这个过程主要分为三个步骤:
数据预处理
数据处理就是把数据按照一定的格式写出来,以便网路自己去读取数据
1准备原始数据
我的cloth数据一共是四个类别,每个类别有衣服47张,一用是188张图片,这些大小不一的原始图片转换成我们训练需要的shape。
原始数据放在同一个文件夹下面:
2 编程实现
制作Tfrecords,读取Tfrecords数据获得iamge和label,打印验证并保存生成的图片。
#将原始图片转换成需要的大小,并将其保存
#========================================================================================
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
#原始图片的存储位置
orig_picture = 'dataset/cloth/'#我的数据放在这个问价加下面
#生成图片的存储位置
gen_picture = 'dataset/image_data/inputdata/'#E:/Re_train/image_data/inputdata/'
#需要的识别类型
classes = {'Graphic_Ringer_Tee','Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse','Sheer_Sequin_Tank','Single_Button_Blazer'}
#样本总数
num_samples = 188
#制作TFRecords数据
def create_record():
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter("cloth_train.tfrecords")
for index, name in enumerate(classes):
class_path = orig_picture +"/"+ name+"/"
for img_name in os.listdir(class_path):
img_path = class_path + img_name
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = img.resize((64, 64)) #设置需要转换的图片大小
img_raw = img.tobytes() #将图片转化为原生bytes
print (index,img_raw)
example = tf.train.Example(
features=tf.train.Features(feature={
"label": tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[index])),
'img_raw': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw]))
}))
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
#=======================================================================================
def read_and_decode(filename):
# 创建文件队列,不限读取的数量
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([filename])
# create a reader from file queue
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
# reader从文件队列中读入一个序列化的样本
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
# get feature from serialized example
# 解析符号化的样本
features = tf.parse_single_example(
serialized_example,
features={
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'img_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
label = features['label']
img = features['img_raw']
img = tf.decode_raw(img, tf.uint8)
img = tf.reshape(img, [64, 64, 3])
#img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32) * (1. / 255) - 0.5
label = tf.cast(label, tf.int32)
return img, label
#=======================================================================================
if __name__ == '__main__':
create_record()
batch = read_and_decode('cloth_train.tfrecords')
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess: #开始一个会话
sess.run(init_op)
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
threads= tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
for i in range(num_samples):
example, lab = sess.run(batch)#在会话中取出image和label
img=Image.fromarray(example, 'RGB')#这里Image是之前提到的
if lab==0:
img.save(gen_picture+'/'+'Graphic_Ringer_Tee'+'/'+str(i)+str(lab)+'.jpg')#存下图片;注意cwd后边加上‘/’
elif lab==1:
img.save(gen_picture+'/'+'Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse'+'/'+str(i)+str(lab)+'.jpg')#存下图片;注意cwd后边加上‘/’
elif lab==2:
img.save(gen_picture+'/'+'Sheer_Sequin_Tank'+'/'+str(i)+str(lab)+'.jpg')#存下图片;注意cwd后边加上‘/’
elif lab==3:
img.save(gen_picture+'/'+'Single_Button_Blazer'+'/'+str(i)+str(lab)+'.jpg')#存下图片;注意cwd后边加上‘/’
print(gen_picture+'/'+str(i)+'samples'+str(lab)+'.jpg')
print(example, lab)
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
sess.close()
#========================================================================================
程序运行结束后就会生成下面的四个文件夹,里面存放就是我们需要的数据
将第一步生成的图片进行sample和label操作,进行batch处理
import os
import math
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#============================================================================
#-----------------生成图片路径和标签的List------------------------------------
train_dir = 'dataset/image_data/inputdata'
Graphic_Ringer_Tee = []
label_Graphic_Ringer_Tee = []
Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse = []
label_Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse = []
Sheer_Sequin_Tank = []
label_Sheer_Sequin_Tank = []
Single_Button_Blazer = []
label_Single_Button_Blazer = []
#step1:获取'E:/Re_train/image_data/training_image'下所有的图片路径名,存放到
#对应的列表中,同时贴上标签,存放到label列表中。
def get_files(file_dir, ratio):
for file in os.listdir(file_dir+'/Graphic_Ringer_Tee'):
Graphic_Ringer_Tee.append(file_dir +'/Graphic_Ringer_Tee'+'/'+ file)
label_Graphic_Ringer_Tee.append(0)
for file in os.listdir(file_dir+'/Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse'):
Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse.append(file_dir +'/Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse'+'/'+file)
label_Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse.append(1)
for file in os.listdir(file_dir+'/Sheer_Sequin_Tank'):
Sheer_Sequin_Tank.append(file_dir +'/Sheer_Sequin_Tank'+'/'+ file)
label_Sheer_Sequin_Tank.append(2)
