Python 3 模块
一、 time模块 时间模块
在Python中,通常有这几种方式来表示时间:
1、1 时间戳(timestamp): 通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。我们运行“type(time.time())”,返回的是float类型。
1、2 格式化的时间字符串(Format String)
1、3 结构化的时间(struct_time): struct_time元组共有9个元素共九个元素:(年,月,日,时,分,秒,一年中第几周,一年中第几天,夏令时)
import time print(time.time()) # 1502348532.8084362 print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X')) #格式化的时间字符串 2017-08-10 15:02:12 print(time.localtime()) #本地时区的struct_time print(time.gmtime()) #UTC区的struct_time
其中计算机认识的时间只能是'时间戳'格式,而程序员可处理的或者说人类能看懂的时间有: '格式化的时间字符串','结构化的时间' ,于是有了下图的转换关系
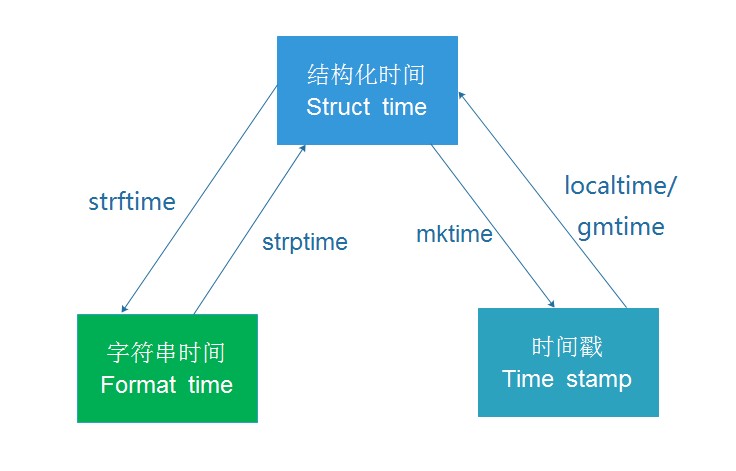
#--------------------------按图1转换时间
# localtime([secs]) # 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。secs参数未提供,则以当前时间为准。 time.localtime() time.localtime(1473525444.037215) # gmtime([secs]) 和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()方法是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time。 # mktime(t) : 将一个struct_time转化为时间戳。 print(time.mktime(time.localtime()))#1473525749.0 # strftime(format[, t]) : 把一个代表时间的元组或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和 # time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t未指定,将传入time.localtime()。如果元组中任何一个 # 元素越界,ValueError的错误将会被抛出。 print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.localtime()))#2016-09-11 00:49:56 # time.strptime(string[, format]) # 把一个格式化时间字符串转化为struct_time。实际上它和strftime()是逆操作。 print(time.strptime('2011-05-05 16:37:06', '%Y-%m-%d %X')) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2011, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=5, tm_hour=16, tm_min=37, tm_sec=6, # tm_wday=3, tm_yday=125, tm_isdst=-1) #在这个函数中,format默认为:"%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y"。

#--------------------------按图2转换时间
# asctime([t]) : 把一个表示时间的元组或者struct_time表示为这种形式:'Sun Jun 20 23:21:05 1993'。 # 如果没有参数,将会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。 print(time.asctime())#Sun Sep 11 00:43:43 2016 # ctime([secs]) : 把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为 # None的时候,将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))。 print(time.ctime()) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016 print(time.ctime(time.time())) # Sun Sep 11 00:46:38 2016 1 #--------------------------其他用法 2 # sleep(secs) 3 # 线程推迟指定的时间运行,单位为秒。
二、random模块
import random print(random.random())#(0,1)----float 大于0且小于1之间的小数 print(random.randint(1,3)) #[1,3] 大于等于1且小于等于3之间的整数 print(random.randrange(1,3)) #[1,3) 大于等于1且小于3之间的整数 print(random.choice([1,'23',[4,5]]))#1或者23或者[4,5] print(random.sample([1,'23',[4,5]],2))#列表元素任意2个组合 print(random.uniform(1,3))#大于1小于3的小数,如1.927109612082716 item=[1,3,5,7,9] random.shuffle(item) #打乱item的顺序,相当于"洗牌" print(item)

import random def make_code(n): res='' for i in range(n): s1=chr(random.randint(65,90)) # 大写字母 关键是chr能够把数字转化成ASCII s2=str(random.randint(0,10)) # 随机生成0-9的数字 res+=random.choice([s1,s2]) # 从列表中随机取 return res print(make_code(9))
三、os模块
os模块是与操作系统交互的接口

os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.') os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..') os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录 os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推 os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 os.remove() 删除一个文件 os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录 os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息 os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\",Linux下为"/" os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为" ",Linux下为" " os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串 win下为;,Linux下为: os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix' os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示 os.environ 获取系统环境变量 os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径 os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回 os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素 os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素 os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略 os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间 os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间 os.path.getsize(path) 返回path的大小
在Linux和Mac平台上,该函数会原样返回path,在windows平台上会将路径中所有字符转换为小写,并将所有斜杠转换为饭斜杠。
>>> os.path.normcase('c:/windows\system32\') 'c:\windows\system32\' 规范化路径,如..和/ >>> os.path.normpath('c://windows\System32\../Temp/') 'c:\windows\Temp' >>> a='/Users/jieli/test1/\a1/\\aa.py/../..' >>> print(os.path.normpath(a)) /Users/jieli/test1

#方式一:推荐使用 import os #具体应用 import os,sys possible_topdir = os.path.normpath(os.path.join( os.path.abspath(__file__), os.pardir, #上一级 os.pardir, os.pardir )) sys.path.insert(0,possible_topdir) #方式二:不推荐使用 os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
四、sys模块
sys是与解释器有关的
1 sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 2 sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) 3 sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 4 sys.maxint 最大的Int值 5 sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 6 sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称

import sys import time for i in range(100): sys.stdout.write(' %s' %('#'*i)) sys.stdout.flush() time.sleep(0.5)

import sys import time for i in range(100): time.sleep(0.5) print(' %s' %('#'*i),end='',file=sys.stdout,flush=True)

#=========知识储备========== #指定宽度 print('<%-10.3f>' %3.22) #总宽度为10,保留3位小数点 #打印结果 #<3.220 > #打印%号,用%% width=10 print('<%%-%ds>' %width) #打印结果 # <%-10s> #嵌套的% width=10 print(('<%%-%ds>' %width) %('hello')) #打印结果 # <hello > #=========实现打印进度条函数========== import sys import time def progress(percent,width=50): if percent >= 100: percent=100 show_str=('[%%-%ds]' %width) %(int(width * percent / 100) * "#") #字符串拼接的嵌套使用 print(" %s %d%%" %(show_str, percent),end='',file=sys.stdout,flush=True) #=========应用========== data_size=3030333 recv_size=0 while recv_size < data_size: time.sleep(0.001) #模拟数据的传输延迟 recv_size+=1024 #每次收1024 recv_per=int(100*(recv_size/data_size)) #接收的比例 progress(recv_per,width=30) #进度条的宽度30
