参考这里)
from queue import Queue from threading import Thread class MyThread(Thread): # 继承线程类 def __init__(self): super().__init__() # 继承类中的属性 self.queue = Queue() # 重写属性 self.daemon = True # 设置守护线程 self.start() # 实例化直接开启线程 def run(self): # 子线程 while True: task, args, kwargs= self.queue.get() # 从队列中取出函数体 task(*args, **kwargs) # 调用函数 self.queue.task_done() # 告诉queue这个任务完成 def apply_async(self, task, args=(), kwargs={}): # 将函数放进队列中 self.queue.put((task, args, kwargs)) # 放入队列中属性 def join(self): # 等待所有的线程任务处理完毕 self.queue.join() # 重写成等待队列计数器是否为0 def func(*args, **kwargs): print('生产了100') print(args, kwargs) def func1(): print('消费了100') mythread = MyThread() mythread.apply_async(func, args=(1, 2), kwargs={'name':'fuck', 'age':19}) mythread.apply_async(func1) # 调用多少次都可以 mythread.join() # 线程守护,主线程执行完毕,子线程会全部关闭 --> 生产了100 (1, 2) {'name': 'fuck', 'age': 19} 消费了100 Process finished with exit code 0
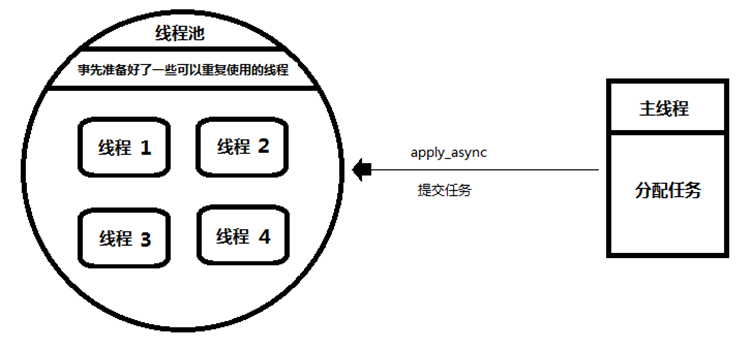
主线程:相当于生产者,只管向线程提交任务,并不关心线程是如何执行任务的。因此,并不关心是哪一个线程执行的
线程池:相当于消费者,负责接收任务,将任务分配到空心的线程中去执行
1 import threading, time 2 from queue import Queue 3 from threading import Thread 4 5 6 class ThreadPool: 7 def __init__(self, n): 8 self.queue = Queue() 9 for i in range(n): 10 Thread(target=self.run, # 开启线程调用的函数 11 args=(self.queue, ), # 注意传入的是元组 12 daemon=True, # 线程守护 13 ).start() # 初始化实例直接开启线程 14 15 def run(self, queue): # 线程内容 16 while True: 17 task = self.queue.get() # 取出队列的函数体 18 task() # 调用函数 19 self.queue.task_done() # 告诉队列任务执行完毕 20 21 def apply_async(self, task): 22 self.queue.put(task) # 函数加入队列 23 24 def join(self): 25 self.queue.join() 26 27 def func(): 28 time.sleep(3) 29 print('子线程开启成功') 30 print(threading.current_thread()) 31 32 33 threadpool = ThreadPool(4) 34 threadpool.apply_async(func) 35 threadpool.apply_async(func) 36 threadpool.apply_async(func) 37 threadpool.apply_async(func) 38 threadpool.apply_async(func) 39 threadpool.apply_async(func) 40 threadpool.apply_async(func) 41 threadpool.join() 42 43 44 --> 45 3秒后 46 子线程开启成功 47 <Thread(Thread-1, started daemon -1223038144)> 48 子线程开启成功 49 <Thread(Thread-2, started daemon -1233126592)> 50 子线程开启成功 51 <Thread(Thread-3, started daemon -1243612352)> 52 子线程开启成功 53 <Thread(Thread-4, started daemon -1254098112)> 54 3秒后 55 子线程开启成功 56 <Thread(Thread-2, started daemon -1233126592)> 57 子线程开启成功 58 <Thread(Thread-1, started daemon -1223038144)> 59 子线程开启成功 60 <Thread(Thread-3, started daemon -1243612352)> 61 62 Process finished with exit code 0
python自带池
python其实自己就有池的库,进程导入方法:from multiprocessing import Pool
线程导入方法:from multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool
线程:
from multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool # 导入线程池的包 def func(): print('pywjh') def func2(*args, **kwargs): print(args, kwargs) pool = ThreadPool(4) pool.apply_async(func) pool.apply_async(func2, args=('hello', 'world'), # 元组 kwds={'name':'pywjh', 'age':22} # 注意此处用的是kwds ) pool.close() # python池中的close要在join之前 pool.join() --> pywjh ('hello', 'world') {'name': 'pywjh', 'age': 22} Process finished with exit code 0
进程:跟线程一模一样
from multiprocessing import Pool # 导入进程池的包 def func(): print('pywjh') def func2(*args, **kwargs): print(args, kwargs) pool = Pool(4) pool.apply_async(func) pool.apply_async(func2, args=('hello', 'world'), # 元组 kwds={'name':'pywjh', 'age':22} # 注意此处用的是kwds ) pool.close() # python池中的close要在join之前 pool.join() --> pywjh ('hello', 'world') {'age': 22, 'name': 'pywjh'} Process finished with exit code 0
用进程池和线程池实现并发的服务器
1 from socket import socket 2 from multiprocessing import Pool, cpu_count 3 from multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool 4 5 def process_accept(server): # 进程运行 6 thread_pool = ThreadPool(n) # 有多少CPU开多少线程 7 while True: 8 conn, addr = server.accept() # 创建连接 9 thread_pool.apply_async(thread_recv, args=(conn, )) # 往线程池中扔函数 10 11 12 def thread_recv(conn): # 线程运行 13 while True: 14 recv_date = conn.recv(1024).decode() 15 if recv_date: 16 print(recv_date) 17 conn.send(recv_date.encode()) 18 else: 19 conn.close() 20 break 21 22 server = socket() 23 server.bind(('', 8899)) 24 server.listen(200) 25 26 n = cpu_count() # 获取cpu数量 27 pool = Pool(n) # 有多少CPU开多少进程池 28 for i in range(n): 29 pool.apply_async(process_accept, args=(server, )) # 往进程池中扔函数 30 pool.close() 31 pool.join()
补充:
往线程池/进程池中扔的函数,如果以return返回结果,需要用.get()取出结果
1 from multiprocessing import Pool 2 3 4 def func(): 5 return 'hello world' 6 7 8 pool = Pool(4) 9 result = pool.apply_async(func) # 将returen结果传给result 10 print(result) 11 print(result.get()) # 用.get()方法取出 12 13 14 pool.close() # python池中的close要在join之前 15 pool.join() 16 17 --> 18 <multiprocessing.pool.ApplyResult object at 0xb7038a0c> 19 hello world 20 21 Process finished with exit code 0