for file in os.listdir(file_dir+'/Single_Button_Blazer'):
Single_Button_Blazer.append(file_dir +'/Single_Button_Blazer'+'/'+file)
label_Single_Button_Blazer.append(3)
#step2:对生成的图片路径和标签List做打乱处理把cat和dog合起来组成一个list(img和lab)
image_list = np.hstack((Graphic_Ringer_Tee, Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse, Sheer_Sequin_Tank, Single_Button_Blazer))
label_list = np.hstack((label_Graphic_Ringer_Tee, label_Sheer_Pleated_Front_Blouse, label_Sheer_Sequin_Tank, label_Single_Button_Blazer))
#利用shuffle打乱顺序
temp = np.array([image_list, label_list])
temp = temp.transpose()
np.random.shuffle(temp)
#从打乱的temp中再取出list(img和lab)
#image_list = list(temp[:, 0])
#label_list = list(temp[:, 1])
#label_list = [int(i) for i in label_list]
#return image_list, label_list
#将所有的img和lab转换成list
all_image_list = list(temp[:, 0])
all_label_list = list(temp[:, 1])
#将所得List分为两部分,一部分用来训练tra,一部分用来测试val
#ratio是测试集的比例
n_sample = len(all_label_list)
n_val = int(math.ceil(n_sample*ratio)) #测试样本数
n_train = n_sample - n_val #训练样本数
tra_images = all_image_list[0:n_train]
tra_labels = all_label_list[0:n_train]
tra_labels = [int(float(i)) for i in tra_labels]
val_images = all_image_list[n_train:-1]
val_labels = all_label_list[n_train:-1]
val_labels = [int(float(i)) for i in val_labels]
return tra_images, tra_labels, val_images, val_labels
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#--------------------生成Batch----------------------------------------------
#step1:将上面生成的List传入get_batch() ,转换类型,产生一个输入队列queue,因为img和lab
#是分开的,所以使用tf.train.slice_input_producer(),然后用tf.read_file()从队列中读取图像
# image_W, image_H, :设置好固定的图像高度和宽度
# 设置batch_size:每个batch要放多少张图片
# capacity:一个队列最大多少
def get_batch(image, label, image_W, image_H, batch_size, capacity):
#转换类型
image = tf.cast(image, tf.string)
label = tf.cast(label, tf.int32)
# make an input queue
input_queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([image, label])
label = input_queue[1]
image_contents = tf.read_file(input_queue[0]) #read img from a queue
#step2:将图像解码,不同类型的图像不能混在一起,要么只用jpeg,要么只用png等。
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_contents, channels=3)
#step3:数据预处理,对图像进行旋转、缩放、裁剪、归一化等操作,让计算出的模型更健壮。
image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image, image_W, image_H)
image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image)
#step4:生成batch
#image_batch: 4D tensor [batch_size, width, height, 3],dtype=tf.float32
#label_batch: 1D tensor [batch_size], dtype=tf.int32
image_batch, label_batch = tf.train.batch([image, label],
batch_size= batch_size,
num_threads= 32,
capacity = capacity)
#重新排列label,行数为[batch_size]
label_batch = tf.reshape(label_batch, [batch_size])
image_batch = tf.cast(image_batch, tf.float32)
return image_batch, label_batch
#========================================================================
建立神经网络模型
#=========================================================================
import tensorflow as tf
#=========================================================================
#网络结构定义
#输入参数:images,image batch、4D tensor、tf.float32、[batch_size, width, height, channels]
#返回参数:logits, float、 [batch_size, n_classes]
def inference(images, batch_size, n_classes):
#一个简单的卷积神经网络,卷积+池化层x2,全连接层x2,最后一个softmax层做分类。
#卷积层1
#64个3x3的卷积核(3通道),padding=’SAME’,表示padding后卷积的图与原图尺寸一致,激活函数relu()
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[3,3,3,64], stddev = 1.0, dtype = tf.float32),
name = 'weights', dtype = tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value = 0.1, dtype = tf.float32, shape = [64]),
name = 'biases', dtype = tf.float32)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, weights, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='SAME')
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name= scope.name)
#池化层1
#3x3最大池化,步长strides为2,池化后执行lrn()操作,局部响应归一化,对训练有利。
with tf.variable_scope('pooling1_lrn') as scope:
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1,3,3,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME', name='pooling1')
norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm1')
#卷积层2
#16个3x3的卷积核(16通道),padding=’SAME’,表示padding后卷积的图与原图尺寸一致,激活函数relu()
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[3,3,64,16], stddev = 0.1, dtype = tf.float32),
name = 'weights', dtype = tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value = 0.1, dtype = tf.float32, shape = [16]),
name = 'biases', dtype = tf.float32)
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weights, strides = [1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name='conv2')
#池化层2
#3x3最大池化,步长strides为2,池化后执行lrn()操作,
#pool2 and norm2
with tf.variable_scope('pooling2_lrn') as scope:
norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0,beta=0.75,name='norm2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1,3,3,1], strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME',name='pooling2')
