决策树优特点:
优点:计算复杂度不高,输出结果易于理解,对中间值的缺失不敏感,可以处理不相关特
征数据。
缺点:可能会产生过度匹配问题。
适用数据类型:数值型和标称型
使用ID3算法划分数据集并构建决策树:
from math import log import pickle #计算香农熵 def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): numEntries = len(dataSet) labelCounts = { } # 统计每个label数据集的个数 for featVec in dataSet: currentLabel = featVec[-1] if(currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys()): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0 labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 # 计算香农熵 shannonEnt = 0.0 for key in labelCounts: prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / float(numEntries); shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2) return shannonEnt #creat data set just for test funcations def creatDataSet(): dataSet = [[1, 1, 'yes'], [1, 1, 'yes'], [1, 0, 'no'], [0, 1, 'no'], [0, 1, 'no']] labels = ['no surfacing', 'flippers'] return dataSet, labels # 按照给定特征 和 特征值 划分数据集(提取数据集) def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value): retDataSet = [] for i in dataSet: if i[axis] == value: dataTemp = i[:axis] dataTemp.extend(i[axis+1:]) retDataSet.append(dataTemp) return retDataSet # 利用信息增益寻找最好的数据集划分方式,返回最适合特征值的索引 def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 # 初始信息熵 baseShannonEnt = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) # 最大信息熵 bestInfoGain = 0.0 # 最好特征值 bestFeature = -1 # 寻找使得信息增益最大的划分方式 for i in range(numFeatures): featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet] uniqueFeatList = set(featList) newEnt = 0.0 for feature in uniqueFeatList: subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, feature) prob = float(len(subDataSet)) / float(len(dataSet)) newEnt += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) infoGain = baseShannonEnt - newEnt if(infoGain > bestInfoGain): bestInfoGain = infoGain bestFeature = i return bestFeature # 当特征值被消耗完,但是剩余数据集并不是同一类时,进行投票 def majorityCnt(classList): classCount = { } for i in classList: if (i not in classCount.keys()): classCount[i] = 0 classCount[i] += 1 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = lambda item:item[1], reverse = True) return sortedClassCount[0][0] # 构造决策树 def creatTree(dataSet, label): labels = label[:] classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] # 类别完全相同时,停止划分, 返回类别 if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): return classList[0] # 当所有特征都已经被消耗完毕 if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: return majorityCnt(classList) # 寻找最好的划分特征值 bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{ }} del(labels[bestFeat]) featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] uniqueFeatValues = set(featValues) for value in uniqueFeatValues: subLabels = labels[:] myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = creatTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), subLabels) return myTree # 使用构造好的决策树对测试集进行分类 def classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVector): firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0] secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr) for key in secondDict.keys(): if testVector[featIndex] == key: if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': classType = classify(secondDict[key], featLabels, testVector) else: classType = secondDict[key] return classType # 存储决策树 def storeTree(inputTree, fileName): fw = open(fileName, 'wb') pickle.dump(inputTree, fw) fw.close() #读取决策树 def grabTree(fileName): fr = open(fileName, 'rb') return pickle.load(fr) fr = open("lenses.txt") allLines = fr.readlines() lensesDataSet = [line.strip().split(' ') for line in allLines] lensesLabels = ['age', 'prescript', 'astigmatic', 'rearRate'] lensesTree = creatTree(lensesDataSet, lensesLabels)
利用matplotlib注解绘制树形图:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pickle decisionNode = dict(boxstyle = "sawtooth", fc = "0.8") leafNode = dict(boxstyle = "round4", fc = "0.8") arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle = "<-") def retrieveTree(i): listOfTrees =[{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}}, {'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: {'head': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}, 1: 'no'}}}} ] return listOfTrees[i] def getNumLeafs(myTree): numLeafs = 0 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) else: numLeafs +=1 return numLeafs def getTreeDepth(myTree): maxDepth = 0 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) else: thisDepth = 1 if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth return maxDepth def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType): createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args ) def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString): xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0] yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1] createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):#if the first key tells you what feat was split on numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #this determines the x width of this tree depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] #the text label for this node should be this cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) secondDict = myTree[firstStr] plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':#test to see if the nodes are dictonaires, if not they are leaf nodes plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #recursion else: #it's a leaf node print the leaf node plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode) plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key)) plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD #if you do get a dictonary you know it's a tree, and the first element will be another dict def createPlot(inTree): fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white') fig.clf() axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[]) createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #no ticks #createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0; plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '') plt.show() # 存储决策树 def storeTree(inputTree, fileName): fw = open(fileName, 'wb') pickle.dump(inputTree, fw) fw.close() #读取决策树 def grabTree(fileName): fr = open(fileName, 'rb') return pickle.load(fr) myTree = grabTree('lensesTree.txt') createPlot(myTree)
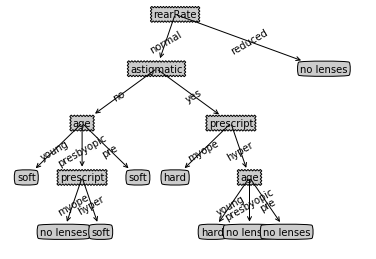
数据集下载以及完整jupyter notebook 代码下载:
https://github.com/qwqwqw110/machineLearningInactionCode/tree/master/%E5%86%B3%E7%AD%96%E6%A0%91