#全连接层3
#128个神经元,将之前pool层的输出reshape成一行,激活函数relu()
with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope:
reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1])
dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[dim,128], stddev = 0.005, dtype = tf.float32),
name = 'weights', dtype = tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value = 0.1, dtype = tf.float32, shape = [128]),
name = 'biases', dtype=tf.float32)
local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
#全连接层4
#128个神经元,激活函数relu()
with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope:
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[128,128], stddev = 0.005, dtype = tf.float32),
name = 'weights',dtype = tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value = 0.1, dtype = tf.float32, shape = [128]),
name = 'biases', dtype = tf.float32)
local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name='local4')
#dropout层
# with tf.variable_scope('dropout') as scope:
# drop_out = tf.nn.dropout(local4, 0.8)
#Softmax回归层
#将前面的FC层输出,做一个线性回归,计算出每一类的得分,在这里是2类,所以这个层输出的是两个得分。
with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(shape=[128, n_classes], stddev = 0.005, dtype = tf.float32),
name = 'softmax_linear', dtype = tf.float32)
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(value = 0.1, dtype = tf.float32, shape = [n_classes]),
name = 'biases', dtype = tf.float32)
softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name='softmax_linear')
return softmax_linear
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
#loss计算
#传入参数:logits,网络计算输出值。labels,真实值,在这里是0或者1
#返回参数:loss,损失值
def losses(logits, labels):
with tf.variable_scope('loss') as scope:
cross_entropy =tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=labels, name='xentropy_per_example')
loss = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='loss')
tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/loss', loss)
return loss
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------
#loss损失值优化
#输入参数:loss。learning_rate,学习速率。
#返回参数:train_op,训练op,这个参数要输入sess.run中让模型去训练。
def trainning(loss, learning_rate):
with tf.name_scope('optimizer'):
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate= learning_rate)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step= global_step)
return train_op
#-----------------------------------------------------------------------
#评价/准确率计算
#输入参数:logits,网络计算值。labels,标签,也就是真实值,在这里是0或者1。
#返回参数:accuracy,当前step的平均准确率,也就是在这些batch中多少张图片被正确分类了。
def evaluation(logits, labels):
with tf.variable_scope('accuracy') as scope:
correct = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1)
correct = tf.cast(correct, tf.float16)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(correct)
tf.summary.scalar(scope.name+'/accuracy', accuracy)
return accuracy
#========================================================================
网路训练
#======================================================================
#导入文件
import os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
#import input_data
#import model
#变量声明
N_CLASSES = 4 #husky,jiwawa,poodle,qiutian
IMG_W = 64 # resize图像,太大的话训练时间久
IMG_H = 64
BATCH_SIZE =20
CAPACITY = 200
MAX_STEP = 200 # 一般大于10K
learning_rate = 0.0001 # 一般小于0.0001
#获取批次batch
train_dir = 'dataset/image_data/inputdata' #训练样本的读入路径
logs_train_dir = 'dataset/log' #logs存储路径
#logs_test_dir = 'E:/Re_train/image_data/test' #logs存储路径
#train, train_label = input_data.get_files(train_dir)
train, train_label, val, val_label = get_files(train_dir, 0.3)
#训练数据及标签
train_batch,train_label_batch = get_batch(train, train_label, IMG_W, IMG_H, BATCH_SIZE, CAPACITY)
#测试数据及标签
val_batch, val_label_batch = get_batch(val, val_label, IMG_W, IMG_H, BATCH_SIZE, CAPACITY)
#训练操作定义
train_logits = inference(train_batch, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES)
train_loss = losses(train_logits, train_label_batch)
train_op = trainning(train_loss, learning_rate)
train_acc = evaluation(train_logits, train_label_batch)
#测试操作定义
test_logits = inference(val_batch, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES)
test_loss = losses(test_logits, val_label_batch)
test_acc = evaluation(test_logits, val_label_batch)
#这个是log汇总记录
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
#产生一个会话
sess = tf.Session()
#产生一个writer来写log文件
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_train_dir, sess.graph)
#val_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logs_test_dir, sess.graph)
#产生一个saver来存储训练好的模型
saver = tf.train.Saver()
#所有节点初始化
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#队列监控
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
#进行batch的训练
try:
#执行MAX_STEP步的训练,一步一个batch
for step in np.arange(MAX_STEP):
if coord.should_stop():
break
#启动以下操作节点,有个疑问,为什么train_logits在这里没有开启?
_, tra_loss, tra_acc = sess.run([train_op, train_loss, train_acc])
#每隔50步打印一次当前的loss以及acc,同时记录log,写入writer
if step % 10 == 0:
print('Step %d, train loss = %.2f, train accuracy = %.2f%%' %(step, tra_loss, tra_acc*100.0))
summary_str = sess.run(summary_op)
train_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
#每隔100步,保存一次训练好的模型
if (step + 1) == MAX_STEP:
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(logs_train_dir, 'model.ckpt')
saver.save(sess, checkpoint_path, global_step=step)
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print('Done training -- epoch limit reached')
finally:
coord.request_stop()
#========================================================================
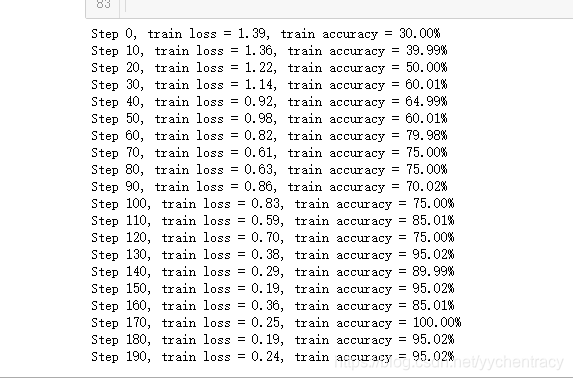
结果如下:
测试
#=============================================================================
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#=======================================================================
#获取一张图片
def get_one_image(train):
#输入参数:train,训练图片的路径
#返回参数:image,从训练图片中随机抽取一张图片
n = len(train)
ind = np.random.randint(0, n)
img_dir = train[ind] #随机选择测试的图片
img = Image.open(img_dir)
plt.imshow(img)
imag = img.resize([64, 64]) #由于图片在预处理阶段以及resize,因此该命令可略
image = np.array(imag)
return image
#--------------------------------------------------------------------
#测试图片
def evaluate_one_image(image_array):
with tf.Graph().as_default():
BATCH_SIZE = 1
N_CLASSES = 4
image = tf.cast(image_array, tf.float32)
image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image)
image = tf.reshape(image, [1, 64, 64, 3])
logit = inference(image, BATCH_SIZE, N_CLASSES)
logit = tf.nn.softmax(logit)
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[64, 64, 3])
# you need to change the directories to yours.
logs_train_dir = 'dataset/log/'
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
print("Reading checkpoints...")
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(logs_train_dir)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1]
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
print('Loading success, global_step is %s' % global_step)
else:
print('No checkpoint file found')
prediction = sess.run(logit, feed_dict={x: image_array})
max_index = np.argmax(prediction)
if max_index==0:
print('This is a 0 with possibility %.6f' %prediction[:, 0])
elif max_index==1:
print('This is a 1 with possibility %.6f' %prediction[:, 1])
elif max_index==2:
print('This is a 2 with possibility %.6f' %prediction[:, 2])
else:
print('This is a 3 with possibility %.6f' %prediction[:, 3])
#------------------------------------------------------------------------
if __name__ == '__main__':
train_dir = 'dataset/image_data/inputdata'
train, train_label, val, val_label = get_files(train_dir, 0.3)
img = get_one_image(val) #通过改变参数train or val,进而验证训练集或测试集
evaluate_one_image(img)
#===========================================================================
结果如下:

来源:https://blog.csdn.net/yychentracy/article/details/85158010